Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Maekawa, Keisuke; Saegusa, Hiromitsu; Inaba, Kaoru*; Shimogochi, Takafumi*
JAEA-Research 2010-001, 238 Pages, 2010/07
In the design and safety assessment of the geological disposal system of the high-level radioactive waste (HLW), it is extremely important to improve the reliability of the evaluation of the investigation of the geological environment, which provides technical basis. Especially, the knowhow and the experience of groundwater flow modeling based on the data acquired in deep underground at the coastal area are needed to be enhanced because these are little. Against this background, we have carried out modeling and groundwater flow simulation of the Horonobe coastal area. The knowledge and the knowhow acquired through this work were accumulated and arranged as a knowledge base by executing the following items. (1)The discussion of applicability of the workflow of evaluation of the groundwater flow for the coast region, and extension and update according to need. (2)Understand of groundwater flow based on existing investigation result in Horonobe coastal area, (2-1)Estimation of distribution of salinity in groundwater, (2-2)Extraction and arrangement of knowhow and judgment basis in modeling and simulation works. As a result, the knowledge was expanded concerning the groundwater flow evaluation methodology needed in design and safety assessment of the geological disposal system that is able to correspond to various geological environments in our country.
Hirano, Toru; Nakama, Shigeo; Yamada, Atsuo*; Seno, Yasuhiro*; Sato, Toshinori*
JAEA-Research 2010-002, 48 Pages, 2010/06
Japan Atomic Energy Agency is advancing the geo-scientific research at the Mizunami Underground Research Laboratory. In Phase II of the research, improvement on the previous conceptual model of the geological environment is one of the objectives. So the additional rock mechanical investigations on the GL.-100m level research gallery was conducted. As a result, the average rock physical and mechanical properties are consistent with the results from MIZ-1 testing. This means that the surface based investigations in MIZ-1 are valid at this level. Almost all in situ stress measurements indicate that the maximum principal stress is oriented in the NW-SE direction and match the observations in MIZ-1 at GL.-200m depth. But the observed stress level is not the expected value extrapolated from the MIZ-1 results. This suggests that the in situ stress has likely been decoupled at the rock boundary located about GL.-150m level between the Toki Lignite-bearing formation and the Toki granite.
Maruyama, Yoichiro; Oba, Masaki; Akaoka, Katsuaki; Miyabe, Masabumi; Wakaida, Ikuo
JAEA-Research 2010-003, 19 Pages, 2010/07
Emission characteristics of gadolinium plasma in the double-pulse LIBS using a femtosecond laser as an ablation source have been studied to achieve high sensitivity for analyzing next generation nuclear fuel in a future. In experiment, effects of the ablation laser focusing lens position and relative position of two plasmas were studied. The optimum ablation laser focusing lens position was about 22 mm from the sample surface, and the emission was maximized with the  x of 1-1.2 mm and the
x of 1-1.2 mm and the  y of 0.5-1 mm. As a result, about 200-times higher emission intensity in the double-pulse reheating mode was obtained than the emission in the single-pulse method. Moreover, the spectral width of the emission did not depend on the reheating laser pulse energy, and the high emission intensity could be obtained without the spectral broadening.
y of 0.5-1 mm. As a result, about 200-times higher emission intensity in the double-pulse reheating mode was obtained than the emission in the single-pulse method. Moreover, the spectral width of the emission did not depend on the reheating laser pulse energy, and the high emission intensity could be obtained without the spectral broadening.
Akaoka, Katsuaki; Maruyama, Yoichiro; Oba, Masaki; Miyabe, Masabumi; Otobe, Haruyoshi; Wakaida, Ikuo
JAEA-Research 2010-004, 13 Pages, 2010/05
For the remote analysis of low DF TRU (Decontamination Factor Transuranic) fuel, Laser Breakdown Spectroscopy (LIBS) was applied to uranium oxide including a small amount of calcium oxide. The characteristics, such as spectrum intensity and plasma excitation temperature, were measured using time-resolved spectroscopy. As a result, in order to obtain the stable intensity of calcium spectrum for the uranium spectrum, it was found out that the optimum observation delay time of spectrum is 4 microseconds or more after laser irradiation.
Hirano, Toru; Seno, Yasuhiro*; Matsui, Hiroya
JAEA-Research 2010-005, 41 Pages, 2010/06
Japan Atomic Energy Agency is carrying out a geoscientific research project at the Mizunami, to establish the scientific and technological basis for geological disposal of HLW. The project is currently in Phase II. The Phase II goals are to construct models of the geological environment from all investigation results obtained during the construction. These models describe the geological environment at the construction points that were affected by excavation of the shafts and the galleries. To achieve these goals, we are examing the relationship between scope of investigation and accuracy of data, an assessment of investigation methods, validation of the Phase I geological environment models and construction of block scale geological environment models. As part of these studies, rock mechanical investigations involving both laboratory testing and in situ stress measurements every 100m along the shaft. This report presents the FY2008 activities undertaken to achieve the above goals.
Nakamura, Takahiro; Sanada, Hiroyuki; Sugita, Yutaka; Teshima, Minoru*; Kasagi, Toshio*; Kishimoto, Munemaru*; Deguchi, Tomonori*; Makuuchi, Ayumu*
JAEA-Research 2010-006, 68 Pages, 2010/06
The present document is to report the result of geophysical survey by electric survey around a site proposed for the Horonobe Underground Research Laboratory Project at Horonobe-cho, Hokkaido by the Japan Atomic Energy Agency. This Electric survey using pole-pole array in Horonobe Underground Research Laboratory Area was the third survey. Resistivity distribution near surface was about 20 
 m and it become to about 2
m and it become to about 2 
 m as the depth increasing. Resistivity distribution was good agreement with existing survey results and existing electrical resistivity log data. By comparing resistivity model with hydrology model, it was confirmed that resistivity reflected the density of salinity. The range and distribution trends of apparent resistivity in this year were similar to the results of last year. It is thought that the data in which reproducibility is high is acquired in this survey. The influence on the underground water flow by construction is not admitted now.
m as the depth increasing. Resistivity distribution was good agreement with existing survey results and existing electrical resistivity log data. By comparing resistivity model with hydrology model, it was confirmed that resistivity reflected the density of salinity. The range and distribution trends of apparent resistivity in this year were similar to the results of last year. It is thought that the data in which reproducibility is high is acquired in this survey. The influence on the underground water flow by construction is not admitted now.
Yoshikawa, Ryuji; Ohshima, Hiroyuki
JAEA-Research 2010-007, 44 Pages, 2010/06
The feasibility assessment of steam generator with straight heat transfer tube is being carried out. In this study, the computer code for water-steam flow in SG was developed. The drift-flux model and semi-implicit method were used. The total flow rate and temperature of flow into the inlet plenum, and the pressure of outlet plenum were given as boundary conditions. The flow instability experiments with two parallel channels were simulated. The capability of computer code on predictions of flow oscillation and stable boundary was confirmed. The sensitivity analysis was also carried out to quantify the impact of each parameter on oscillation period and the stable boundary. It can be expected to improve the accuracy of the computer code by using appropriate drift velocity and two-phase frictional multiplier correlations.
 fuel rods in fuel assembly designs for plutonium conservation in FLWR
fuel rods in fuel assembly designs for plutonium conservation in FLWRUchikawa, Sadao; Nakano, Yoshihiro; Okubo, Tsutomu
JAEA-Research 2010-008, 30 Pages, 2010/06
The FLWR is an innovative BWR-type reactor with hard neutron spectrum based on the well-experienced LWR technologies. It aims at effective and flexible utilization of uranium and plutonium resources by adopting a two-stage concept of core designs corresponding to the advancement of the fuel cycle technologies and related infrastructures. A new concept of the fuel assembly design named FLWR/MIX has been proposed for the first stage of FLWR to conserve plutonium effectively with a fissile-plutonium conversion ratio of around 1.0, keeping negative void reactivity characteristics. The enriched UO fuel rods are arranged in the peripheral region of the assembly, surrounding the MOX fuel rods in the central region. Performance evaluation shows that the FLWR/MIX concept is feasible and promising under the framework of the UO
fuel rods are arranged in the peripheral region of the assembly, surrounding the MOX fuel rods in the central region. Performance evaluation shows that the FLWR/MIX concept is feasible and promising under the framework of the UO and MOX fuel technologies and related infrastructures which have been established for the current LWR-MOX utilization.
and MOX fuel technologies and related infrastructures which have been established for the current LWR-MOX utilization.
Iwamoto, Yukiharu*; Sogo, Motosuke*; Aizawa, Kosuke; Nakanishi, Shigeyuki*; Yamano, Hidemasa
JAEA-Research 2010-009, 58 Pages, 2010/06
Experimental studies of the 1/10-scale model of a hot leg piping and their numerical analyses were carried out in order to guarantee the designing of the sodium-cooled fast breeder reactor. The structure of the flow fluctuation was clarified by means of pressure measurements, laser doppler velocimetry (LDV) and flow visualization. LDV measurements were examined for Reynolds number of 50000. FFT analyses of axial velocities indicate that two kinds of flow fluctuations exist in the present elbow. One is the fluctuation with approximate Strouhal number of 1.0 (3.2 Hz) occurring in a shear flow region. The other is with approximate Strouhal number of 0.5 (1.6 Hz) occurring in the separated and its downstream regions. These fluctuations were also observed by flow visualization. The analyses showed that the stream regime was in good agreement with visualization test results.
