Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Sasaki, Toshiki; Aoyama, Yoshio; Yamashita, Toshiyuki
JAEA-Technology 2009-001, 33 Pages, 2009/03
A thermal treatment that can automatically unpack TRU waste and remove hazardous materials has been developed to reduce the risk of radiation exposure and save operation cost. The thermal treatment is a process of removing plastic wrapping and hazardous material from TRU waste by heating waste at 500 to 700  C. Plastic wrappings of simulated wastes were removed using a laboratory scale thermal treatment system. Celluloses and isoprene rubbers that must be removed from waste for disposal were pyrolyzed by the treatment. Although the thermal treatment can separate lead and aluminum from the waste, a further technical development is needed to separate lead and aluminum. Future technology development subjects for the TRU waste thermal treatment system are summarized.
C. Plastic wrappings of simulated wastes were removed using a laboratory scale thermal treatment system. Celluloses and isoprene rubbers that must be removed from waste for disposal were pyrolyzed by the treatment. Although the thermal treatment can separate lead and aluminum from the waste, a further technical development is needed to separate lead and aluminum. Future technology development subjects for the TRU waste thermal treatment system are summarized.
Takahashi, Nobuo; Yokoyama, Kaoru; Ikegami, Sohei; Shimaike, Masamitsu; Sugitsue, Noritake
JAEA-Technology 2009-002, 51 Pages, 2009/03
At the conversion facility, dismantlement and removal of the equipment are executed according to the decommissioning plan. The radioactivity of the spent bed material discharged along with the reprocessed uranium conversion is high. So, there is concern that the external exposure caused by the dismantlement of the spent bed material storage is high. Therefore, the uranium isotopic analysis using the  -ray measurement intended for the spent bed material was done, and the external exposure at site boundary was evaluated. As a result, the external exposure at site boundary is low. The external exposure caused by dismantlement work was evaluated, and the points to remember for dismantlement of the spent bed material storage are considered.
-ray measurement intended for the spent bed material was done, and the external exposure at site boundary was evaluated. As a result, the external exposure at site boundary is low. The external exposure caused by dismantlement work was evaluated, and the points to remember for dismantlement of the spent bed material storage are considered.
Ishimi, Akihiro; Katsuyama, Kozo; Abe, Kazuyuki; Nagamine, Tsuyoshi; Nakamura, Yasuo
JAEA-Technology 2009-003, 58 Pages, 2009/05
Japan Atomic Energy Agency executed the irradiation examination of the MA content mixed oxide fuel by Experimental Fast Reactor "JOYO". This examination was used that the mixed oxide fuel that contained Americium by 3% and 5%, and the mixed oxide fuel of Americium and Neptunium that contained 2% for each. The irradiation examination executed a short term irradiation (For ten minutes and 24 hours) by the high linear heat, and achieved maximum linear heat about 430 W/cm in "JOYO". After it had irradiated it, the post irradiation examination of the fuel pin was executed in the Fuels Monitoring facilities. On the results of X ray CT examination, the result that the density decrease is forecast to the vicinity of the center of the fuel was obtained for ten minutes in the irradiation. The formation of the central void was confirmed to the center of the fuel in 24 hour irradiation.
Ishikawa, Koki; Takamatsu, Misao; Kawahara, Hirotaka; Mihara, Takatsugu; Kurisaka, Kenichi; Terano, Toshihiro; Murakami, Takanori; Noritsugi, Akihiro; Iseki, Atsushi; Saito, Takakazu; et al.
JAEA-Technology 2009-004, 140 Pages, 2009/05
Probabilistic safety assessment (PSA) has been applied to nuclear plants as a method to achieve effective safety regulation and safety management. In order to establish the PSA standard for fast breeder reactor (FBR), the FBR-PSA for internal events in rated power operation is studied by Japan Atomic Energy Agency (JAEA). The level1 PSA on the experimental fast reactor Joyo was conducted to investigate core damage probability for internal events with taking human factors effect and dependent failures into account. The result of this study shows that the core damage probability of Joyo is 5.0 10
10 per reactor year (/ry) and that the core damage probability is smaller than the safety goal for existed plants (10 ry) and future plants (10
per reactor year (/ry) and that the core damage probability is smaller than the safety goal for existed plants (10 ry) and future plants (10 /ry) in the IAEA INSAG-12 (International Nuclear Safety Advisory Group) basic safety principle.
/ry) in the IAEA INSAG-12 (International Nuclear Safety Advisory Group) basic safety principle.
Tochio, Daisuke; Nojiri, Naoki; Hamamoto, Shimpei; Inoi, Hiroyuki; Sekita, Kenji; Kondo, Masaaki; Saikusa, Akio; Kameyama, Yasuhiko; Saito, Kenji; Fujimoto, Nozomu
JAEA-Technology 2009-005, 47 Pages, 2009/05
HTTR is now conducted in-service operation through the rise-to power operation with rated operation or high-temperature test operation from achievement of first criticality at 1998. In order to demonstrate to supply stable heat to heat utilization system for long-term, HTTR was conducted rated/parallel-loaded 30-days operation. This paper reports the characteristics of long-term operation for HTTR.
Totsuka, Toshiyuki; Sakata, Shinya
JAEA-Technology 2009-006, 36 Pages, 2009/05
The functions of JT-60 discharge control computer system and the data processing computer system will be integrated into a new JT-60SA supervisory control system to improve the operational efficiency of the JT-60 control computer system. In this report, we first show the necessary requirements for the new JT-60SA supervisory control system that should have high cost performance and maintenability. Next, overall system image of the new JT-60SA supervisory control system is presented and the necessary functions and the issues to be solved in the development are shown. Finally, the necessary manpower for this development and performance of the computer hardware, and the expected reduction of maintenance cost of the computer system are described.
Hayashi, Kimio; Nakagawa, Tetsuya; Onose, Shoji; Ishida, Takuya; Nakamichi, Masaru; Katsuyama, Kozo; Iwamatsu, Shigemi; Hasegawa, Teiji; Kodaka, Hideo; Takatsu, Hideyuki; et al.
JAEA-Technology 2009-007, 168 Pages, 2009/03
In-pile functional tests of breeding blankets have been planned by Japan Atomic Energy Agency (JAEA), using a test blanket module (TBM) which will be loaded in the International Thermonuclear Experimental Reactor (ITER). In preparation for the in-pile functional tests, JAEA has been being performed irradiation experiments of lithium titanate (Li TiO
TiO ), which is the first candidate of solid breeder materials for the blanket of the demonstration reactor (DEMO) under designing in Japan. The present report describes (1) results of a detailed design and trial fabrication tests of a dismantling apparatus for irradiation capsules which were used in irradiation experiments by the Japan Materials Testing Reactor (JMTR) of JAEA, and (2) results of a preliminary investigation of a glove box facility for post-irradiation examinations (PIEs). In the detailed design of the dismantling apparatus, datailed specifications and the installation methods were examined, based on results of a conceptual design and basic design. In the trial fabrication, cutting tests were curried out by making a mockup of a cutting component. Furthermore, a preliminary investigation of a glove box facility was carried out in order to secure a facility for PIE work after the capsule dismantling, which revealed a technical feasibility.
), which is the first candidate of solid breeder materials for the blanket of the demonstration reactor (DEMO) under designing in Japan. The present report describes (1) results of a detailed design and trial fabrication tests of a dismantling apparatus for irradiation capsules which were used in irradiation experiments by the Japan Materials Testing Reactor (JMTR) of JAEA, and (2) results of a preliminary investigation of a glove box facility for post-irradiation examinations (PIEs). In the detailed design of the dismantling apparatus, datailed specifications and the installation methods were examined, based on results of a conceptual design and basic design. In the trial fabrication, cutting tests were curried out by making a mockup of a cutting component. Furthermore, a preliminary investigation of a glove box facility was carried out in order to secure a facility for PIE work after the capsule dismantling, which revealed a technical feasibility.
Abe, Hiroyoshi; Haga, Takahisa; Fukaya, Hiroyuki; Sonoda, Takashi; Sakazume, Yoshinori; Ito, Mitsuo; Shirahashi, Koichi
JAEA-Technology 2009-008, 24 Pages, 2009/03
Analysis of the uranyl nitrate solution fuel is carried out at the analytical laboratory of NUCEF (Nuclear Fuel Cycle Engineering Research Facility), which provides essential data for operation of STACY (Static Experiment Critical Facility), TRACY (Transient Experiment Critical Facility) and the fuel treatment system. Analyzed in FY 2007 were uranyl nitrate solution fuel samples taken before and after experiments of STACY and TRACY, samples for the preparation and pulification of uranyl nitrate solution fuel in the fuel treatment system and samples for nuclear material accountancy purpose. The total number of the samples analyzed in FY 2007 was 143. This report summarizes work related to the analysis and management of the analytical laboratory in the FY 2007.
Noda, Masaru*; Suyama, Yasuhiro*; Nobuto, Jun*; Ijiri, Yuji*; Mikake, Shinichiro; Matsui, Hiroya
JAEA-Technology 2009-009, 194 Pages, 2009/07
In construction phase in MIU, the study on engineering technology consist of following four subjects, which are Demonstration of design methodology of a greatly deepr underground structure, Demonstration of excavation and supplymentary methods of a greatly deepr underground structure, Demonstration of the countermeasure during excavation of a greatly deepr underground structure and Demonstration of the safe construction for a greatly deepr underground structure. In the study in FY2007, the design methodlogy in Phase 1 is verified until 200 m depth on excavation of ventilation shaft. A plan, countermeasure and concept for influence of differential water pressure, long-term maintenance and risk management in the view of geological disposal project were proposed.
Kasugai, Yoshimi; Kai, Tetsuya
JAEA-Technology 2009-010, 46 Pages, 2009/05
Evaluations of radiation dose at the site boundary for the Materials and Life Science Experimental Facility (MLF) at J-PARC were carried out supposing that the mercury used as the neutron target happened to leak from the mercury circulation system during 1 MW operation. As a result of the evaluation, the dose of external exposure at the site boundary was estimated to be 30 Sv, which was almost given by the radioactive noble gas produced via spallation reactions. The inner exposure of radioactive mercury and tritium was estimated to be 0.1
Sv, which was almost given by the radioactive noble gas produced via spallation reactions. The inner exposure of radioactive mercury and tritium was estimated to be 0.1 Sv in total. Since the estimated dose was enough low in comparison with a personal annual dose from natural radioactivity, even though the event scenario was made conservatively, it was shown that MLF has high safety margin for the leak of radioactivity.
Sv in total. Since the estimated dose was enough low in comparison with a personal annual dose from natural radioactivity, even though the event scenario was made conservatively, it was shown that MLF has high safety margin for the leak of radioactivity.
Izumo, Hironobu; Chimi, Yasuhiro; Ishida, Takuya; Kawamata, Kazuo; Inoue, Shuichi; Ide, Hiroshi; Saito, Takashi; Ise, Hideo; Miwa, Yukio; Ugachi, Hirokazu; et al.
JAEA-Technology 2009-011, 31 Pages, 2009/04
Regarding Irradiation Assisted Stress Corrosion Cracking (IASCC) for austenitic stainless steel of the light water reactor (LWR), a lot of data that concerns the post irradiation evaluation (PIE) is acquired. However, IASCC occurs in LWR condition. Therefore, it is necessary to confirm adequacy of the PIE data comparing the experiment data under the simulated LWR condition. Bigger specimen is needed to acquire the effective data for the destruction dynamics in the study of stress corrosion cracking under neutron irradiation condition. Therefore, development of a new crack growth unit which can load to bigger is necessary to the neutron irradiation test. As a result, a prospect was provided in the unit that could load to specimen by changing load mechanism to the lever type from the linear type. And also, in the development of crack propagation unit, some technical issues were extracted from the discussion of the unit structure adopting the LVDT (Linear Variable Differential Transformer).
 Mo production by solution irradiation method, 1; Characterization of aqueous molybdate solutions under unirradiation
Mo production by solution irradiation method, 1; Characterization of aqueous molybdate solutions under unirradiationInaba, Yoshitomo; Ishikawa, Koji*; Iimura, Koichi; Tatenuma, Katsuyoshi*; Ishitsuka, Etsuo
JAEA-Technology 2009-012, 80 Pages, 2009/05
In the present study, the schematic structure of the  Mo production system with the solution irradiation method was investigated, and two kinds of aqueous molybdate solutions (an aqueous ammonium molybdate solution and an aqueous potassium molybdate solution) were selected as candidates for the irradiation target of the solution irradiation method, and then the molybdenum adsorption performance of PZC with the solutions, the properties of the molybdates to be materials of the solutions, the compatibility between the solutions and structural materials, and the chemical stability of the solutions were investigated under unirradiation. As a result, it was found that the aqueous potassium molybdate solution is promising as the target in terms of the molybdenum content, the compatibility with the structural materials, and the chemical stability and that the aqueous ammonium molybdate solution with suitable pH adjustment has an aptitude for the target. In addition, it became clear that stainless steel having good compatibility with the solutions has a potential as the structural material of capsules, pipes and so on.
Mo production system with the solution irradiation method was investigated, and two kinds of aqueous molybdate solutions (an aqueous ammonium molybdate solution and an aqueous potassium molybdate solution) were selected as candidates for the irradiation target of the solution irradiation method, and then the molybdenum adsorption performance of PZC with the solutions, the properties of the molybdates to be materials of the solutions, the compatibility between the solutions and structural materials, and the chemical stability of the solutions were investigated under unirradiation. As a result, it was found that the aqueous potassium molybdate solution is promising as the target in terms of the molybdenum content, the compatibility with the structural materials, and the chemical stability and that the aqueous ammonium molybdate solution with suitable pH adjustment has an aptitude for the target. In addition, it became clear that stainless steel having good compatibility with the solutions has a potential as the structural material of capsules, pipes and so on.
 Mo production by solution irradiation method, 2; Characterization of aqueous molybdate solutions under
Mo production by solution irradiation method, 2; Characterization of aqueous molybdate solutions under  -ray irradiation
-ray irradiationInaba, Yoshitomo; Ishikawa, Koji*; Iimura, Koichi; Tatenuma, Katsuyoshi*; Ishitsuka, Etsuo
JAEA-Technology 2009-013, 72 Pages, 2009/05
In the present study, using two kinds of aqueous molybdate solutions (an aqueous ammonium molybdate solution and an aqueous potassium molybdate solution) selected as candidates for the irradiation target of the solution irradiation method for  Mo production, the compatibility between the solutions and structural materials, the chemical stability, circulation characteristics, radiolysis and
Mo production, the compatibility between the solutions and structural materials, the chemical stability, circulation characteristics, radiolysis and  heating of the solutions were investigated under
heating of the solutions were investigated under  -ray irradiation. In addition, the integrity of PZC was investigated under
-ray irradiation. In addition, the integrity of PZC was investigated under  -ray irradiation. As a result, the following were found: (1) the compatibility between the solutions and stainless steel is very well, (2) the solutions are chemically stable and have a smooth circulation, (3) the ratios of hydrogen in the gases generated by the radiolysis of the solutions are higher than that of pure water, (4) the effect of
-ray irradiation. As a result, the following were found: (1) the compatibility between the solutions and stainless steel is very well, (2) the solutions are chemically stable and have a smooth circulation, (3) the ratios of hydrogen in the gases generated by the radiolysis of the solutions are higher than that of pure water, (4) the effect of  heating on the solutions is the same level as that on pure water, and (5) the integrity of PZC is maintained.
heating on the solutions is the same level as that on pure water, and (5) the integrity of PZC is maintained.
Inaba, Yoshitomo; Ishida, Takuya; Onuma, Yuichi; Saito, Takashi
JAEA-Technology 2009-014, 42 Pages, 2009/05
In order to carry out low-temperature irradiation tests under the high neutron flux in the JMTR core, desirable capsules were investigated from a survey and evaluation of current heat removal techniques. As a result, it was found that the low-temperature irradiation tests can be realized by the development of the capsule with cooling fins or the capsule using a boiling medium. In the case of the irradiation tests at about 100 C, the capsule with the fins can be used, and the reactor cooling water cools the capsule including specimens. This technique has few subjects to realize. In the case of the irradiation tests at below 0
C, the capsule with the fins can be used, and the reactor cooling water cools the capsule including specimens. This technique has few subjects to realize. In the case of the irradiation tests at below 0 C, the capsule using the boiling medium can be used, and the cooling of specimens in the capsule by liquid nitrogen is needed. In the present status, it is difficult that the liquid nitrogen is supplied to the capsule, and this technique has to overcome various subjects to realize. The investigation to solve these subjects will be carried out in the near future.
C, the capsule using the boiling medium can be used, and the cooling of specimens in the capsule by liquid nitrogen is needed. In the present status, it is difficult that the liquid nitrogen is supplied to the capsule, and this technique has to overcome various subjects to realize. The investigation to solve these subjects will be carried out in the near future.
Saito, Kenji; Shimizu, Atsushi; Hirato, Yoji; Kondo, Makoto; Kawamata, Takanori; Nemoto, Masumi; Motegi, Toshihiro
JAEA-Technology 2009-015, 52 Pages, 2009/05
As In-core temperature monitoring system, Type N thermocouples arranged at hot plenum block measures the primary coolant temperature at each hot plenum block in order to monitor the condition of the reactor core during the reactor operation. Type N thermocouples should have a long lifetime with high reliability under the high temperature environment of about 1000 C, because they are used in HTTR reactor pressure vessel. This report shows that the characteristic change of Type N thermocouples was confirmed from operation and maintenance data of current HTTR.
C, because they are used in HTTR reactor pressure vessel. This report shows that the characteristic change of Type N thermocouples was confirmed from operation and maintenance data of current HTTR.
Kuroki, Ryoichiro; Ito, Fuminori*; Nakata, Hisakazu; Yamamoto, Shuji; Takahashi, Kuniaki
JAEA-Technology 2009-016, 124 Pages, 2009/06
The concept of "Waste Management System" which manages all the waste data from generation to disposal in Japan Atomic Energy Agency (JAEA) was studied. At first, development policy was defined on investigation results of the present state and problem of waste management in JAEA, and target information supplied by "Waste Management System" were extracted. Then over 400 data items to be managed in this system, system configuration and specific functions were shown as system concept. The waste data managed on this system are classified into two categories; for quality assurance of waste packages and for optimization study of waste conditioning and disposal and information service. This system consists of analytical part (i.e. program) and management part (i.e. database) for each data, then all these parts are constructed on network.
Ogawa, Mitsuhiro; Iimura, Koichi; Tomita, Kenji; Tobita, Masahiro
JAEA-Technology 2009-017, 254 Pages, 2009/05
In JMTR, upgrade of irradiation facilities is advanced to re-operate from 2011 F.Y. In order to irradiate test fuels of high-burnup, external exposure reassessment by direct and skyshine gamma rays of the nuclear fuel handling facility at JMTR was performed. In evaluation method, radiation source of maximum use of the nuclear fuel was calculated by using ORIGEN2 code. Dose equivalent rate for supervised area boundary was calculated by modeling reactor building at using shielding calculation codes QAD-CGGP2 and G33-GP2. As a result of evaluation, it was confirmed that the effective dose equivalent during year was low enough at supervised area boundary of the JMTR site.
Mio, Keigo; Ogiwara, Norio; Furukori, Hisayoshi*; Arai, Hideyuki*; Nishizawa, Daiji*; Nishidono, Toshiro*; Hikichi, Yusuke
JAEA-Technology 2009-018, 86 Pages, 2009/04
Material characterization and development has been carried out for cable insulation suitable for use in the J-PARC 3-GeV RCS radiation environment. In spite of its high cost, PEEK (polyether-ether-ketone) has emerged as the leading candidate satisfying requirements of being non-halogen based, highly incombustible and with radiation resistant at least 10 MGy, along with the usual mechanical characteristics such as good elongation at break, which are needed in a cable insulation.  -ray irradiation tests have been done in order to study radiation resistance of PEEK cable. Further, mechanical, electrical and fire retardant characteristics of a complete cable such as would be used at the J-PARC RCS were investigated. As a result, PEEK cables were shown to be not degraded by radiation up to at least 10 MGy, and thus could be expected to operate stably under the 3-GeV RCS radiation environment.