Kikuchi, Takahiro; Hoshi, Harutaka; Asakura, Toshihide; Morita, Yasuji; Kimura, Takaumi; Dodbiba, G.*; Fujita, Toyohisa*
JAEA-Research 2010-010, 45 Pages, 2010/07
We have investigate that separation of Mo from simulated HLLW using various metal oxides adsorbent. Fe-Pb oxides and manganese oxide showed very high solubility in nitric acid solution. The distribution coefficient of Mo was decreased with increasing nitric acid concentration among tested adsorbents. Adsorption ability of Mo on alumina and cobalt oxide was low in 3M nitric acid. Hematite type iron oxide (Fe adsorbent) and amorphous zirconium oxide had high Mo adsorption ability, in 3M nitric acid. TRU, U and major fission products were not adsorbed on the adsorbent. So, separation of Mo can be achieved by using Fe adsorbent. A part of Mo was adsorbed irreversibly on Fe adsorbent, but reversibly-adsorbed Mo was recovered by oxalic acid, and the adsorbent was able to use repeatedly. Behavior of break-through of Mo is estimated from adsorption isotherm and overall mass transfer coefficient. We found that amount of throughput of Mo increased with decreasing grain size of the adsorbent.
Mizuta, Yoshiaki*; Kaneko, Katsuhiko*; Matsuki, Koji*; Sugawara, Katsuhiko*; Sudo, Shigeaki*; Hirano, Toru; Tanno, Takeo; Matsui, Hiroya
JAEA-Research 2010-011, 35 Pages, 2010/06
The best way to know the initial stress clearly is to measure it in the location where a tunnel will be excavated. However, it is difficult to measure a large number of the initial stresses, budgetary considerations notwithstanding, because of the large scale of underground structures like a radioactive waste disposal facility. Therefore we developed a method for determination of initial stress for arbitrary points from limited results of initial stress measurements. This report is a summary of the contract work about this development. At first, we made local scale numerical models of the Tono area. Using these models, we determined the regional stress state from limited initial stress measurements results. Then we applied the regional stress state to boundary conditions of other numerical models and estimated initial stress at arbitrary points. The result is an estimated initial stress that matched the original stress measurement results from the first analytical results.
Tsujimoto, Kazufumi; Nishihara, Kenji; Takei, Hayanori; Sugawara, Takanori; Kurata, Yuji; Saito, Shigeru; Obayashi, Hironari; Sasa, Toshinobu; Kikuchi, Kenji*; Tezuka, Masao; et al.
JAEA-Research 2010-012, 59 Pages, 2010/07
The design of an accelerator-driven system was modified and its feasibility was investigated on the basis of new data and knowledge for corrosion by lead-bismuth eutectic and irradiation behavior of candidate materials. The neutronics and thermal design was carried out and a modified core concept was established. As a result of evaluation for the integrity of fuel cladding tubes and a beam window, it was confirmed that their structural strength was sufficient under the conditions of design temperature and corrosion environment without irradiation. Though irradiation effects on material properties were considered not to be so serious under the practical conditions of the ADS according to existing irradiation data, it was needed to accumulate further experimental data for more detailed evaluation. According to level-1 PSA and dynamic analysis of beyond-design-basis accidents, it was shown that there was little possibility of core disruption and re-criticality accidents for ADS.
Hirano, Toru; Seno, Yasuhiro*; Matsui, Hiroya
JAEA-Research 2010-013, 51 Pages, 2010/06
Japan Atomic Energy Agency is proceeding with the geoscientific research at the Mizunami Underground Research Laboratory. In this project, developing a conceptual model of the geological environment is one of the scientific and technical objectives. Once excavation of research galleries began, the model could be improved using more detailed information from underground-based investigations. The investigation described here in is the measurement of the rock mechanical properties and initial stress of the rock mass around the GL.-200m level research gallery. The average physical and mechanical properties determined using core from the Toki Granite on this level is consistent with the properties from MIZ-1 testing. In situ stress measurements indicate that the  1 is 10.6 MPa and horizontal in the NW-SE direction matched to the observations in MIZ-1 at the same depth. This indicates that the surface based investigations in MIZ-1 are valid at this level.
1 is 10.6 MPa and horizontal in the NW-SE direction matched to the observations in MIZ-1 at the same depth. This indicates that the surface based investigations in MIZ-1 are valid at this level.
Nakajima, Takahiro; Kunitomo, Takahiro; Kumazawa, Mineo*; Nagao, Hiromichi*
JAEA-Research 2010-014, 66 Pages, 2010/07
ACROSS(Accurately Controlled Routinely Operated Signal System) has developed to acquire the detailed information on the tectonically active zone. The technology for example the transmission and receiving technique, the data analysis and the interpretation technique of the ACROSS signal is able to apply not only to seismology but also to other field. We considered the ACROSS technology may apply to the engineering technology of the Mizunami Underground Research Laboratory (MIU) project, for example monitoring of the change of the geological environment around shafts and also the strength of the shaft concrete itself. It is planned that the examination for three years will be made from fiscal year 2007, and the new observation site around the MIU was established, and the data acquisition and data analysis have been carried out. This report compiled technical matters among the results obtained in the research and the development of the EM-ACROSS.
Yui, Mikazu; Ishikawa, Hirohisa; Watanabe, Atsuo*; Yoshino, Kyoji*; Umeki, Hiroyuki; Hioki, Kazumasa; Naito, Morimasa; Seo, Toshihiro; Makino, Hitoshi; Oda, Chie; et al.
JAEA-Research 2010-015, 106 Pages, 2010/05
This report summarizes the activity of Phase I of Waste Management Working Group of the United States - Japan Joint Nuclear Energy Action Plan started in 2007. The working group focused on consolidation of the existing technical basis between the U.S. and Japan and the joint development of a plan for future collaborative activities. Firstly, the political/regulatory frameworks related to nuclear fuel cycles in both countries were reviewed. The various advanced fuel cycle scenarios in both countries were surveyed and summarized. Secondly, the waste management/disposal system optimization was discussed. Repository system concepts for the various classifications of nuclear waste were reviewed and summarized, then disposal system optimization processes and techniques were reviewed, and factors to consider in future repository design optimization activities were also discussed. Finally the potential collaboration areas and activities related to the optimization problem were extracted.
Hoshi, Harutaka; Kikuchi, Takahiro; Asakura, Toshihide; Morita, Yasuji; Kimura, Takaumi
JAEA-Research 2010-016, 70 Pages, 2010/07
We have studied selective separation of Cs and Sr, which are included in high level liquid waste (HLLW) generated from reprocessing of spent nuclear fuel and are major heat generators, by using extractant impregnated adsorbents. Cs adsorbent using calix arane derivatives showed excellent selectivity for Cs. It also showed significant stability against  -irradiation. Sr adsorbent using crown ether derivatives also showed high selectivity for Sr from nitric acid solution, except for Ba and Tc. Dynamic capacity decreased ca. 30% after
-irradiation. Sr adsorbent using crown ether derivatives also showed high selectivity for Sr from nitric acid solution, except for Ba and Tc. Dynamic capacity decreased ca. 30% after  -irradiation. Hot test using genuine HLLW stored in NUCEF was performed for separation of Cs and Sr through columns, respectively. Each Cs and Sr was separated from other typical fission product elements as well as the results obtained in preliminary experiments. Finally, Cs and Sr were separated according to a supposed separation scheme. Although some complexing agents were added in simulate HLLW, no negative effect was found.
-irradiation. Hot test using genuine HLLW stored in NUCEF was performed for separation of Cs and Sr through columns, respectively. Each Cs and Sr was separated from other typical fission product elements as well as the results obtained in preliminary experiments. Finally, Cs and Sr were separated according to a supposed separation scheme. Although some complexing agents were added in simulate HLLW, no negative effect was found.
Nakamura, Takahiro; Sanada, Hiroyuki; Sugita, Yutaka; Kato, Harumi*
JAEA-Research 2010-017, 105 Pages, 2010/07
For the purpose of studying the in situ state of stress around Horonobe Underground Research Laboratory, hydraulic fracturing technique was carried out three boreholes drilled from the 140m niche located near the bottom of the east shaft. The results of the measurements are summarized as follows. Evaluation of stress in a plane perpendicular to the borehole axis was impossible because transverse fractures which developed along a pre-existing plane of weakness were created at eleven depths. Therefore, the relation between the shut-in pressure of a transverse fracture and the in situ stress was used to obtain the in situ stress state on the assumption that all of the target zones of hydraulic fracturing were in a uniform stress state. The determined in situ stress state showed that none of the principal stress axis was coaxial with respect to E-N-V coordinate system where E, N and V represent east, north and vertical direction.
Takeuchi, Ryuji; Saegusa, Hiromitsu; Oyama, Takuya; Keya, Hiromichi; Sato, Atsuya; Kosaka, Hiroshi; Takeda, Masaki; Daimaru, Shuji; Takeuchi, Shinji
JAEA-Research 2010-018, 133 Pages, 2010/08
The Mizunami Underground Laboratory Project is a comprehensive research project investigating the deep underground environment within crystalline rock. The project goals of the project from surface-based investigation phase (Phase I) through to operation phase (Phase III) are: to establish techniques for investigation, analysis and assessment of the deep geological environment, and to develop a range of engineering for deep underground application. Currently, the project is under the construction phase (Phase II). One of the Phase II goals, which is for the project goal, was set to develop and revise models of the geological environment using the investigation results obtained during excavation, and determine and assess changes in the geological environment in response to excavation. This document presents the overview of results of the research and development on "hydrogeology" performed in fiscal year 2008, with regard to the Phase II goal.
Tobita, Kenji; Nishio, Satoshi*; Enoeda, Mikio; Nakamura, Hirofumi; Hayashi, Takumi; Asakura, Nobuyuki; Uto, Hiroyasu; Tanigawa, Hiroyasu; Nishitani, Takeo; Isono, Takaaki; et al.
JAEA-Research 2010-019, 194 Pages, 2010/08
This report describes the results of the conceptual design study of the SlimCS fusion DEMO reactor aiming at demonstrating fusion power production in a plant scale and allowing to assess the economic prospects of a fusion power plant. The design study has focused on a compact and low aspect ratio tokamak reactor concept with a reduced-sized central solenoid, which is novel compared with previous tokamak reactor concept such as SSTR (Steady State Tokamak Reactor). The reactor has the main parameters of a major radius of 5.5 m, aspect ratio of 2.6, elongation of 2.0, normalized beta of 4.3, fusion out put of 2.95 GW and average neutron wall load of 3 MW/m . This report covers various aspects of design study including systemic design, physics design, torus configuration, blanket, superconducting magnet, maintenance and building, which were carried out increase the engineering feasibility of the concept.
. This report covers various aspects of design study including systemic design, physics design, torus configuration, blanket, superconducting magnet, maintenance and building, which were carried out increase the engineering feasibility of the concept.
Oda, Yoshihiro; Watahiki, Takanori*; Sato, Hisashi; Sawada, Atsushi
JAEA-Research 2010-020, 23 Pages, 2010/08
For the geological disposal of high level radioactive waste, it is important to know the groundwater flow to evaluate the geological isolation system. Simulation codes are used for the evaluation of the saline groundwater flow and distribution, because various and a lot of investigations and experiments are needed. At in-situ, simulation codes have to solve advection-dispersion flow coupling with density flow which occurs by the density difference between saline and fresh groundwater. But the results of laboratory experiments are qualitative data, then the verification cannot be done in quantitatively. The quantitative data of saltwater intrusion experiment, then we try to simulate saltwater intrusion by Dtransu2D-EL code which can calculate advection-dispersion flow coupled with density flow. Between the results of the simulation and the experiments, the toe point of wedge by the simulation shows good coincidence, but the top point is not good coincidence. As for the transition zone of saltwater intrusion, the band width of the experimental result decrease from the toe to the top, but the simulation result shows countertrend.
Onoe, Hironori; Saegusa, Hiromitsu; Motoshima, Takayuki*; Ijiri, Yuji*; Otsu, Hiroyasu*
JAEA-Research 2010-021, 73 Pages, 2010/10
It is important to evaluate the influence of water inrush into underground facility on costs and schedules for construction of deep underground facility based on prior information. In this study, risk assessment method using a combination of discrete fracture network model with financial engineering theory has been developed taking into account unexpected water inrush into the underground facility constructed in crystalline fractured rock. The risk assessment method has been applied to the construction of the Mizunami Underground Research Laboratory. The relationship between the amount of information due to the progress of investigations and the risk regarding cost variation for the countermeasure against water inrush has been evaluated. As a result, site characterization procedure for decreasing the water inrush risk efficiently was suggested. The applicability of the risk assessment method for the ex-post-facto assessment of construction of the underground facility was also confirmed.
Kato, Shoichi; Furukawa, Tomohiro; Yoshida, Eiichi
JAEA-Research 2010-022, 37 Pages, 2010/08
It is known that the cyclic thermal stress caused by the thermal striping is occurred at the parts which the coolant of the different temperatures mixes in FBR plants, and the maximum number of cycles in the service life reaches to 10 -10
-10 cycles. So, it is important to understand experimentally the relationship between the mechanical strength and the damage mechanism in the high cycle fatigue region. This report summarizes about the results of the high cycle fatigue properties of a candidate material for FBR structures, FBR grade type 316 stainless steel (316FR).
cycles. So, it is important to understand experimentally the relationship between the mechanical strength and the damage mechanism in the high cycle fatigue region. This report summarizes about the results of the high cycle fatigue properties of a candidate material for FBR structures, FBR grade type 316 stainless steel (316FR).
Nagasawa, Hirokazu; Takeda, Seiji; Kimura, Hideo
JAEA-Research 2010-023, 44 Pages, 2010/08
In the safety assessment of geological disposal for high level radioactive wastes, it is important to develop the modelling for evaluating mechanical effects of crustal movements on the disposal system in Japan. In this study, the model on crustal movements is represented by accumulating two components of velocity magnitude of the crust to horizontal direction, caused by transient movements associated with fault and/or volcanic activities and ordinary movements with the other continuous factors. In this report, we provide the specification of the model on crustal movement and analyze the horizontal velocity in Tohoku region using the model. The results indicate that the spatial distribution of longitudinal velocities in Tohoku region is similar to that of the ordinary movements.
Honda, Akira; Yamaguchi, Kohei*; Inagaki, Manabu; Oda, Chie
JAEA-Research 2010-024, 44 Pages, 2010/08
An analysis method was attempted of the impact of hyper-alkaline pore water on the mass transport in a single fracture of a host rock. Initial mass transport fields were generated using the computer program "Mathematica", which were then used for the chemistry-mass transport coupling analyses by the computer program "PHREEQC-TRANS".
Tanai, Kenji; Kikuchi, Hirohito; Nakamura, Kunihiko*; Tanaka, Yukihisa*; Hironaga, Michihiko*
JAEA-Research 2010-025, 186 Pages, 2010/08
Bentonite-based material is used as one of the components of the LLW, TRU and HLW disposal facilities. Required characteristics of bentonite-based material are low permeability, swelling property, etc. Those are evaluated in many cases by laboratory test results. However the uncertainty exists in the evaluation of those characteristics in construction. Because even if the index of the dry density etc is the same, laboratory test results have variability. In addition, the uncertainty in construction has the possibility to increase the uncertainty of long-term evaluation of characteristics. On the other hand, several of laboratory test methods of bentonite are not standardized. So, this is a possibility that is one of the uncertain causes of the evaluation of characteristics of the bentonite. Therefore, it is hoped that the laboratory tests of bentonite are standardized. Therefore, this study analysis the uncertainty on the physical properties by laboratory tests and put together the problem and ponts of concern in the tests.
Honda, Akira; Yamaguchi, Kohei*; Oda, Chie
JAEA-Research 2010-026, 19 Pages, 2010/08
More significant alteration of montmorillonite was estimated if the precipitation of meta-stable as opposed to stable secondary minerals was assumed in a chemical/mass-transport coupled analyses of cement/bentonite engineered barrier system for TRU-2. In general, this tendency is reversal. In order to understand the reason of this reversal tendency, geochemical calculations of batch system were conducted. The S.I. of montmorillonite is lower in the case of meta-stable secondary minerals, except for the very short initial period. Because the S.I. of montmorillonite is higher throughout most of the reaction period in the case of meta-stable secondary minerals, the alteration is more significant.
Kawamura, Makoto; Makino, Hitoshi; Sasao, Eiji; Niizato, Tadafumi; Yasue, Kenichi; Asamori, Koichi; Umeda, Koji; Ishimaru, Tsuneari; Osawa, Hideaki; Ebashi, Takeshi; et al.
JAEA-Research 2010-027, 85 Pages, 2010/09
Japan Atomic Energy Agency (JAEA) have developed a formal evaluation method to assess the potential impacts of natural phenomena (earthquakes and faulting; volcanism; uplift, subsidence, denudation and sedimentation; climatic and sea-level changes) on a high level radioactive waste (HLW) disposal system for the purpose of maintenance of evaluation method for potential impacts of natural phenomena within more realistic view. In this report, we developed a framework as a part of the total system performance assessment for two purposes: the first one is quantification of relationship of characteristic of natural phenomena between geological environmental conditions (T-H-M-C-G), and the other one is quantification of relationship of T-H-M-C-G condition between parameters of performance assessment. We tried to apply the framework to all natural phenomena to confirm the effectiveness of the framework. On the other hand, we applied an argument-diagram that was developed one of the methods of the knowledge management to elicit future tasks. As a result, to apply the framework, we could show that information integration could carry out efficiently, and information integration was attained by the common framework by combining information on geohistory and existing information of natural phenomena and geological environmental conditions as modern-analogue. We could show that suitable scenarios might be chosen by information integration. Furthermore, we were able to elicit future tasks to this study by applying the argument-diagram.