-ray irradiation tests have been done in order to study radiation resistance of PEEK cable. Further, mechanical, electrical and fire retardant characteristics of a complete cable such as would be used at the J-PARC RCS were investigated. As a result, PEEK cables were shown to be not degraded by radiation up to at least 10 MGy, and thus could be expected to operate stably under the 3-GeV RCS radiation environment.
Ide, Hiroshi; Sakuta, Yoshiyuki; Hanawa, Yoshio; Tsuji, Tomoyuki; Tsuboi, Kazuaki; Nagao, Yoshiharu; Miyazawa, Masataka
JAEA-Technology 2009-019, 28 Pages, 2009/06
The main body of the JMTR is composed of reactor pressure vessel, core and reactor pool. At the bottom of the reactor pool, the Diaphragm-seal (2.6m outer diameter, 2m inner diameter, thickness 1.5mm) of the JMTR made of stainless steel is installed to prevent the water leak of the reactor pool and to absorb the expansion of the reactor pressure vessel due to pressure and temperature changes. Prior to the refurbishment of the JMTR, the inspection device which is a deposition-collection apparatus with underwater-camera was developed, and the visual inspection was carried out to confirm the soundness of the diaphragm-seal. As a result, harmful flaws and/or corrosions were not inspected in the visual inspection, and the soundness of the diaphragm seal was confirmed. In future, the long-term integrity of the diaphragm-seal will could be achieved by conducting the periodic inspection.
Shimaike, Masamitsu; Yokoyama, Kaoru; Ikegami, Sohei; Takahashi, Nobuo; Sugitsue, Noritake
JAEA-Technology 2009-020, 55 Pages, 2009/06
At the conversion facility, 48Y homogenization treatment equipment (cylinder processing room), UO pneumatic dispatch equipment (fluoride precipitation process room), gas trapping and filling equipment (cold trap room and UF
pneumatic dispatch equipment (fluoride precipitation process room), gas trapping and filling equipment (cold trap room and UF filling room) and the second grade UF
filling room) and the second grade UF drying equipment (UF
drying equipment (UF feed chamber and UF
feed chamber and UF treatment room) are scheduled to be dismantled, in 2008 fiscal year. The
treatment room) are scheduled to be dismantled, in 2008 fiscal year. The  -ray measurement intended for the equipment was done before dismantlement and the radioactivity inventory was evaluated. As a result, the part that the uranium recovery had to be executed was forecast for reasonable dismantlement. Additionally, the reprocessed uranium was used at the conversion facility, so the feature nuclide affecting the air dose was evaluated. In addition,
-ray measurement intended for the equipment was done before dismantlement and the radioactivity inventory was evaluated. As a result, the part that the uranium recovery had to be executed was forecast for reasonable dismantlement. Additionally, the reprocessed uranium was used at the conversion facility, so the feature nuclide affecting the air dose was evaluated. In addition,  -ray analysis results are organized for using as the waste data and the radionuclide distribution data in the process.
-ray analysis results are organized for using as the waste data and the radionuclide distribution data in the process.
Iimura, Koichi; Ogawa, Mitsuhiro; Tomita, Kenji; Tobita, Masahiro
JAEA-Technology 2009-021, 71 Pages, 2009/05
The preparation of a fuel transient test using the JMTR is advanced to conduct its irradiation test from 2011 F.Y. after re-operation of the JMTR. The fuel behavior for high burn-up BWR's under power ramping condition will be evaluated in simulating the BWR environmental condition using the shroud irradiation facility (Oarai Shroud Facility No.1) and  He power-control type BOCA (Boiling Water Capsule) irradiation facility, which is composed of the capsule control device,
He power-control type BOCA (Boiling Water Capsule) irradiation facility, which is composed of the capsule control device,  He power-control device and boiling water capsule. In order to change the fuel irradiation conditions so as to treat high burn-up fuels (from 50 GWD/t-UO
He power-control device and boiling water capsule. In order to change the fuel irradiation conditions so as to treat high burn-up fuels (from 50 GWD/t-UO to 110 GWD/t-U), it is necessary to revaluate the dose for the safety evaluation at the test fuel failure. In this report, evaluations for equivalent dose rate of each device and exposure dose of handling operators when all fission products released in the coolant of the capsule control device and the BOCA at fuel failure in the fuel transient test are summarized.
to 110 GWD/t-U), it is necessary to revaluate the dose for the safety evaluation at the test fuel failure. In this report, evaluations for equivalent dose rate of each device and exposure dose of handling operators when all fission products released in the coolant of the capsule control device and the BOCA at fuel failure in the fuel transient test are summarized.
Murazaki, Minoru; Tonoike, Kotaro; Uchiyama, Gunzo
JAEA-Technology 2009-022, 49 Pages, 2009/06
We have re-evaluated the dose measurements at SILENE with TLDs for neutrons and with TLDs for  rays, and at TRACY with TLDs for neutrons. The measurements with TLDs for neutrons were re-evaluated by revising factors used for calculation of doses from measured data. The re-evaluated results of TLDs for neutrons at SILENE agreed with the reference value given by IRSN within 10%. The re-evaluated results of TLDs for neutrons at TRACY are consistent with dose and distance from the surface of the core tank. The re-evaluated results at TRACY were about 50% larger than results of polymer-alanine dosimeters and those of TLDs for neutrons measured by the authors. The measurements at SILENE with TLDs for
rays, and at TRACY with TLDs for neutrons. The measurements with TLDs for neutrons were re-evaluated by revising factors used for calculation of doses from measured data. The re-evaluated results of TLDs for neutrons at SILENE agreed with the reference value given by IRSN within 10%. The re-evaluated results of TLDs for neutrons at TRACY are consistent with dose and distance from the surface of the core tank. The re-evaluated results at TRACY were about 50% larger than results of polymer-alanine dosimeters and those of TLDs for neutrons measured by the authors. The measurements at SILENE with TLDs for  rays were re-evaluated by revising the method for obtaining doses from measurement data. By the re-evaluation, it was confirmed that the methods described in the present report are valid for processing measured data of TLDs for neutrons and those for
rays were re-evaluated by revising the method for obtaining doses from measurement data. By the re-evaluation, it was confirmed that the methods described in the present report are valid for processing measured data of TLDs for neutrons and those for  rays.
rays.
Sone, Tomoyuki; Nakagawa, Akinori; Koyama, Hayato; Gunji, Kiyoshi; Nonaka, Kazuharu; Sasaki, Toshiki; Tashiro, Kiyoshi; Yamashita, Toshiyuki
JAEA-Technology 2009-023, 33 Pages, 2009/06
Steam reforming (SR) method consists of the gasification process in which organics are vaporized and decomposed with superheated steam and the oxidation process in which vaporized organics are decomposed by oxidizing reaction with heated air. 2,500L of waste TBP/n-dodecane contaminated with uranium was treated using the demonstration scale steam reforming system to examine the performance of the system. Results obtained in this study show that the temperature in the SR system was controlled under the self-regulation temperature, the concentration of CO and NOx in the off-gas were controlled less than 100ppm and 250ppm respectively, the distribution ratio of uranium to off-gas treatment system was under 0.12% and the gasification ratio of waste TBP was more than 99%. This long-term waste treatment test has demonstrated that the SR system can safely and effectively reduce the volume of the waste.
Editorial Committee of Refining and Conversion Facility Decommissioning Results
JAEA-Technology 2009-024, 101 Pages, 2009/06
The Refining and Conversion Facility located in the Ningyo-toge Environmental Engineering Center. Process of natural uranium conversion facility (PNC Process) and reprocessed uranium conversion facility (two-stage dry fluorination system) is in a Refining and Conversion Facility. This building started construction in 1979 and was completed in October 1981. The PNC process operated from March 1982 to March 1991. As a result, uranium hexafluoride of about 385 tonU was manufactured. Also, the reprocessed uranium conversion process operated from December 1982 to July 1999. As a result, uranium hexafluoride of about 338 tonU was manufactured. The demonstration of the demolition method was done using the PNC process after the end of operation. The schedule which will finish dismantling of all equipment in a radiation controlled area is by the 2011 fiscal year. This report summarized the present situation by the first half of the 2008 fiscal year of a Refining and Conversion Facility decommissioning.
Tomimoto, Hiroshi; Kato, Yasushi; Owada, Hiroyuki; Sato, Nao; Shimazaki, Yosuke; Kozawa, Takayuki; Shinohara, Masanori; Hamamoto, Shimpei; Tochio, Daisuke; Nojiri, Naoki; et al.
JAEA-Technology 2009-025, 29 Pages, 2009/06
The first driver fuel of the HTTR (High Temperature Engineering test Reactor) was loaded in 1998 and the HTTR reached first criticality state in the same year. The HTTR has been operated using the first driver fuel for a decade. In Fuel elements assembling, 4770 of fuel rods which consist of 12 kinds of enrichment uranium are loaded into 150 fuel graphite blocks for HTTR second driver fuel elements. Measures of prevention of fuel rod miss loading, are employed in fuel design. Additionally, precaution of fuel handling on assembling are considered. Reception of fuel rods, assembling of fuel elements and storage of second driver fuels in the fresh fuel storage rack in the HTTR were started since June, 2008. Assembling, storage and pre-service inspection were divided into three parts. The second driver fuel assembling was completed in September, 2008. This report describes concerns of fuel handling on assembling and storage work for the HTTR fuel elements.
Tomimoto, Hiroshi; Hamamoto, Shimpei; Tochio, Daisuke; Ueta, Shohei; Umeda, Masayuki; Nishihara, Tetsuo
JAEA-Technology 2009-026, 37 Pages, 2009/08
HTTR (High Temperature Engineering Test Reactor) loaded the first driver fuel in July 1998 and reached first criticality state in November 1998. After power increasing examination, HTTR has been conducting safety demonstration test and sequentially acquiring basic technical data of high temperature gas cool reactor. Temperature measurement inside the reactor is planed in the next midterm plan to improve HTTR performance. This report describes the investigation result of fuel temperature measurement method which is applicable to critical irradiation test.