Hazama, Taira; Sato, Wakaei*
JAEA-Research 2010-028, 101 Pages, 2010/09
This report describes analysis results on BFS-69 and BFS-66-2 critical experiments carried out under the collaboration with Russian Institute of Physics and Power Engineering. In the experiments, various nuclear characteristics were measured in 2 kinds of cores with/without Np loading of about 8 kg. JAEA's standard analysis results were presented with 4 kinds of nuclear data (JENDL-3.2, JENDL-3.3, JENDL/AC-2008, and ENDF/B-VII). The results show (1) An overestimation trend appears in BFS-69 criticality results, especially with JENDL-3.3 and JENDL/AC-2008. The difference from ENDF/B-II mainly lies in the average cosine of the scattering angle around 1 MeV; (2) A discrepancy exists in BFS-69 Na void reactivity results with the three JENDL nuclear data. The difference from ENDF/B-II mainly lies in scattering cross sections around 1 MeV and fission cross section around 1 keV; (3) The analysis results simulate measured Np effects on nuclear characteristics within experimental errors.
Yamaji, Akifumi; Suzuki, Motoe; Okubo, Tsutomu
JAEA-Research 2010-029, 54 Pages, 2010/09
This study has evaluated uncertainties in FEMAXI-6 calculations and clarified key models and parameters for predicting LWR MOX fuel rod behavior. Irradiation data obtained from the Halden reactor experiments (IFA-597.4 rod-10, rod-11, and IFA-514 rod-1) were used. The maximum discharge burnup was about 40 GWd/tMOX (IFA-514 rod-1). The results showed that uncertainties in fission gas release calculations were particularly high, and contributions of pellet relocation, densification and swelling models on pellet temperature were also evaluated. The basic fission gas release mechanism of MOX fuels should be the same as that of UO fuels, but the parameters in the model need to be revised for MOX fuels. More experimental data are needed. However, frequent reactor shutdowns and restarts may cause pellet relocation changes which need to be considered in the evaluations.
fuels, but the parameters in the model need to be revised for MOX fuels. More experimental data are needed. However, frequent reactor shutdowns and restarts may cause pellet relocation changes which need to be considered in the evaluations.
Sasamoto, Hiroshi; Ishii, Tomoko*; Sato, Hisao*; Sazarashi, Masami
JAEA-Research 2010-030, 64 Pages, 2010/09
It is necessary to evaluate the alteration behavior of buffer material by interactions of overpack (iron) and buffer (bentonite) materials for geological disposal of high level radioactive waste. In the present study, laboratory experiments were carried out for the better understanding of phenomena caused by iron-bentonite (smectite) interactions. Before conducting the experiments, literature survey was performed to summarize the existing knowledge about iron-bentonite interactions and to identify the dominant factors affecting the alteration behavior. As the results of experiment, experimental conditions caused remarkable alteration, secondary minerals suggested as alteration product, different behavior of alteration between batch and compacted systems etc. were revealed.
Okubo, Seisuke*; Hikima, Ryoichi; Hirano, Toru*; Matsui, Hiroya
JAEA-Research 2010-031, 45 Pages, 2010/10
Rock shows time-dependent behavior such as creep/relaxation. With respect to high-level radioactive waste disposal, knowledge of the long-term mechanical stability of shafts and galleries excavated in rock are required, not only during construction and operation but also over a period of thousands of years after closure. Therefore, it is very important to understand the time-dependent behavior of rock for evaluating long-term mechanical stability. The purpose of this study is determining the mechanisms of time-dependent behavior of rock by the precise test, observation and measurement, to develop methods for evaluating long-term mechanical stability. In previous work, testing techniques have been established and basic evaluation methods were developed. Recently, some parameters needed for simulation of time-dependent behavior were determined at the Mizunami underground research facilities. However, we did not have enough data to check on the reliability of the evaluation method for these parameters. This report describes the results of the activities in fiscal year 2009. In Chapter 1, we provide an overview and the background to this study. In Chapter 2, the results of the long-term creep test on Tage tuff, started in fiscal year, 1997 are described. In Chapter 3, methods for obtaining parameters of the constitutive equation for rock are reviewed and summarized. The time dependent behavior of Toki granite and Inada granite (40-80  C) are also summarized based on data obtained prior to the previous fiscal year. In Chapter 4, the FEM analysis implemented with a generalized variable-compliance-type constitutive equation carried out to clarify the long-term behavior of Toki granite is described. Finally, based on the numerical analysis, an in situ testing method is proposed.
C) are also summarized based on data obtained prior to the previous fiscal year. In Chapter 4, the FEM analysis implemented with a generalized variable-compliance-type constitutive equation carried out to clarify the long-term behavior of Toki granite is described. Finally, based on the numerical analysis, an in situ testing method is proposed.
Hyakutake, Toru*; Muto, Akinori*; Sasakura, Mariko*; Minowa, Hirotsugu*; Suzuki, Kazuhiko*; Yokoyama, Kaoru; Takahashi, Nobuo; Hata, Haruhi; Sugitsue, Noritake
JAEA-Research 2010-032, 32 Pages, 2010/10
System decontamination has been generally carried out with the aim of reducing the amount of radioactive waste generated and minimizing human exposure to radiation released from nuclear fuel facilities. At the Ningyo-Toge Environmental Engineering Center, metal surfaces that are contaminated by uranium are dry decontaminated by using iodine heptafluoride (IF ) as a system decontaminator. In this dry decontamination technique, a chemical reaction occurs between the uranium compound attached to the metal surface and IF
) as a system decontaminator. In this dry decontamination technique, a chemical reaction occurs between the uranium compound attached to the metal surface and IF . Only a few studies have been carried out on the decontamination efficiency, mechanism, level, etc. of dry decontamination techniques that use a decontamination gas. Therefore, the generalization of dry decontamination technique was assessed by a numerical method using decontamination data obtained at the Ningyo-Toge Environmental Engineering Center. A concrete analytical content is a depositing of Uranium Hexafluoride.
. Only a few studies have been carried out on the decontamination efficiency, mechanism, level, etc. of dry decontamination techniques that use a decontamination gas. Therefore, the generalization of dry decontamination technique was assessed by a numerical method using decontamination data obtained at the Ningyo-Toge Environmental Engineering Center. A concrete analytical content is a depositing of Uranium Hexafluoride.
Hosoma, Takashi
JAEA-Research 2010-033, 47 Pages, 2010/10
An accurate volume measurement system for plutonium nitrate solution stored in an accountability tank with dip-tubes has been developed and demonstrated over fifteen years at Plutonium Conversion Development Facility of Japan Atomic Energy Agency. It was proved, as a result of calibrations during the demonstration, that measurement uncertainty practically achieved and maintained was less than 0.1% (systematic character) and 0.15% (random) as one sigma which was half of the current target uncertainty admitted internationally. It was also proved that discrepancy between measured density and analytically determined density was less than 0.002 g cm
cm as one sigma. These uncertainties include effects by long term use of the accountability tank where plutonium throughput is six ton. The system consists of high precision differential pressure transducers and a dead weight tester, sequentially controlled valves for periodical zero adjustment, dampers to reduce pressure oscillation and a procedure to correct measurement biases. The sequence was also useful to carry out maintenances safely without contamination. Longevity of the transducer was longer than 15 years. Principles and essentials to determine solution volume and weight of plutonium, measurement biases and corrections, accurate pressure measurement system, maintenances and diagnostics, operational experiences, evaluation of measurement uncertainty are introduced.
as one sigma. These uncertainties include effects by long term use of the accountability tank where plutonium throughput is six ton. The system consists of high precision differential pressure transducers and a dead weight tester, sequentially controlled valves for periodical zero adjustment, dampers to reduce pressure oscillation and a procedure to correct measurement biases. The sequence was also useful to carry out maintenances safely without contamination. Longevity of the transducer was longer than 15 years. Principles and essentials to determine solution volume and weight of plutonium, measurement biases and corrections, accurate pressure measurement system, maintenances and diagnostics, operational experiences, evaluation of measurement uncertainty are introduced.
Kimura, Makoto*; Sazarashi, Masami; Fujita, Tomoo; Nakama, Shigeo; Suzuki, Hideaki
JAEA-Research 2010-034, 131 Pages, 2010/10
Numerical model which can quantify the complex evolution of the coupled thermo-hydro-mechanical-chemical processes in the near-field of a HLW repository has been developed and the outline of the model considering heat flow, fluid flow, mass transport and a variety of chemical reactions such as mineral dissolution/precipitation, gas dissolution/exsolution, ion-exchange and surface complexation are described. The applicability of the numerical model was shown by the following three efforts. (1) Intercomparison analysis against another coupled model, TOUGHREACT which has been developed in the Lawrence Berkeley National Laboratory. (2) Comparison with the measured data in the designed laboratory tests for the salt accumulation/precipitation. (3) Perspective simulation on chemical changes in the near-field involving the radioactive decay heat arising from the vitrified waste and infiltration of ground water into the buffer material.