Nishida, Nobuho
JAEA-Technology 2009-027, 16 Pages, 2009/07
Japan Atomic Energy Agency (JAEA) is constructing an Underground Research Laboratory in Mizunami in the vicinity of its Tono Geoscience Centre (TGC). Waste water from the construction including groundwater inflow into the shafts and drifts had been treated before released into the local drainage system. However in October 2005, it was found in the local river water that the concentration level of fluorine and boron was exceeding the environmental standard set by the law and the construction and drainage was immediately suspended. In order to conquer this incident, TGC had chosen the Environmental Management System (EMS) which is based on the ISO14001 standard to improve its Risk-Crisis management capabilities. As a result, such capabilities have been substantially improved by advancing temporary system to sustainable system.
Sato, Takeshi; Watanabe, Norio; Yoshida, Kazuo
JAEA-Technology 2009-028, 29 Pages, 2009/05
The importance to make use of lessons learned and knowledge from accidents and troubles in safety management of nuclear research facilities is recognized widely. By the root cause analysis of accidents and troubles, lessons learned and knowledge have been arrived about safety management of facilities. The root cause analysis has been performed for accidents and troubles generated at nuclear research facilities in Japan Atomic Energy Agency (JAEA) from about 1990. Because the analysis is performed for various facilities, anyone have been used the analysis method of possible of utilize. On this account the analysis method has been developed and adopted an existing analysis method. This report introduces the analysis method that has been used for the root cause analysis of these accidents and troubles. Furthermore, this report apply a generally well known JCO Criticality Accident to each analysis method as an example and explain on the direction for uses.
Taguchi, Taketoshi; Kato, Yoshiaki; Sozawa, Shizuo
JAEA-Technology 2009-029, 18 Pages, 2009/07
This report is concerned with the preparation of test-specimens for the post irradiation examination to contribute to the research on the aged deterioration and damage of the structure material of the light-water reactor, that consists of cutting, grinding, and the surface treatment of the irradiated material in the hot-cell at the JMTR Hot Laboratory. Two types of test-specimen preparation methods were developed for the electron beam backscatter diffraction (EBSD) observation and for the TEM observation. The specimens for those observations were sampled from fractions of the CT and the SSRT test specimens which were used in the irradiation-associated stress-corrosion cracking (IASCC) test. The technical difficulty in remote handling of the minimized specimens and of the fragile part where the crack progresses was overcome by a trial and error approach, and the adequate preparation technique for those tests was established.
Ebisawa, Hiroyuki; Hanakawa, Hiroki; Asano, Norikazu; Kusunoki, Hidehiko; Yanai, Tomohiro; Sato, Shinichi; Miyauchi, Masaru; Oto, Tsutomu; Kimura, Tadashi; Kawamata, Takanori; et al.
JAEA-Technology 2009-030, 165 Pages, 2009/07
The condition of facilities and machinery used continuously were investigated before the renewal work of JMTR on FY 2007. The subjects of investigation were reactor building, primary cooling system tanks, secondary cooling system piping and tower, emergency generator and so on. As the result, it was confirmed that some facilities and machinery were necessary to repair and others were used continuously for long term by maintaining on the long-term maintenance plan. JMTR is planed to renew by the result of this investigation.
Tohei, Toshio; Someya, Keita; Takahashi, Kenji; Iseda, Hirokatsu; Kozawa, Kazushige; Momma, Toshiyuki
JAEA-Technology 2009-031, 29 Pages, 2009/06
The Waste Volume Reduction Facility (WVRF) was constructed for volume reduction and the chemical stabilization of the low level radioactive waste (LLW). The metal melting system in the WVRF treats radioactive metal waste. This system has been conducted commissioning since the FY 2003. It was found, from the experience of commissioning, that the improvement of casting process in the metal melting system can be reduced the processing cost, maintenance load, and dose to workers. We planed modification of the device, and embodied from FY 2006 to FY 2007. As a result, we properly improved the casting process. In this report, we describe the idea for improvement of the casting process, the detail of improvement and the estimate of improvement.
Inaba, Yoshitomo; Ogawa, Mitsuhiro; Yamaura, Takayuki; Tobita, Masahiro
JAEA-Technology 2009-032, 51 Pages, 2009/07
The fuel transient tests for light water reactors are to be carried out in the Japan Materials Testing Reactor (JMTR), and the capsule-type test facilities (fuel transient test capsules) are to be used in the tests. In order to investigate the thermal-hydraulic behavior in the capsules, the multi-dimensional two-fluid model code ACE-3D is used. At first, the functions of ACE-3D were expanded for the pre-process and the post-process. Then, the BWR power calibration test capsule, which had been tested in JMTR, was modeled, and the BWR power calibration tests were simulated numerically for the verification of ACE-3D. The numerical results agreed well with the test data. As a result, it was found that ACE-3D is applicable to the numerical simulation of the fuel transient tests. In addition, the fuel transient tests with a natural convection capsule were simulated numerically with ACE-3D, and the thermal-hydraulic behavior in the capsule was investigated.
Iimura, Koichi; Yamaura, Takayuki; Ogawa, Mitsuhiro
JAEA-Technology 2009-033, 45 Pages, 2009/07
At Oarai Research and development center, Japan Atomic Energy Agency (JAEA), the plan of repairing and refurbishing Japan Materials Testing Reactor (JMTR) has progressed in order to restart JMTR operation in the fiscal 2011. By using Oarari Shroud Facility and fuel irradiation facility with the He-3 gas control system for power lamping test using boiling water capsules. By using saturated temperature capsules and the water environment control system, the material irradiation tests under the water chemistry condition of LWL will be carried out to clarify the mechanism of IASCC. The detailed design for renewal or remodeling was carried out based on the new design condition in order to be correspondent to the irradiation test plan after restart JMTR operation. Stress calculation and evaluation were carried out by fem piping analysis code SAP and structure analysis code ABAQUS. It was proven by the analysis that these facilities maintain the structural integrity under earthquake condition.
Onuma, Yuichi; Tomita, Kenji; Okada, Yuji; Hanawa, Hiroshi
JAEA-Technology 2009-034, 79 Pages, 2009/07
Toward the re-operation of Japan Materials Testing Reactor on 2011 F.Y., the construction of new material irradiation facility for the stress corrosion cracking research under the LWR irradiation environment had been planed, and the design study of water control unit for BWR and water chemical study which supply the LWR simulated water to the material irradiation capsule were carried out on 2007 F.Y. The design study of new material irradiation facility was examined including the reflection of the operation experience and the reuse of components on old material irradiation facility. These examination results were summarized in this report.
Kiriyama, Koji; Mitsui, Takaya; Fukuda, Yoshihiro
JAEA-Technology 2009-035, 24 Pages, 2009/07
Single crystal for experiment using by synchrotron radiation X-ray is needed to have high quality and performance as optics element. Therefore, quantitative estimation of performance of the single crystal must be done before the experiment. Precise X-ray optics system has been developed at JAEA/Quantum Beam Science Directorate/Synchrotron Radiation Unit at SPring-8. This system can measure small sample that is less than 0.01 mm in size, and have resolving ability of sample rotation that is less than 0.01 degree. And, scanning of sample, it is possible to measure distribution of quality at sample surface. For example, single crystal of FeBO which was measured by this system have been installed in synchrotron radiation M
which was measured by this system have been installed in synchrotron radiation M ssbauer spectroscopy using Doppler-shifted 14.4 keV single line
ssbauer spectroscopy using Doppler-shifted 14.4 keV single line  Fe-M
Fe-M ssbauer radiation.
ssbauer radiation.
 standardization method; Development of irradiation silicon technology in productivity using research reactor (Joint research)
standardization method; Development of irradiation silicon technology in productivity using research reactor (Joint research)Motohashi, Jun; Takahashi, Hiroyuki; Magome, Hirokatsu; Sasajima, Fumio; Tokunaga, Okihiro*; Kawasaki, Kozo*; Onizawa, Koji*; Isshiki, Masahiko*
JAEA-Technology 2009-036, 50 Pages, 2009/07
JRR-3 and JRR-4 have been providing neutron-transmutation-doped silicon (NTD-Si) by using the silicon NTD process. We have been considering to introduce the neutron filter, which is made of high-purity-titanium, into uniform doping. Silicon carbide (SiC) semiconductors doped with NTD technology are considered suitable for high power devices with superior performances to conventional Si-based devices. The impurity contents in the high-purity-titanium and SiC were analyzed by neutron activation analyses (NAA) using k standardization method. Analyses showed that the number of impurity elements detected from the high-purity-titanium and SiC were 6 and 9, respectively. Among these impurity elements, Sc detected from the high-purity-titanium and Fe detected from SiC were comparatively long half life nuclides. From the viewpoint of exposure in handling them, we need to examine the impurity control of materials.
standardization method. Analyses showed that the number of impurity elements detected from the high-purity-titanium and SiC were 6 and 9, respectively. Among these impurity elements, Sc detected from the high-purity-titanium and Fe detected from SiC were comparatively long half life nuclides. From the viewpoint of exposure in handling them, we need to examine the impurity control of materials.
Takeuchi, Masaki; Magome, Hirokatsu; Komeda, Masao; Kawasaki, Kozo*
JAEA-Technology 2009-037, 28 Pages, 2010/03
Japan Research Reactor No.3 (JRR-3) has been providing Neutron Transmutation Doping Silicon (NTD-Si). Though the inverse method is employed for producing NTD-Si in JRR-3, it is possible to increase the production rate of NTD-Si by using the neutron filter method. As the result, the prospect that the neutron filter method was able to develop without changing a geometrical size of NTD-Si facility in JRR3 was obtained.
Ouchi, Yasuhiro; Ito, Masatoshi; Oba, Toshinobu; Kawamata, Satoshi; Ishizaki, Katsuhiko
JAEA-Technology 2009-038, 38 Pages, 2009/07
The primary cooling system of JRR-3 is one of important facility which removes heat from reactor core. Therefore, it is necessary for safe and stable reactor operation to keep performance of four pumps which are main equipments of primary cooling system. These four pumps have been checked and maintained appropriately since the operation of JRR-3 started. Maintenance items and its records of primary cooling pumps are reported in this paper. Furthermore, aging problems of primary cooling pumps is investigated to contribute to management for maintenance of primary cooling pumps.
 Mo production by Mo-solution irradiation method, 3; Activation analysis of irradiation target
Mo production by Mo-solution irradiation method, 3; Activation analysis of irradiation targetHuynh, T. P.*; Inaba, Yoshitomo; Ishida, Takuya; Ishikawa, Koji*; Tatenuma, Katsuyoshi*; Ishitsuka, Etsuo
JAEA-Technology 2009-039, 21 Pages, 2009/07
The impurity concentration in both (NH )
) Mo
Mo O
O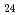 and K
and K MoO
MoO solutions, which are selected as advanced targets of Mo-solution irradiation method for
solutions, which are selected as advanced targets of Mo-solution irradiation method for  Mo production, was determined by the Instrumental Neutron Activation Analysis (NAA) using k
Mo production, was determined by the Instrumental Neutron Activation Analysis (NAA) using k -standardization method. As a result, Na, Mn and W were identified as impurities in the as received molybdate. After the compatibility test with structural material (SUS304) under
-standardization method. As a result, Na, Mn and W were identified as impurities in the as received molybdate. After the compatibility test with structural material (SUS304) under  -ray irradiation, activation analysis of molybdate solutions was also carried out. It was found that the identified impurity concentration was stably staying in solutions and no element comes from the structural material by the NAA method. However, small corrosion of structural material was observed from the ICP measurement.
-ray irradiation, activation analysis of molybdate solutions was also carried out. It was found that the identified impurity concentration was stably staying in solutions and no element comes from the structural material by the NAA method. However, small corrosion of structural material was observed from the ICP measurement.
Wakui, Takashi; Kogawa, Hiroyuki; Haga, Katsuhiro; Futakawa, Masatoshi; Hayashi, Ryoichi*; Uchiyama, Naoyoshi*; Okamoto, Yoshinao*; Nakamura, Koji*
JAEA-Technology 2009-040, 96 Pages, 2010/03
The construction of materials and life science experimental facility in J-PARC project had been completed. The mercury target vessel consists of triple-walled structure in order to prevent the leak of mercury to outside at the failure of the mercury vessel and to remove the heat of the safety hull, which covers the mercury vessel, due to the injection of the pulsed proton beams. The high fabrication accuracy is required for the mercury target vessel assembled by the welding. In this report, the required specification and basic structure of parts in the mercury target vessel are described and the fabrication procedure of the mercury target vessel by the vender is reported. In the fabrication of the mercury target vessel, there were many troubles such as large deformation due to the welding and then the vender repaired and brought the mercury target vessel to completion. Furthermore, improvements for the design and fabrication of the mercury target are reported.
Wakui, Takashi; Kogawa, Hiroyuki; Haga, Katsuhiro; Futakawa, Masatoshi; Uchiyama, Naoyoshi*; Nakamura, Koji*
JAEA-Technology 2009-041, 71 Pages, 2010/03
The mercury target vessel installed in J-PARC consists of the mercury vessel and the safety hull, which corves the mercury vessel, to prevent the leak of mercury to outside at the failure of the mercury vessel. The safety hull is a double-walled structure to make the cooling channel of heavy water. The helium gas in a space between the mercury vessel and the safety hull can prevent the inflow of mercury into heavy water at the failure of the mercury vessel. The design pressure of each medium is 0.5 MPaG. The temperature of the mercury target vessel and mercury rises at a moment of the proton beam injection and then the thermal shock and the deformation of the mercury vessel occur. The mercury target vessel is imposed by not only static load due to the inner pressure and dead weight but also repeated dynamic load. Based on loading conditions, the structural integrity of the mercury target vessel was evaluated using numerical analyses. The results were described as following.
Sakai, Kenji; Oi, Motoki; Kai, Tetsuya; Watanabe, Akihiko; Nakatani, Takeshi; Higemoto, Wataru; Shimomura, Koichiro*; Kinoshita, Hidetaka; Kaminaga, Masanori
JAEA-Technology 2009-042, 44 Pages, 2009/08
A general control system for the Materials and Life Science Experimental Facility (MLF-GCS) at J-PARC has an advanced and independent system for control of the mercury target, including a large amount of mercury, three moderators with supercritical hydrogen, and cooling systems with radioactive water. Although the MLF-GCS is an independent system, it works closely with the accelerator and other facility control systems within J-PARC. The MLF have succeeded in the first proton beam injection and neutron beam generation in May 2008, and succeeded the muon beams generation in September 2008. The design and construction of the MLF-GCS has finished before the first proton beam injection. It has been operated stably and efficiently in the off- and on- beam commissioning. This paper reports on the design, construction and operation of the MLF-GCS.
Kanamori, Masashi; Tanaka, Kenichi*; Takada, Jun*
JAEA-Technology 2009-043, 32 Pages, 2009/08
At the time of the JCO criticality accident termination, dose estimation from the preliminary neutron and  measurement, it was about around 50 times lower. The estimation might effect from the surrounding buildings. In this report, re-estimation based on the measurements at short distances from the criticality, around 40 m to 100 m, which are 20 mSv/h to 3 mSv/h was done. The re-estimated doses are correspond with the measured doses within 60-80% error. Dose estimation under the high radiation field, around 100 mSv, in order to decide the dose limit for the preliminary measurement, annual dose limit, other exposure possibility and measurement error have to be considered. From this point of view, the dose limit for the preliminary measurement itself considered to be 10 mSv, which is half of annual 20 mSv limit.
measurement, it was about around 50 times lower. The estimation might effect from the surrounding buildings. In this report, re-estimation based on the measurements at short distances from the criticality, around 40 m to 100 m, which are 20 mSv/h to 3 mSv/h was done. The re-estimated doses are correspond with the measured doses within 60-80% error. Dose estimation under the high radiation field, around 100 mSv, in order to decide the dose limit for the preliminary measurement, annual dose limit, other exposure possibility and measurement error have to be considered. From this point of view, the dose limit for the preliminary measurement itself considered to be 10 mSv, which is half of annual 20 mSv limit.
Asakawa, Shuji; Tsuchiya, Katsuhiko; Kuramochi, Masaya; Yoshida, Kiyoshi
JAEA-Technology 2009-044, 55 Pages, 2009/09
The upgrade of JT-60U magnet system to superconducting coils (JT-60SA: JT-60 Super Advanced) has been decided by parties of Japanese government (JA) and European commission (EU). The magnet system for JT-60SA consists of a central solenoid (CS), equilibrium field (EF) coils, toroidal field (TF) coils. The central solenoid consists of the four winding pack modules. In order to counteract the thermal contraction as well as the electric magnetic repulsion and attraction together with other forces generated in each module, it is necessary to apply pre-loading to the support structure of the solenoid and to pursue a structure which is capable of sustaining such loading. In the present report, the structural design of the supporting structure of the solenoid and the jackets of the conducting coils in the modules is verified analytically, and the results indicate that the structural design satisfies the "Codes for Fusion Facilities Rules on Superconducting Magnet Structure".
Murazaki, Minoru; Nobuhara, Fumiyoshi*; Iwai, Shohei*; Tonoike, Kotaro; Uchiyama, Gunzo
JAEA-Technology 2009-045, 46 Pages, 2009/09
Neutron doses under criticality accident conditions at TRACY were measured using ebnites, which are hard rubber containing sulfur. To evaluate a neutron dose, beta rays emitted from  P induced by
P induced by  S(n,p) reaction are measured with Geiger-M
S(n,p) reaction are measured with Geiger-M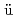 ller (GM) counter. A calibration factor (Gy/cpm), which is pre-determined using a
ller (GM) counter. A calibration factor (Gy/cpm), which is pre-determined using a  Cf source, is applied to the count rates to obtain neutron doses. Factors to correct for the difference between responses of
Cf source, is applied to the count rates to obtain neutron doses. Factors to correct for the difference between responses of  S(n,p) to the spectrum of
S(n,p) to the spectrum of  Cf source and to spectra of TRACY were calculated and applied to the doses. Ebonites were exposed by TRACY with and without the water reflector. Neutron doses in TRACY without a reflector were evaluated with an uncertainty of less than about 40%. On the other hand, average of neutron doses in TRACY with the water reflector were accurate. By these measurements, it was found that ebonites can be used as a neutron dosimeter for criticality accidents.
Cf source and to spectra of TRACY were calculated and applied to the doses. Ebonites were exposed by TRACY with and without the water reflector. Neutron doses in TRACY without a reflector were evaluated with an uncertainty of less than about 40%. On the other hand, average of neutron doses in TRACY with the water reflector were accurate. By these measurements, it was found that ebonites can be used as a neutron dosimeter for criticality accidents.
Omori, Junji; Koizumi, Norikiyo; Shimizu, Tatsuya; Okuno, Kiyoshi; Hasegawa, Mitsuru*
JAEA-Technology 2009-046, 60 Pages, 2009/09
In the winding pack (WP) of the ITER TF coil, cover plates (CPs) are welded to radial plate (RP) after placing the conductors into the RP groove to fix it. The dimensions of the RP are 15 m high and 9 m wide, while its required tolerances are very severe such as flatness of 2 mm and in-plane deformation of about 2.5 mm. It is therefore necessary to reduce the deformation of the RP by CP welding. In order to estimate the weld deformation, a 1 m RP mock-up was fabricated and weld deformations were measured. From the test results, inherent strains have been obtained and the weld deformations of the full scale RP have been estimated. The RP deformations could be within the tolerances by the CP welding thickness of 2.5 mm in inboard region and 1.0 mm in outboard region. In addition, an alternative design, which improve the fabricability of the WP, was proposed. The analyses for the alternative design is performed and the results show the deformations could be reduced more.