Kunimaru, Takanori; Ota, Kunio; Alexander, W. R.*; Yamamoto, Hajime*
JAEA-Research 2010-035, 109 Pages, 2010/11
A quality management system (QMS) will save on effort by reducing errors and the requirement to re-sample and re-analysis and eventually lead to ensuring the reliability of the investigation results. In the Horonobe Underground Research Laboratory project, work has been ongoing to develop an appropriate QMS which is applicable to surface-based investigations. A quality assurance (QA) audit of hydrochemical datasets for boreholes HDB-9 - 11 has been carried out by applying both the groundwater QA methodology employed in the recent site assessments in Sweden and the porewater QA regime newly proposed for assigning the QA categories. This QA audit exercise indicates that the HDB-9 - 11 hydrochemical data are classified into lower categories because mainly of contamination of waters by drilling fluids, poor time-series data coverage and oxidation of core materials and also clarifies areas where additional information/work would be required to the ongoing programme.
Akaoka, Katsuaki; Maruyama, Yoichiro; Oba, Masaki; Miyabe, Masabumi; Otobe, Haruyoshi; Wakaida, Ikuo
JAEA-Research 2010-036, 14 Pages, 2010/10
For the remote analysis of low DF TRU (Decontamination Factor Transuranic) fuel, Laser Induced Breakdown Spectroscopy (LIBS) was applied to uranium oxide including a small amount of calcium oxide (3306ppm(weight)) as a sample, and the spectrum emitted from laser-breakdown plasma was examined. The characteristics, such as spectrum intensity and plasma excitation temperature as a function of laser power, were measured using time-resolved spectroscopy. As a result, the laser power of around 5 mJ was found optimum to obtain the stable intensity and narrow line width of spectrum.
Kosaka, Hiroshi; Saegusa, Hiromitsu; Onoe, Hironori; Takeuchi, Ryuji
JAEA-Research 2010-037, 42 Pages, 2011/01
Mizunami Underground Research Laboratory (MIU) Project is being carried out by Japan Atomic Energy Agency (JAEA) in the Cretaceous Toki granite in the Tono area, central Japan. The MIU project is a broad scientific study of the deep geological environment as a component of the research and development supporting geological disposal of high-level radioactive wastes. One of the main goals of the project is to establish techniques for comprehensive investigation, analysis and assessment of the deep geological environment in fractured crystalline rock. In this study, hydrogeological modeling and groundwater flow simulation taking into consideration the long-term pumping test has been carried out in order to reflect making test specifications of long-term pumping test. The pumping test will be carried out using the borehole, which will be drilled from underground research gallery in fiscal 2010. In this groundwater flow simulation, the sensitive analysis focused on location of pumping interval along the borehole, pumping time and pumping flow rate was conducted to predict the influence of these test specifications on the pressure response in pressure monitoring boreholes. As a result, the different variations of pressure response were indicated by the differences of the location of pumping interval bounded by the fault. In addition, small effect of difference of pumping time (2 weeks or 4 weeks) on pressure response was predicted. The recommendation of test specifications of long-term pumping test was made based on this study.
Takamatsu, Kuniyoshi; Ueta, Shohei; Sumita, Junya; Goto, Minoru; Hamamoto, Shimpei; Tochio, Daisuke; Nakagawa, Shigeaki
JAEA-Research 2010-038, 59 Pages, 2010/11
Research and development and hydrogen production technologies by HTGRs will establish future hydrogen energy system. Additionally, the R&D will contribute to innovative hydrogen production technologies by nuclear powers as one of nuclear heat utilizations. We are making an effort to propose a prototype of reactor hydrogen production system until about 2020. Therefore, JAEA is promoting the R&D for confirming the technical basis of HTGRs with the HTTR in the first midterm plan. In 2007, we accomplished the rated power operation for continuous 30 days of the HTTR. In the high temperature operation for continuous 50 days, JAEA evaluated the experimental data such as core burn-up, helium purity control, performance of high temperature equipments, structural integrity in the core, etc. and demonstrated the nuclear thermal availability of heat source for thermo-chemical hydrogen production technology.
Tsuruta, Tadahiko; Matsuoka, Toshiyuki; Hodotsuka, Yasuyuki; Tagami, Masahiko; Ishida, Hideaki; Hayano, Akira; Kurihara, Arata; Yuguchi, Takashi
JAEA-Research 2010-039, 131 Pages, 2011/01
Tono Geoscientific Unit of Geological Isolation and Development Directoratte is performing Mizunami Underground Research Laboratory (MIU) Project, which is a broad scientific study of the deep geological environment as a basis of research and development for geological disposal of nuclear wastes, in order to establish comprehensive techniques for the investigation, analysis and assessment of the deep geological environment in fractured crystalline rock. The MIU Project has three overlapping 3 phases, with a total duration of 20 years. The project goals of the MIU Project from Phase I through to Phase III are: to establish techniques for investigation, analysis and assessment of the deep geological environment, and to develop a range of engineering for deep underground application. Currently, the project is under the Phase II. This document presents the overview of results of the research and development on "geology" performed in fiscal year 2008, with regard to the Phase II goal.
Shimo, Michito*; Kumamoto, So*; Ito, Akira*; Karasaki, Kenji*; Sawada, Atsushi; Oda, Yoshihiro; Sato, Hisashi
JAEA-Research 2010-040, 57 Pages, 2010/11
In safety analysis of geological disposal of the high-level nuclear waste, it is important to evaluate appropriately the mass transport characteristics of the bedrock as the natural barrier. Especially, it has been found that the porosity of the rock matrix is high and fractured zones are developing and therefore the mass transport characteristics will be the mixture of those for porous media and the fractured media. In this work, we conducted, (1) a study on the method to mine out the rock block sample of tens of-centimeter to maximum 1 m scale, (2) a study on a method of the tracer test using a rock block sample and a series of scoping analysis. We also examined the uncertainty associated the hydrogeological model using a method combining a forward and inverse analysis, based on the various type of data sets obtained at Horonobe site, such as the temperature distribution and hydraulic head and salinity distribution.
Tetsu, Keiichi*; Sawada, Atsushi
JAEA-Research 2010-041, 24 Pages, 2010/11
In this study, we measured fracture aperture by using a series of the digital image data of a single natural fracture in the 50 cm scale of the granite rock block by grinding the rock surface in 1 mm increment perpendicular to the fracture. The fracture aperture was measured by scaling of the width of void space in between fracture walls, without taking account fracture infilling materials. Thus, we obtained both fracture characteristics, fracture width (separation distance between the fracture walls) and fracture aperture, in 50 cm scale of a natural rock. Ratio of infilling to fracture width is large in which fracture width is relatively small. In this area, fracture aperture tended to become small. Consequently, the flow channel by connecting the fracture aperture become to be localized.
Chiba, Go
JAEA-Research 2010-042, 92 Pages, 2010/12
Using the experimental data in the IRPhEP handbook, an experimental analysis of the MOZART experiment is carried out with JENDL-4.0. The C/E values for K are 0.9981 and 1.0006 for MZA and MZB. In reaction rate ratios at the core center, C values agree with E values within 1.0% for F25/F49 and C28/F49, and within 4.0% for F28/F25, F40/F49 and F41/F49. In sodium void reactivity worths, C values are about 10% larger than experimental values for the non-leakage-dominated data. For the leakage-dominated data, absolute differences normalized by the leakage component are less than 10%. In material worths, C values are about 5% larger than E values for plutonium. C values agree with E values within 10% differences for uranium and SS. In control rod worths, C values are 2% to 5% larger than E values. In reaction rate distributions, C values agree well with E values in core regions. Underestimation is observed systematically in C values of threshold reactions in blanket regions.
are 0.9981 and 1.0006 for MZA and MZB. In reaction rate ratios at the core center, C values agree with E values within 1.0% for F25/F49 and C28/F49, and within 4.0% for F28/F25, F40/F49 and F41/F49. In sodium void reactivity worths, C values are about 10% larger than experimental values for the non-leakage-dominated data. For the leakage-dominated data, absolute differences normalized by the leakage component are less than 10%. In material worths, C values are about 5% larger than E values for plutonium. C values agree with E values within 10% differences for uranium and SS. In control rod worths, C values are 2% to 5% larger than E values. In reaction rate distributions, C values agree well with E values in core regions. Underestimation is observed systematically in C values of threshold reactions in blanket regions.
Matsui, Hiroya; Tanno, Takeo; Hirano, Toru*; Goke, Mitsuo*; Kumasaka, Hiroo*; Tada, Hiroyuki*; Ishii, Takashi*
JAEA-Research 2010-043, 87 Pages, 2010/12
The results are as follows (1) For the ventilation shaft at GL-350m, the crack tensor deformation analysis based on FY2004 work's results showed the calculated displacement was smaller than the measured displacement. A geometrical parameters of fractures in FY2004 work's result was different from one based on geological observation in the shaft. Therefore, the crack tensor of FY2004 work's results seems to be underestimated. (2) Large discontinuities with NE strike and high dipping observed in a shaft were major reason for the difference of crack tensors determined by borehole investigation from surface and geological observations in a shaft. Therefore, the crack tensor for pilot borehole investigation in a shaft was calculated as well and compared with each results. It was found that the fabric tensor is similar with it of geological observation and the vale was medium. (3) The crack tensor around GL-500m was estimated by relation of statistical quantities for fractures between GL-300m and GL-500m. Consequently, the deformation analysis based on the estimated crack tensor showed an increase in convergence and stress in the support system compared to FY2004 work's results.
Kusano, Tomohiro; Asamori, Koichi; Kurosawa, Hideki; Kokubu, Yoko; Tanikawa, Shinichi; Negi, Tateyuki; Hanamuro, Takahiro; Yasue, Kenichi; Yamasaki, Seiko; Yamada, Kunimi; et al.