Okawachi, Yasushi; Maeda, Shigetaka; Ito, Chikara; Kawahara, Hirotaka; Aoyama, Takafumi; Ishida, Koichi
JAEA-Technology 2009-047, 130 Pages, 2009/09
This report summarizes the contents about "Reactor physics and plant dynamics experiments using the Joyo simulator" which is one of the training themes. Training is performed using the full scope nuclear reactor simulator for Joyo operation training. While pushing from starting of a nuclear reactor in each experiment of criticality, a control rod proofreading examination, measurement of the temperature of a nuclear reactor, or the reactivity coefficient accompanying output change, feedback reactivity measurement of a fast reactor, etc. and understanding self-regulating characteristics peculiar to a nuclear reactor, the operation of a nuclear reactor can be experienced.
Inoi, Hiroyuki; Shimizu, Atsushi; Kameyama, Yasuhiko; Kobayashi, Shoichi; Shinozaki, Masayuki; Ota, Yukimaru; Kubo, Tsukasa*; Emori, Koichi
JAEA-Technology 2009-048, 48 Pages, 2009/10
The emergency power feeders of the High Temperature Engineering Test Reactor (HTTR) have gas turbine generators which are composed of gas turbin engines, generators and current breakers. The gas turbine generators have been overhauled and maintained to keep the performance. The maintenance technology was upgraded by improving their parts and surveillance method on the basis of the operational and maintenance experience. It can be clarified that the deterioration levels and the sudden deterioration timing are judged at an early stage by measuring the max exhaust temperature at the time of start in addition to check the starting time of the Gas Turbine Engines.
Kikuchi, Hironobu; Nakamura, Kinya*; Iwai, Takashi; Arai, Yasuo
JAEA-Technology 2009-049, 22 Pages, 2009/10
Irradiation tests of metallic fuels elements in fast test reactor JOYO are planned under the joint research of Japan Atomic Energy Agency (JAEA) and Central Research Institute of Electric Power Industry (CRIEPI). Six U-Pu-Zr fuel elements clad with ferritic martensitic steel are fabricated in Plutonium Fuel Research Facility (PFRF) of JAEA-Oarai for the first time in Japan. In PFRF, the procedures of fabrication of the fuel elements were determined and the test runs of the equipments were carried out before the welding execution tests for the fuel elements. Test samples for confirming the welding condition between the cladding tube and top and bottom endplugs were prepared, and various test runs were carried out before the welding execution tests. As a result, the welding conditions were finalized by passing the welding execution tests.
Kudo, Hisaaki*; Yoshii, Fumio; Kume, Tamikazu*
JAEA-Technology 2009-050, 54 Pages, 2009/10
This report summarizes the current status of development of hydrogel and oligosaccharides by radiation (electron and  rays) processing in Asia countries, as an outcome of activities of the FNCA (Forum for Nuclear Co-operation in Asia) industry group during the phase 2 (2006-2008), as one of FNCA Guidelines. The nine countries participates in the phase 2 of the FNCA-industry group, focusing on radiation processing of natural polymers. Participating countries have been studying radiation processing of natural polymer such as chitosan from shrimp/crab shell and carrageenan taken from seaweeds, in terms of crosslinking for gel and degradation for oligosaccharides. The hydrogel and oligosaccharides obtained by radiation processing are expected application in the fields of medical,environmental conservation and aqua-cultures.
rays) processing in Asia countries, as an outcome of activities of the FNCA (Forum for Nuclear Co-operation in Asia) industry group during the phase 2 (2006-2008), as one of FNCA Guidelines. The nine countries participates in the phase 2 of the FNCA-industry group, focusing on radiation processing of natural polymers. Participating countries have been studying radiation processing of natural polymer such as chitosan from shrimp/crab shell and carrageenan taken from seaweeds, in terms of crosslinking for gel and degradation for oligosaccharides. The hydrogel and oligosaccharides obtained by radiation processing are expected application in the fields of medical,environmental conservation and aqua-cultures.
Kameo, Yutaka; Shimada, Asako; Ishimori, Kenichiro; Haraga, Tomoko; Katayama, Atsushi; Hoshi, Akiko; Nakashima, Mikio
JAEA-Technology 2009-051, 81 Pages, 2009/10
Simple and rapid determination methods were developed for an evaluation of important nuclides, U, and Th in wastes generated from research facilities at Nuclear Science Research Institute and Oarai Research and Development Center. The present methods were assumed to apply to solidified products made from miscellaneous wastes by plasma melting at the Advanced Volume Reduction Facilities. In order to reduce costs of radiochemical analysis and to establish a routine analytical system, counting efficiency of non-destructive  -ray measurements was improved, and times for pretreatment of solidified product samples and subsequent radiochemical separations were shortened. In addition to this, rapid and high sensitive detection methods were developed for a determination of long-lived nuclides. The present paper describes guidelines for the determination of radionuclides in the low-level radioactive wastes by using the present simple and rapid methods.
-ray measurements was improved, and times for pretreatment of solidified product samples and subsequent radiochemical separations were shortened. In addition to this, rapid and high sensitive detection methods were developed for a determination of long-lived nuclides. The present paper describes guidelines for the determination of radionuclides in the low-level radioactive wastes by using the present simple and rapid methods.
Hotoku, Shinobu; Morita, Yasuji
JAEA-Technology 2009-052, 16 Pages, 2009/10
The UF is one of the most important U chemical forms in nuclear fuel cycle, which is used in the U enrichment process and in the study of fluoride volatility process, one of the dry reprocessing methods. Normally, UF
is one of the most important U chemical forms in nuclear fuel cycle, which is used in the U enrichment process and in the study of fluoride volatility process, one of the dry reprocessing methods. Normally, UF is confined in the solid state in the cylinder container and handled as gas by adjusting the temperature and pressure. Since it is highly reactive with water vapor in the air, it must be carefully handled. By the reaction with water vapor, particle of UO
is confined in the solid state in the cylinder container and handled as gas by adjusting the temperature and pressure. Since it is highly reactive with water vapor in the air, it must be carefully handled. By the reaction with water vapor, particle of UO F
F appeared as a white cloud and corrosive HF gas are released to the atmosphere. The purpose of this report is to describe safety handling for clean out of empty UF
appeared as a white cloud and corrosive HF gas are released to the atmosphere. The purpose of this report is to describe safety handling for clean out of empty UF cylinder and to summarize physical and chemical properties of uranium compounds in relation to treatment for UF
cylinder and to summarize physical and chemical properties of uranium compounds in relation to treatment for UF . The clean-out of the UF
. The clean-out of the UF cylinder was carried out successfully by trapping the generated UO
cylinder was carried out successfully by trapping the generated UO F
F and HF adequately in a temporary globe box made of the PVC that set up in a laboratory hood.
and HF adequately in a temporary globe box made of the PVC that set up in a laboratory hood.
Goto, Minoru; Takamatsu, Kuniyoshi; Nakagawa, Shigeaki; Ueta, Shohei; Hamamoto, Shimpei; Ohashi, Hirofumi; Furusawa, Takayuki; Saito, Kenji; Shimazaki, Yosuke; Nishihara, Tetsuo
JAEA-Technology 2009-053, 48 Pages, 2009/10
Preliminary studies on the HTTR (High Temperature engineering Test Reactor) tests were conducted to obtain characteristics and demonstration data which were required to develop commercial HTGRs (high temperature gas-cooled reactors). The tests proposed in this study are as follows: nuclear heat supply characteristics tests, burned core tests, reactivity insertion tests, safety demonstration tests, fuel characteristics tests, annular core tests, fuel failure tests, tritium measurement tests, and health confirmation tests of high temperature equipments. Requirements for a development of commercial HTGRs and confirmation methods of the requirements by the HTTR tests were summarized. Preliminary analyses were performed for the burned core test and the safety demonstration test to obtain prediction data, which is compared with experimental data. Additionally, a feasibility analysis was performed on four types annular cores, which is composed of the HTTR's fresh fuels, from the point of view of shutdown margin and excess reactivity.
Iyatomi, Yosuke; Shimada, Akiomi; Ogata, Nobuhisa; Sugihara, Kozo; Seko, Noriaki; Kasai, Noboru; Hoshina, Hiroyuki; Ueki, Yuji; Tamada, Masao
JAEA-Technology 2009-054, 10 Pages, 2009/11
The concentrations of fluorine and boron dissolved in groundwater pumped from shafts during excavation at the Mizunami Underground Research Laboratory (MIU), Tono Geoscience Centre, are reduced to the levels below the environmental standards at a water treatment facility. Collaborative research on groundwater treatment for fluorine and boron has been started by the Environment and Industrial Materials Research Division, Quantum Beam Science Directorate and the Tono Geoscientific Research Unit, Geological Isolation Research and Development Directorate. This is because the Quantum Beam Science Directorate in JAEA has synthesized fibrous adsorbents with radiation-induced graft polymerization and applied them to collect rare metals dissolved in hot springs and sea water. Boron adsorbent synthesized by grafting showed higher removal rate than that of the ion-exchange resin. Additionally, the durability and the repetition use of the boron adsorbent were evaluated to estimate the performance of boron adsorption. Therefore we produced the test equipment to do scale-up test of the adsorbent. Effect of flow rate and the repetition use on the adsorption performance of boron was investigated. As a result, it concluded that adsorption performance did not change even when the flow rate increased from SV 50h to SV 100h
to SV 100h . In addition, enough durability was confirmed for the repetition use of the adsorbent. The adsorption performance of the adsorbent was affected by pH of the groundwater especially in alkaline region.
. In addition, enough durability was confirmed for the repetition use of the adsorbent. The adsorption performance of the adsorbent was affected by pH of the groundwater especially in alkaline region.
Kikuchi, Hironobu; Iwai, Takashi; Arai, Yasuo
JAEA-Technology 2009-055, 35 Pages, 2009/11
Glovebox 702-D for electron probe micro-analysis for plutonium fuels was installed about thirty years ago in the room 107 of Plutonium Fuel Research Facility(PFRF) in Oarai Research Establishment of former Japan Atomic Energy Research Institute(JAERI). The glovebox was scrapped for replacing the old-type electron probe micro-analyzer by a new-type scanning electron microscope. This report summarizes the scrapping work of the glovebox from the technical viewpoints.