JAEA-Research 2010-044, 153 Pages, 2011/01
This progress report (H22 report) documents progress made during JAEA 1st Midterm Plan (FY 2005 - 2009) to provide the scientific base for assessing geosphere stability for long-term isolation of the high-level radioactive waste. For the current 5-year R&D programme, three major goals have been defined as follows: (1) development and synthesis of investigation techniques for selecting suitable sites in geosphere stability, (2) development, application, and evaluation of prediction models for evaluating the changes of geological environment in thermal, hydraulic, mechanical and geochemical conditions for a long period of time, and (3) development of new dating techniques for providing information about geologic history and the timing of geologic events. In this paper, the current status of R&D activities with previous scientific and technological progress is summarized.
Chiba, Go
JAEA-Research 2010-045, 24 Pages, 2011/01
We evaluate a gamma-ray transport effect on a heating distribution in a fast reactor fuel subassembly by gamma-ray transport calculations. We carry out calculations by using a gamma cross section library UFGLIB.J40 based on the latest nuclear data file JENDL-4.0 and a radiation transport code system CBG which is under development at Japan Atomic Energy Agency. Numerical calculations with a Monju fuel subassembly model reveal that a heating rate in a fuel pin decreases about 1.35% by considering a gamma-ray transport. In addition, the uncertainty of this gamma-ray transport effect is estimated at 0.25%. It is also shown that a heating rate in a region inside of a wrapper tube decreases about 0.5% by considering the gamma-ray transport.
 )
) Mo
MoJun, B. J.; Tanimoto, Masataka; Kimura, Akihiro; Hori, Naohiko; Izumo, Hironobu; Tsuchiya, Kunihiko
JAEA-Research 2010-046, 103 Pages, 2011/01
The world is currently suffering from a severe shortage of  Mo and various R&Ds have been given for its availability. The only but critical shortage of (n,
Mo and various R&Ds have been given for its availability. The only but critical shortage of (n, )
) Mo is its extremely low specific activity, which gives inconveniency in the extraction of
Mo is its extremely low specific activity, which gives inconveniency in the extraction of  Tc and is consequently converted to additional cost. Potential technologies which make the (n,
Tc and is consequently converted to additional cost. Potential technologies which make the (n, )
) Mo competitive by reducing the additional cost are already available. Because Japan and Korea import all
Mo competitive by reducing the additional cost are already available. Because Japan and Korea import all  Mo from long distance, the cost benefit of local (n,
Mo from long distance, the cost benefit of local (n, )
) Mo production in these countries is especially large. In this report, we studied feasibility of the mass (n,
Mo production in these countries is especially large. In this report, we studied feasibility of the mass (n, )
) Mo production from viewpoints of global and regional status of
Mo production from viewpoints of global and regional status of  Mo demand and supply, competitiveness with other production methods, requirements and flow of the
Mo demand and supply, competitiveness with other production methods, requirements and flow of the  Mo, production capability, cost, convenience in usage, and alternative technologies to overcome its shortage.
Mo, production capability, cost, convenience in usage, and alternative technologies to overcome its shortage.
Yoshida, Kazuo
JAEA-Research 2010-047, 15 Pages, 2011/02
Entrainment of liquid droplets from a bubbling or boiling pool surface is one of important phenomena for analysis of accidents postulated in nuclear installations. The Kataoka-Ishii correlation, which is based on a mechanistic modeling, has been developed for application to wide range of phenomena. These includes heat and mass transfer processes during loss-of-coolant accidents and radioactive carryover form flashing water pool caused by containment failure during a severe accident. In case of nuclear fuel facilities, radioactive material transport with liquid droplets entrained by very low steam flow velocity is also important in boiling event of radioactive solution storage tank caused by the loss of cooling function. Kataoka-Ishii correlation is however not applied to that analysis directly because of out of range of gas velocity. Therefore, a correlation has been developed analytically with considering features of phenomena of entrainment with very low gas velocity (Stokes regime).
Oikawa, Yasuki*; Soma, Nobukazu*; Tosha, Toshiyuki*; Matsui, Hiroya; Hirano, Toru*; Tanno, Takeo; Hikima, Ryoichi
JAEA-Research 2010-048, 45 Pages, 2011/02
In excavating a gallery or a shaft in deep underground, an excavation disturbed zone (EDZ) develops around the opening with new cracks due to both stress redistribution and excavation induced damage. The investigation and the evaluation of an EDZ are needed because the changes in rock properties and the EDZ development influence performance assessment of geological disposal and design of the underground structures. However, the in situ investigation of an EDZ is time consuming and costly because investigations are large-scale and required specialized equipment. We conducted a fundamental study for the development of an EDZ investigation method that is easy and inexpensive using the information obtained from only drilling. This report describes the results of the joint research carried out in fiscal year 2008 and fiscal year 2009. In Chapter 1, we provide the overview and the background of this study. In Chapter 2, we discuss the estimation of stress state around the research gallery at a depth of 200m in Mizunami Underground Research Laboratory (MIU) by Acoustic Emission / Deformation Rate Analysis (AE/DRA) method using rock cores obtained from the drilling. In Chapter 3, results of the evaluation of geological structure around the research gallery at a depth of 200m in MIU based on Seismic While Drilling (SWD) method using the vibrations caused by the drilling are described.
Kojima, Keiji*; Onishi, Yuzo*; Watanabe, Kunio*; Nishigaki, Makoto*; Tosaka, Hiroyuki*; Shimada, Jun*; Aoki, Kenji*; Tochiyama, Osamu*; Yoshida, Hidekazu*; Ogata, Nobuhisa; et al.
JAEA-Research 2010-049, 282 Pages, 2011/02
This report summarizes studies that have been carried out with the aim of assessing and systemizing the technology used for the investigation and analysis of the deep underground geological environment in relation to the disposal of radioactive waste. The main studies were: (1) a study on the research and development (R&D) topics proven to have practical application for the investigation, and analysis and understanding of the deep underground geological environment, and, (2) a study on leading edge technology that can provide the advanced technical basis for the investigation, analysis and understanding of the deep underground geological environment. Regarding the R&D topics (1, above), specific investigations, measurements, numerical analyses and chemical analyses were performed and reviewed with respect to the topics, (a) Repository design, engineering technology (b) Geological environment and (c) Safety evaluation. Based on the result of the review, topics requiring collaboration research in overlapping research fields, including safety assessment, were identified. Also, the near field concept (NFC) was reconsidered in terms of its realistic construction model. Regarding advanced technology (2, above), based on the objectives of the JAEA (Japan Atomic Energy Agency) research project, the study was implemented considering previous R&D results and detailed research result at the research site and thus an assessment of the need for advanced technical basis for investigation and analysis. This study contributed to the R&D development and its practical application.
Nakatani, Takayoshi; Ishitoya, Kimihide; Funabashi, Hideyuki; Sasaki, Ryoichi*; Kurosawa, Mitsuru*
JAEA-Research 2010-050, 104 Pages, 2011/02
In July 2007, the Nuclear Safety Commission of Japan (NSC) formulated "Basic Policy for Safety Regulation Concerning Land Disposal of Low-Level Radioactive Waste (Interim Report)". "Classification of Scenarios into Three Types" and their "Standard Dose Values" were indicated in this report. In this study, some scenarios for safety assessment were developed as "Inadvertent Human Intrusion or Rare Natural Event Scenarios" based on the previous technical documents. The parameters were set up for dose calculation and the exposure doses were calculated. As the result, exposure doses in all cases were less than 10 mSv/y 100 mSv/y (standard exposure dose of "Inadvertent Human Intrusion or Rare Natural Event Scenarios").
100 mSv/y (standard exposure dose of "Inadvertent Human Intrusion or Rare Natural Event Scenarios").
Ishikawa, Jun; Moriyama, Kiyofumi
JAEA-Research 2010-051, 42 Pages, 2011/02
At the late phase of severe accident (SA), there is a possibility that gaseous iodine species which dissolved in the pool water at the early phase of accident are released to the containment (CV) atmosphere due to radiation chemical reactions. In order to evaluate the influence on the CV source terms considering iodine chemistry, a coupling analysis method of SA analysis code THALES2 and iodine chemistry analysis code Kiche was developed. The evaluation of thermal-hydraulics conditions and source term in the CV at the late phase of severe accident were conducted for 4 accident scenarios of BWR4/Mark-I by using this coupling method. As for the re-vaporization of iodine to the CV atmosphere, the influence of pH is larger than that of difference of accident sequences. Total release fractions of I to the CV atmosphere at 50 h for pH = 5, 7 and 9 were 10
to the CV atmosphere at 50 h for pH = 5, 7 and 9 were 10 -10
-10 , 10
, 10 and 10
and 10 for the initial core inventory. The lower the pH was, the larger the release fraction of I
for the initial core inventory. The lower the pH was, the larger the release fraction of I was.
was.