Kobayashi, Fuyumi; Ishii, Junichi; Shirahashi, Koichi; Umeda, Miki; Sakuraba, Koichi
JAEA-Technology 2009-056, 16 Pages, 2009/11
The silver mediated electrochemical oxidation (Ag/MEO) process with the ultrasound agitation has been developed for the purpose of the mineralization of organic wastes containing transuranium nuclides at the nuclear fuel reprocessing process. In the Ag/MEO process, organic solvents are decomposed by divalent silver cations under the relatively low temperature and the ambient pressure condition. The ultrasound agitation is effective in mixing the electrolytic solutions and the organic solvents, and is expected to promote the oxidation of the organic solvents. Therefore, the Ag/MEO process with the ultrasound agitation could be a candidate for the treatment of organic solvents. Destruction tests of TBP and dodecane by the Ag/MEO process were conducted to optimize some treatment conditions. Under optimized conditions, the destruction tests of kerosene and TODGA were carried out. It was confirmed that the Ag/MEO process is effective for the mineralization of these organic solvents.
Shinohara, Masanori; Hamamoto, Shimpei; Fujimoto, Nozomu
JAEA-Technology 2009-057, 33 Pages, 2009/12
3-dimensional floating support system is adopted to the cooling system of HTTR is meaningful to verify the thermal displacement behavior of the equipment and piping system applied the 3-dimensional floating support system. In the rated operation of HTTR, thermal displacement behavior of the high temperature equipment and piping system was measured. This paper describes the experimental and analytical results of thermal displacement characteristics of the high temperature equipment and piping system. The results showed that the resistance force induced from the supporting system effects to the thermal displacement behavior of cooling system, and the analytical results have a good agreement with the experimental results by optimizing the resistant force of the floating support system.
Okajima, Yuka; Matsumura, Daiju; Nishihata, Yasuo; Konishi, Hiroyuki; Mizuki, Junichiro
JAEA-Technology 2009-058, 45 Pages, 2009/12
From 2004 to 2006, the Dispersive XAFS system was constructed at JAEA beamline BL14B1 in SPring-8, and has been developed. Recently, the application of this system to materials science started. We report on the outline of this Dispersive XAFS system and explain its operations.
Kato, Shoichi; Furukawa, Tomohiro; Hirakawa, Yasushi; Kondo, Hiroo; Nakamura, Hiroo
JAEA-Technology 2009-059, 42 Pages, 2009/12
In order to obtain the engineering data of the lithium target system which is the neutron source of the International Fusion Material Irradiation Facility (IFMIF), design and fabrication of the liquid lithium test loop are carrying out under the Engineering Validation and Engineering Design Activity (EVEDA). Since lithium is specified as the dangerous substance by the Japanese law, the countermeasure which assumed the lithium combustion incident is indispensable. This report summarizes the results of basic experiment on fire-extinguishing of the lithium. In this experiment, the fire-extinguishing behavior of the fire extinguishers to the lithium was experimentally confirmed, and the fire extinguisher for the liquid lithium test loop is proposed. In addition, the fire-extinguishing performance for the determination of the amount of dispositions of the fire extinguisher was experimentally estimated.
Satoyama, Tomonori; Kishimoto, Katsumi; Takaizumi, Hirohide; Hoshi, Akiko; Okoshi, Minoru; Tachibana, Mitsuo
JAEA-Technology 2009-060, 42 Pages, 2010/01
In the modification activities of JRR-3, a large volume of extremely low-level radioactive concrete debris were generated from dismantling of concrete structure around reactor body during one-piece removal of reactor body. These concrete debris are stored in the waste storage facility NL of the Nuclear Science Research Institute. The applicability of clearance to concrete debris generated from the modification activities of JRR-3 was examined as waste measures in the Nuclear Science Research Institute. First, generated place, amount of volume and radioactivity of concrete debris in the waste storage facility NL were surveyed from records in the modification of JRR-3 and data sheets of radioactive waste stored in the waste storage facility. Next, the radioactivity of samples taken from concrete debris stored in the waste storage facility NL was measured, and distribution of those radioactivity concentration was investigated to evaluate the contamination situation. In addition, activated contamination situation of concrete structure was evaluated by activated calculation. As a result, radioactivity of concrete debris was enough lower than clearance levels, so it was found that concrete debris in the waste storage facility NL was able to treat as clearance materials.
Editorial Committee of Refining and Conversion Facility Decommissioning Results
JAEA-Technology 2009-061, 140 Pages, 2010/01
The Refining and Conversion Facility located in the Ningyo-toge Environmental Engineering Center had the natural uranium conversion process and reprocessed uranium conversion process. The construction of this facility was started in 1979 and completed in October 1981. Dismantling of equipments in radiation controlled area of this facility was started from 2008, and all equipments in radiation controlled area will be dismantled by the 2011 fiscal year. This report describes the master plan of this decommissioning and shows as the progress in latter half year of 2008FY, the actual time schedule, the method of decommissioning, the decommissioning progress appearance with photographs, work rates of each room/each worker class, and the quantity of dismantled materials and secondary wastes.
U-Mo Fuel Research Working Group
JAEA-Technology 2009-062, 54 Pages, 2010/01
A silicide fuel enriched less than 20%  U has been used for research reactors JRR-3, JRR-4 and JMTR. The spent silicide fuel elements generated before May 2016 will have been shipped to the United States under the contract between the United States Department of Energy (DOE) and the JAEA. After termination of the contract, the spent silicide fuel elements will have to be straged in each research reactor. Therefore, we have reviewed possibilities of U-Mo fuel as alternative fuel to the silicide fuel. The U-Mo fuel has been reported to increase reactor performance due to the high uranium density and the good reprocessing feasibility. We confirmed that the reprocessing U-Mo was possible by dissolving with light water reactor fuel. However, there is still unsolved swelling problem of U-Mo fuel. We have decided that conversion from silicide fuel to U-Mo fuel is not possible at present.
U has been used for research reactors JRR-3, JRR-4 and JMTR. The spent silicide fuel elements generated before May 2016 will have been shipped to the United States under the contract between the United States Department of Energy (DOE) and the JAEA. After termination of the contract, the spent silicide fuel elements will have to be straged in each research reactor. Therefore, we have reviewed possibilities of U-Mo fuel as alternative fuel to the silicide fuel. The U-Mo fuel has been reported to increase reactor performance due to the high uranium density and the good reprocessing feasibility. We confirmed that the reprocessing U-Mo was possible by dissolving with light water reactor fuel. However, there is still unsolved swelling problem of U-Mo fuel. We have decided that conversion from silicide fuel to U-Mo fuel is not possible at present.
Tachibana, Yukio; Nishihara, Tetsuo; Sakaba, Nariaki; Ohashi, Hirofumi; Sato, Hiroyuki; Ueta, Shohei; Aihara, Jun; Goto, Minoru; Sumita, Junya; Shibata, Taiju; et al.
JAEA-Technology 2009-063, 155 Pages, 2010/02
This report describes full scope of the feasible future test plan mainly using the HTTR. The test items cover fuel performance and radionuclide transport, core physics, reactor thermal hydraulics and plant dynamics, and reactor operations, maintenance, control, etc. The test results will be utilized for realization of Japan's commercial Very High Temperature Reactor (VHTR) system, GTHTR300C.
Mio, Keigo; Ogiwara, Norio; Marushita, Motoharu*; Arai, Hideyuki*; Goto, Keiichi*
JAEA-Technology 2009-064, 40 Pages, 2010/03
Intense of radiation fields will be expected since large intensity proton beam current of J-PARC 3GeV RCS (Rapid-Cycling Synchrotron).  -ray irradiation tests of vacuum system equipment were carried out to evaluate radiation resistance for RCS. Requirement of radiation resistance of vacuum equipment is assumed as 10 MGy.
-ray irradiation tests of vacuum system equipment were carried out to evaluate radiation resistance for RCS. Requirement of radiation resistance of vacuum equipment is assumed as 10 MGy.  -ray irradiation examination has been done to select the vacuum equipment. As a result, cooling-fan, feed-through-connector, baking heater, piping sealants have been shown to have radiation resistance as 10 MGy. Dry scroll vacuum pump was shown as only 1 MGy from the restriction of the material of the chip seal (Teflon).
-ray irradiation examination has been done to select the vacuum equipment. As a result, cooling-fan, feed-through-connector, baking heater, piping sealants have been shown to have radiation resistance as 10 MGy. Dry scroll vacuum pump was shown as only 1 MGy from the restriction of the material of the chip seal (Teflon).
Ichige, Satoru; Yamaguchi, Kohei; Oda, Chie
JAEA-Technology 2009-065, 120 Pages, 2010/02
The focus of the present study was to examine the alteration of bentonite in high pH saline groundwaters. Two solutions were used in batch immersion experiments of bentonite. The first solution was prepared using a mixture of NaOH and NaCl (NN), and the second solution was prepared using synthetic Region 1 water (high K and Na content) and synthetic seawater (SR). Analysis showed that bentonite altered to analcime in the NN solution and to analcime and phillipsite-K in the SR solution. Moreover, the generation of calcium silicate hydrate and calcium aluminosilicate hydrate were extrapolated in the SR solution based on the concentrations of dissolved species. These alteration products were in accord with Oda et al. (2005), who summarized the possible relationships between the secondary mineral assemblage of bentonite under high pH conditions and the influence of solution composition.
Ishiyama, Toru; Asano, Naoki; Kawasaki, Ichio
JAEA-Technology 2009-066, 79 Pages, 2010/02
Tokai Utility Center (TUC) is the facility that products and feeds steam for Tokai Reprocessing Plant (TRP), Plutonium Fuel Production Facility (PFPF), etc. The boiler system needs the management based on the law of "Industrial safety and Health Act" and "Act on the Regulation of Nuclear Source Material, Nuclear Fuel Material and Reactors". In this situation, activity of preservation of environment and energy-save are carried out by means of the improvement of steam generation process and the change of additive to water. Quality assurance procedure has been applied in order to improve the boiler operation continuously. This report describes about various activities of the management, the environment, the energy-saving, and a future action.