Ochs, M.*; Tachi, Yukio; Ganter, C.*; Suyama, Tadahiro; Yui, Mikazu
JAEA-Research 2010-052, 59 Pages, 2011/02
For reliable parameter setting in performance assessment of geological disposal, JAEA has developed the integrated sorption and diffusion (ISD) model/database in bentonite systems. The main goal of the mechanistic model/database development is to provide a tool for a consistent explanation, prediction, and uncertainty assessment. This report focuses on developing the thermodynamic sorption model (TSM) including selection of model design and surface species, and on the quantification and handling of model uncertainties, based on illustrating by example of Ni sorption on montmorillonite/bentonite. Two fundamentally different approaches are presented and compared for representing TSM uncertainties: (1) TSM parameter uncertainties based on optimization routines and statistical procedure, (2) overall error estimated by direct comparison of modeled and experimental Kd values. The overall error in Kd is viewed as the best representation of model uncertainty in ISD model/database development.
Kunieda, Satoshi; Chiba, Satoshi; Shibata, Keiichi; Ichihara, Akira; Iwamoto, Osamu; Iwamoto, Nobuyuki; Fukahori, Tokio; Sukhovitskij, E.*
JAEA-Research 2010-053, 59 Pages, 2011/02
The soft-rotator model Hamiltonian parameters were deduced for 63 even-even medium and heavy nuclei in a mass range 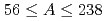 . We obtained those values by the combination of the low-lying level structure and the coupled-channels proton scattering analyses. It was found that the values of the effective quadrupole and octupole deformations obtained were consistent with those derived from experimental data. Besides, the equilibrium ground-state quadrupole deformation parameters were also in reasonable accord with the theoretical mass-models results for deformed heavy nuclei. In this report, we present a complete set of the Hamiltonian parameters for each nucleus. The obtained values of the parameters often varied with the constituent neutron and/or proton numbers anomalously. On the other hand, some clear systematic trends were seen among the major Hamiltonian parameters.
. We obtained those values by the combination of the low-lying level structure and the coupled-channels proton scattering analyses. It was found that the values of the effective quadrupole and octupole deformations obtained were consistent with those derived from experimental data. Besides, the equilibrium ground-state quadrupole deformation parameters were also in reasonable accord with the theoretical mass-models results for deformed heavy nuclei. In this report, we present a complete set of the Hamiltonian parameters for each nucleus. The obtained values of the parameters often varied with the constituent neutron and/or proton numbers anomalously. On the other hand, some clear systematic trends were seen among the major Hamiltonian parameters.
Tanaka, Masaru*; Gofuku, Akio*; Ishizaka, Kaoru*; Tokizawa, Takayuki; Sato, Kazuhiko; Koga, Osamu
JAEA-Research 2010-054, 76 Pages, 2011/02
To obtain public understanding on the uranium mining sites reclamation at Ningyo-toge Environmental Engineering Center, it is necessary to conduct appropriate Risk Communication (RC). In this study, to discuss the appropriate Risk communication method on the uranium mining sites reclamation, making of explanatory material by university student, and questionnaire survey on the risk perception were conducted.
Nakayama, Masashi; Sato, Haruo; Sugita, Yutaka; Noguchi, Akira
JAEA-Research 2010-055, 25 Pages, 2011/02
In Japan, any high level radioactive waste repository is to be constructed at over 300 m depth below surface. Tunnel support is used for safety during the construction and operation, and shotcrete and concrete lining are used as the tunnel support. Concrete is a composite material comprised of aggregate, cement and various additives. Low alkaline cement has been developed for the long term stability of the barrier systems whose performance could be negatively affected by highly alkaline conditions arising due to cement used in a repository. JAEA has developed a low alkaline cement, named as HFSC, containing over 60wt% of SF and FA. JAEA are presently constructing an URL at Horonobe for research and development in the geosciences and repository engineering technology. HFSC was used experimentally as the shotcrete material in construction of part of the 140 m deep gallery in Horonobe URL. The objective of this experiment was to assess the performance of HFSC shotcrete in terms of mechanics, workability, durability, and so on. HFSC used in this experiment is composed of 40wt% OPC, 20wt% SF, and 40wt% FA. This composition was determined based on mechanical testing of various mixes of the above components. Because of the low OPC content, the strength of HFSC tends to be lower than that of OPC in normal concrete. The total length of tunnel using HFSC shotcrete is about 73 m and about 500 m of HFSC was used. This experimental construction confirmed the workability of HFSC shotcrete. Although several in-situ experiments using low alkaline cement as shotcrete have been performed at a small scale, this application of HFSC at the Horonobe URL is the first full scale application of low alkaline cement in the construction of a URL in the world. In this report, we present detailed results of the in-situ construction test.
of HFSC was used. This experimental construction confirmed the workability of HFSC shotcrete. Although several in-situ experiments using low alkaline cement as shotcrete have been performed at a small scale, this application of HFSC at the Horonobe URL is the first full scale application of low alkaline cement in the construction of a URL in the world. In this report, we present detailed results of the in-situ construction test.
Nakayasu, Akio; Niizato, Tadafumi; Yasue, Kenichi; Doke, Ryosuke; Shigehiro, Michiko*; Tanaka, Takenobu*; Aoki, Michinori*; Sekiya, Ayako*
JAEA-Research 2010-056, 116 Pages, 2011/02
The investigation methods for characterizing natural events and processes in a coastal field have been extracted on the basis of analysis of previous research. Collected information is classified into three groups according to characteristics of natural events/processes and investigation methods. First group is the methods for evaluation of uplift, subsidence and sedimentation rates. Second group is the methods for evaluation ob denudation rates. The third group is the methods for reconstruction of the climatic and sea-level changes. Based on an analysis of the above information, investigation method that can be applied to a coastal region was extracted. The methods and indices are as follows: (1) Uplift rate: the heights of marine terraces are the most important index in an upheaval region. (2) Subsidence and sedimentation rate: the depths of strata underlying an alluvial plain are main indices in a subsidence region. (3) Denudation rate: the features of marine terrace are main indices and the inspection of denudation processes by the use of a numerical simulation is necessary. (4) Climate change: lacustrine deposits are main object for investigation. (5) Sea-level change: reconstruction of relative sea-level change curve including uplift/subsidence factor and paleography based on acoustic exploration and the investigation of marine terraces.
Hayashi, Katsuhiko; Noguchi, Akira; Kishi, Hirokazu; Kabayashi, Yasushi*; Nakama, Shigeo; Fujita, Tomoo; Naito, Morimasa; Tada, Hiroyuki*; Kumasaka, Hiroo*; Goke, Mitsuo*; et al.
JAEA-Research 2010-057, 101 Pages, 2011/03
Cement-type materials that are used for supports or grouting at high-level radioactive waste disposal facilities leach into the groundwater and create a highly alkaline environment. Of concern in highly alkaline environments are the alteration of bentonite used as buffers or backfill materials, and of surrounding rock mass, and the increased uncertainty regarding the provision of performance of the disposal system over a long period of time. In this study, to reduce the quantity of cement-type materials that cause highly alkaline environments, technical feasibility of the support structure including the materials which considered the long-term performance of the HLW disposal system are discussed by using knowledge and technology accumulated in JAEA and Shimizu Construction. Moreover, based on the results, the problems remained in the application to the future HLW disposal institution are summarized.
Matsumoto, Kazuhiro; Fujita, Tomoo
JAEA-Research 2010-058, 56 Pages, 2011/03
Bentonite buffer material is envisaged as a component of the engineered barrier system for high-level radioactive waste disposal. As a result of its swelling property, the buffer may extrude into the surrounding host rock through open fractures. If this persists for extremely long periods of time, the buffer extrusion could lead to a reduction of buffer density, which may in turn degrade the expected performance. In this report, verification of the solid phase diffusion theory of the past was performed and future problems were extracted based on expertise.
Hayashi, Katsuhiko; Kishi, Hirokazu; Kabayashi, Yasushi*; Takebe, Atsuji*; Fujiyama, Tetsuo*; Hiramoto, Masayuki*; Mizutani, Kazuhiko*; Morita, Atsushi*
JAEA-Research 2010-059, 92 Pages, 2011/03
In this study, the first investigation is the order of the multi-tunnels excavation. The second is the strain-softening model for multi-tunnels which is based on test data at Horonobe site. As results of first investigation, we showed as 2 dimensional analyses that it was desirable to excavate the tunnel of the remote distance at first and excavate the tunnel between these tunnels next, and it is necessary for the examination that reflected a real plan, such as evacuation machine and actual multi tunnel layout. As the results of second investigation, we also showed the more reliable EDZ by using the strain-softening model that is based on test data at Horonobe site. Furthermore, we standardized the design method (draft) for the practical use by referring the past studies of multi tunnel design method.
Nakatsuka, Noboru; Hatanaka, Koichiro; Sato, Haruo; Sugita, Yutaka; Nakayama, Masashi; Miyahara, Shigenori; Asano, Hidekazu*; Saito, Masahiko*; Suyama, Yasuhiro*; Hayashi, Hidero*; et al.
JAEA-Research 2010-060, 50 Pages, 2011/02
Japan Atomic Energy Agency (JAEA) and Radioactive Waste Management Funding and Research Center (RWMC) concluded the letter of cooperation agreement on the research and development of radioactive waste disposal in April, 2005, and have been carrying out the collaboration work described above based on the agreement. JAEA have been carrying out the Horonobe Underground Research Laboratory (URL) Project which is intended for sedimentary rock in the Horonobe town, Hokkaido, since 2001. In the project, geoscientific research and research and development on geological disposal technology are being promoted. Meanwhile, the government (the Agency for Natural Resources and Energy, Ministry of Economy, Trade and Industry) has been promoting construction of equipments for the full-scale demonstration of engineered barrier system and operation technology for high-level radioactive waste (HLW) disposal since 2008, to enhance publics understanding to the geological disposal of HLW, using underground facility, etc. RWMC received an order of the project in fiscal year 2009 (2009/2010) continuing in fiscal year 2008 (2008/2009). Since topics in this project are included in the Horonobe URL Project, JAEA carried out this project as collaboration work continuing in fiscal year 2008. This report summarizes the results of engineering technology carried out in this collaboration work in fiscal year 2009. In fiscal year 2009, a part of the equipments for equipment of buffer material and visualization test apparatus for water penetration in buffer material were produced and house for the equipments and apparatus was constructed.
Irwanto, D.*; Chiba, Go; Nagaya, Yasunobu; Obara, Toru*
JAEA-Research 2010-061, 28 Pages, 2011/03
It is rather difficult to measure the effective delayed neutron fraction with experiments, so it becomes important to obtain their accurate calculation values. We study calculation methods for the effective delayed neutron fraction by analyzing various fast neutron systems including the bare spherical systems (Godiva, Jezebel, Skidoo, Jezebel-240), the reflective spherical systems (Popsy, Topsy, Flattop-23), MASURCA-R2 and MASURCA-ZONA2, and FCA XIX-1, XIX-2 and XIX-3. These analyses are performed by using SLAROM-UF and CBG for the deterministic method and MVP-II for the Monte Carlo method. We calculate the effective delayed neutron fraction with various definitions such as the fundamental value, the standard definition, Nauchi's definition and Meulekamp's definition, and compare these results with each other.
Ito, Kei; Ohshima, Hiroyuki; Kawamura, Takumi*
JAEA-Research 2010-062, 69 Pages, 2011/03
In the design study of a sodium-cooled fast reactor, the suppression of gas entrainment (GE) occurrences is considered as a key to achieve stable operations of the fast reactor. The authors are developing a high-precision numerical simulation algorithm for gas-liquid two-phase flows to evaluate the GE more efficiently than high-cost large-scale experiments. In this study, numerical simulations were performed on (1) the GE behavior in a simple experiment, (2) the mechanisms of GE occurrences in a large-scale test and (3) the entrained flow rate in a basic experiment. From the results of (1) simulation, it was confirmed that the developed simulation algorithm could reproduce the GE induced by vortical flows. Similarly, (2) and (3) simulations showed that the GE in the fast reactor and the entrained flow rate could be evaluated by the numerical simulations.
Ito, Kei; Ohshima, Hiroyuki; Xu, Y.*; Imai, Yasutomo*
JAEA-Research 2010-063, 58 Pages, 2011/03
Japan Atomic Energy Agency has conducted the FaCT project to study a conceptional design of a large-scale sodium-cooled fast reactor in which the coolant in the vessel has relatively higher velocity than conventional designs and may causes cover gas entrainment (GE) in an upper plenum region. The authors has been studied a evaluation method of GE in fast reactors and the 1st proposal (prototype) of "Design Guideline for Gas Entrainment Prevention Using CFD Method" was published in 2006. In this study, the prototype evaluation method was improved by introducing the surface tension and turbulent effects. The improved GE evaluation method was validated by analyzing the gas core lengths observed in simple experiments. Results showed that the analytical gas core lengths calculated by the improved GE evaluation method were shorter in comparison to the prototype GE evaluation method, and gave better agreement with the experimental data.
Ito, Kei; Ohshima, Hiroyuki
JAEA-Research 2010-064, 29 Pages, 2011/03
In accordance with the revision of "Regulatory guide for seismic design of nuclear power plants", Japan Atomic Energy Agency evaluated the seismic safety of the prototype fast breeder reactor "Monju" based on the revised guide. In this study, the seismic safety of the rear slope was analyzed by mechanistic simulation methods. In the distinct element method simulations, the seismic safety was evaluated in the simulation cases of various seismic wave amplitudes. As a result, the design earthquake ground motion did not cause any collapse (landslide) on the rear slope. In the moving particle semi-implicit simulations, the simulation results showed that the movements of the surface layer is at most several tem meters and therefore, the rocks in the rear slope could not attack the "Monju" plant. In conclusion, the mechanistic simulations showed that the rear slope of "Monju" had a sufficient seismic safety for the design earthquake ground motion.
Kimura, Nobuyuki; Hayashi, Kenji; Tobita, Akira; Kamide, Hideki; Nagasawa, Kazuyoshi*
JAEA-Research 2010-065, 191 Pages, 2011/03
Thermal stratification water experiments using a 1/10th scale model were carried out for an advanced loop type sodium cooled reactor. Experimental parameters were core outlet velocity, temperature difference during scram, and height of the plug which infill the hole at the dipped plates for setup of a fuel handling machine. It was found that the height and the rising speed of stratification interface depended on the Richardson number. Furthermore the temperature gradient of the stratification interface depended on the Peclet number.
Sakai, Ryutaro; Munakata, Masahiro; Kimura, Hideo; Ichikawa, Yasuo*; Nakamura, Masaru*
JAEA-Research 2010-066, 20 Pages, 2011/03
In the safety assessment for a geological disposal of radioactive waste, it is important to establish modelling methods and validation methods for regional groundwater flow system in the depth of 300 1000m to estimate radionuclide migration to human environment through groundwater flow system. The study discussed application of data and assessment methods for model validation based on multiple indicators such as hydrology, groundwater chemistry, temperature and age of groundwater in case of the Boso Peninsula in Chiba Prefecture where a lot of in-situ data about groundwater was measured. This results show that existing hydrochemical and thermal data are applicable to explain freshwater and saltwater distribution and groundwater flow pattern in case of regional scale. It also indicates that gravitational groundwater is likely to flow into the deep part of fresh-saltwater interface based on the exist of Na-HCO
1000m to estimate radionuclide migration to human environment through groundwater flow system. The study discussed application of data and assessment methods for model validation based on multiple indicators such as hydrology, groundwater chemistry, temperature and age of groundwater in case of the Boso Peninsula in Chiba Prefecture where a lot of in-situ data about groundwater was measured. This results show that existing hydrochemical and thermal data are applicable to explain freshwater and saltwater distribution and groundwater flow pattern in case of regional scale. It also indicates that gravitational groundwater is likely to flow into the deep part of fresh-saltwater interface based on the exist of Na-HCO type water above fresh-saltwater interface mixed with meteoric water and that multiple indicators are applicable to evaluate groundwater flow property and groundwater flow boundary in case of site scale region.
type water above fresh-saltwater interface mixed with meteoric water and that multiple indicators are applicable to evaluate groundwater flow property and groundwater flow boundary in case of site scale region.
Saegusa, Hiromitsu; Matsuoka, Toshiyuki
JAEA-Research 2010-067, 377 Pages, 2011/03
The Mizunami Underground Research Laboratory (MIU) Project is a comprehensive research project investigating the deep underground environment within crystalline rock being conducted by Japan Atomic Energy Agency at Mizunami City in Gifu Prefecture, central Japan. This report summarizes the results of the surface-based investigation phase, identifies future issues and provides direction for research to be conducted during construction phase and operation phase. The results compiled in this report will be utilized for the technical knowledge base on geological disposal of HLW, and can be used to enhance the technical basis for waste disposal in general and for development of government regulations.
Ota, Kunio; Abe, Hironobu; Kunimaru, Takanori
JAEA-Research 2010-068, 370 Pages, 2011/03
The Horonobe Underground Research Laboratory (URL) Project is a comprehensive research and development project aimed at studying the host sedimentary formations at Horonobe in Hokkaido, northern Japan. In phase I, following the selection of the URL area and site in Horonobe, stepwise surface-based investigations were carried out from March 2001 to March 2005. The relevant surface-based investigation techniques were developed and the design and safe construction plans for the URL finalised. Integration of the results ensures that the phase I goals were successfully achieved and identifies key issues that need to be addressed in phases II and III. More importantly, efforts have been made to summarise as many lessons learnt from the phase I investigations as possible to form a "knowledge base" that will reinforce the technical basis for both implementation and the formulation of safety regulations. The present report summarises the results of the phase I geoscientific research.
Sato, Hisashi; Yasuhara, Hideaki*; Sawada, Atsushi
JAEA-Research 2010-069, 45 Pages, 2011/03
Considering a safe, long-term sequestration of energy byproducts such as high level radioactive wastes, it is of significant importance to well-constrain the hydraulic and transport behavior of targeted permeants within fractured rocks. Specifically, fluid flow within low-permeability crystalline rock masses (e.g., granite) is often dominated by transport in through-cutting fractures, and thus careful considerations are needed on the behavior. There are three planes along that granites fail most easily under tension, and those may be identified as the rift, grain, and hardway planes. In this research, geometrical properties of tension-induced fractures were evaluated. Results show that rift planes are less rougher than the other planes of grain and hardway, and grain planes are generically rougher than the other planes of rift and hardway.