Ide, Hiroshi; Kimura, Akihiro; Miura, Hiroshi; Hori, Naohiko; Nagao, Yoshiharu
JAEA-Technology 2009-067, 39 Pages, 2010/02
Visual inspection of inner side of a reactor pressure vessel was carried out using a underwater camera before the JMTR refurbishment work from the view point of its long term utilization because the reactor pressure vessel of the JMTR will be used continuously after restart of the JMTR. As a result, adhesion materials which can be easily removed using the gauze were observed around nozzles in a top head of the reactor pressure vessel. A major component of the adhesion materials is an iron as a result of the componential analysis. However, no significant problem affecting the integrity of the reactor pressure vessel was observed, and thus the integrity of the reactor pressure vessel was confirmed. As for the view point of the aged effect, it became clear that the reactor pressure vessel of the JMTR can be used for more than 20 years. The visual inspection by the underwater camera is to be carried out periodically to confirm the integrity of the reactor pressure vessel.
Ishii, Junichi; Kobayashi, Fuyumi; Uchida, Shoji; Sumiya, Masato; Kida, Takashi; Shirahashi, Koichi; Umeda, Miki; Sakuraba, Koichi
JAEA-Technology 2009-068, 20 Pages, 2010/03
At Nuclear Fuel Cycle Safety Engineering Research Facility, the cerium mediated electrolytic oxidation method which is a decontamination technique to decrease the radioactivity of TRU wastes to the clearance-level has been developed for the effective reduction of TRU wastes generated from the decommissioning of a nuclear fuel reprocessing facility and so on. This method corrodes the oxide layer and the surface of metallic TRU metal wastes by the strong oxidation power of Ce in nitric acid. In this study, parameter tests were conducted to optimize the solution condition of Ce
in nitric acid. In this study, parameter tests were conducted to optimize the solution condition of Ce initial concentrations and nitric acid concentrations. The target corrosion rate of metallic TRU wastes set to be 2
initial concentrations and nitric acid concentrations. The target corrosion rate of metallic TRU wastes set to be 2 4
4 m/h for the practical use of this method. Under the optimized solution condition, a dissolution test of stainless steel simulating wastes was carried out. From the result of the dissolution test, the average corrosion rate was 3.3
m/h for the practical use of this method. Under the optimized solution condition, a dissolution test of stainless steel simulating wastes was carried out. From the result of the dissolution test, the average corrosion rate was 3.3  m/h during the test time of 90 hours. Based on the supposition that the corrosion depth of metallic TRU wastes was 20
m/h during the test time of 90 hours. Based on the supposition that the corrosion depth of metallic TRU wastes was 20  m enough to achieve the clearance-level, the treatment time for the decontamination was about 6 hours. It was confirmed from the result that the decontamination could be performed within one day and the decontamination solution could repeatedly reuse 15 times.
m enough to achieve the clearance-level, the treatment time for the decontamination was about 6 hours. It was confirmed from the result that the decontamination could be performed within one day and the decontamination solution could repeatedly reuse 15 times.
Sozawa, Shizuo; Nakagawa, Tetsuya; Omi, Masao; Hayashi, Koji; Iwamatsu, Shigemi; Kawamata, Kazuo; Kato, Yoshiaki; Kanazawa, Yoshiharu
JAEA-Technology 2009-069, 32 Pages, 2010/03
Refurbishment of the Japan Materials Testing Reactor (JMTR), which is recognized as one of important facilities in Japan for safety research, is in progress by the JAEA. In Extensive safety research of light-water reactor (LWR) fuels and materials under a contract with the Nuclear and Industrial Safety Agency of Ministry of Economy, Trade and Industry of Japan, the irradiation tests are planned in order to examine integrity of the LWR fuels and structure materials. For the irradiation tests of high burnup fuels and irradiated materials in the JMTR, modification of the hot laboratory facilities are needed, which are (1) strengthening JMTR hot-lab. cell-shielding, (2) the capsule assembling device, (3) domestic transportation cask, (4) fuel-rod center-hole processing device, (5) master-slave manipulators, (6) power manipulator, and (7) scanning electron microscope.
Sozawa, Shizuo; Nakagawa, Tetsuya; Iwamatsu, Shigemi; Hayashi, Koji; Tayama, Yoshinobu; Kawamata, Kazuo; Yonekawa, Minoru; Taguchi, Taketoshi; Kanazawa, Yoshiharu; Omi, Masao
JAEA-Technology 2009-070, 27 Pages, 2010/03
Refurbishment of the Japan Materials Testing Reactor (JMTR), which is recognized as one of important facilities in Japan for safety research, is in progress by the JAEA. In Extensive safety research of light-water reactor (LWR) fuels and materials under a contract with the Nuclear and Industrial Safety Agency of Ministry of Economy, Trade and Industry of Japan, the irradiation tests are planned in order to examine integrity of the LWR fuels and structure materials. For the irradiation tests of high burnup fuels and irradiated materials in the JMTR, modification of the hot laboratory facilities are needed, which are (1) making of application books for strengthening JMTR hot-lab. cell-shielding, (2) the capsule assembling device of detailed design, (3) safety analysis for domestic transportation cask and (4) confirmatory testing of diamond drill of fuel-rod center-hole processing device.
Sakuraba, Naotoshi; Numata, Masami; Komiya, Tomokazu; Ichise, Kenichi; Nishi, Masahiro; Tomita, Takeshi; Usami, Koji; Endo, Shinya; Miyata, Seiichi; Kurosawa, Tatsuya; et al.
JAEA-Technology 2009-071, 34 Pages, 2010/03
As a part of maintenance technology of a large-sized glove box for handling of TRU nuclides, we developed replacement technology for front acrylic panels using the bag-in/bag-out method and applied this technology to replace the deteriorated front acrylic panels at Waste Safety Testing Facility (WASTEF) in Nuclear Science Research Institute of Japan Atomic Energy Agency (JAEA). As a consequence, we could safely replace the front acrylic panels under the condition of continuous negative pressure only with partial decontamination of the glove box. We also demonstrated that the present technology is highly effective in points of safety, workability and cost as compared to the usual replacement technology for front acrylic panels of a glove box, where workers in an air-line suit replace directly the front acrylic panels in a green house.
Matsui, Yoshinori; Takahashi, Hiroyuki; Yamamoto, Masaya; Nakata, Masahito; Yoshitake, Tsunemitsu; Abe, Kazuyuki; Yoshikawa, Katsunori; Iwamatsu, Shigemi; Ishikawa, Kazuyoshi; Kikuchi, Taiji; et al.
JAEA-Technology 2009-072, 144 Pages, 2010/03
"R&D Project on Irradiation Damage Management Technology for Structural Materials of Long-life Nuclear Plant" was carried out from FY2006 in a fund of a trust enterprise of the Ministry of Education, Culture, Sports, Science and Technology. The coupled irradiations or single irradiation by JOYO fast reactor and JRR-3 thermal reactor were performed for about two years. The irradiation specimens are very important materials to establish of "Evaluation of Irradiation Damage Indicator" in this research. For the acquisition of the examination specimens irradiated by the JOYO and JRR-3, we summarized about the overall plan, the work process and the results for the study to utilize these reactors and some facilities of hot laboratory (WASTEF, JMTR-HL, MMF and FMF) of the Oarai Research-and-Development Center and the Nuclear Science Research Institute in the Japan Atomic Energy Agency.
Kanamori, Masashi
JAEA-Technology 2009-073, 40 Pages, 2010/03
The JCO criticality accident occurred at about 10:35 A.M. on September 30, 1999 in Tokai-mura, Ibaraki Prefecture, Japan. This year (2009) is full 10 years from that truly unfortunate accident. I was then the manager of safety section of Japan Nuclear Cycle Development Institute (JNC) Tokai Works, and engaged in the operation of the criticality accident termination in JCO sites as an expert of the disaster prevention of national government. This report is summarized the circumstances surrounding termination of the JCO criticality accident based on testimony in the Mito District Court in 2001. Since then, comments have been received and I rewritten in this tenth year with my thought not to have to forget the accident. We hope that this report will be useful in some way in preventing nuclear disaster in the future.
Kitamura, Akira; Shibata, Masahiro; Yamaguchi, Tetsuji; Iida, Yoshihisa; Yui, Mikazu
JAEA-Technology 2009-074, 48 Pages, 2010/03
Investigations on systematics of thermodynamic data were performed for performance assessment of geological disposal of high-level and TRU waste. Correlation between standard free energy of formation and standard enthalpy of formation was investigated, and it was shown that estimation of the standard enthalpy of formation from the standard free energy of formation was possible using the correlation. Three models on systematics of formation constant of actinides were compared and the best model was proposed. It was shown that estimation of formation constant for unpublished species was possible using the model. Furthermore, two models for estimation of activity coefficient which was required to estimate solubility of elements of interest and the estimated activity coefficient were compared. It was expected that the obtained results were useful for the performance assessment of geological disposal.
 Mo adsorption and
Mo adsorption and  Tc elution characteristics of molybdenum adsorbents for (n,
Tc elution characteristics of molybdenum adsorbents for (n, ); Method-joint experiment report on irradiation technology of RI production (STC No. 2-II) (Joint research)
); Method-joint experiment report on irradiation technology of RI production (STC No. 2-II) (Joint research)Kimura, Akihiro; Izumo, Hironobu; Tsuchiya, Kunihiko; Hori, Naohiko; Ishihara, Masahiro; Bannykh, V.*; Gluschenko, N.*; Chakrova, Y.*; Chakrov, P.*
JAEA-Technology 2009-075, 23 Pages, 2010/02
Japan Materials Testing Reactor (JMTR) of the Japan Atomic Energy Agency (JAEA) has a plan to produce  Mo, which is the parent nuclide of radiopharmaceutical
Mo, which is the parent nuclide of radiopharmaceutical  Tc, by (n,
Tc, by (n, ) method. The
) method. The  Mo adsorption and
Mo adsorption and  Tc elution characteristics of molybdenum adsorbents should be evaluated since the specific activity of
Tc elution characteristics of molybdenum adsorbents should be evaluated since the specific activity of  Mo obtained by (n,
Mo obtained by (n, ) method is low. Therefore,
) method is low. Therefore,  Mo adsorption and
Mo adsorption and  Tc elution tests with molybdenum adsorbents for the (n,
Tc elution tests with molybdenum adsorbents for the (n, ) method such as poly-zirconium compound (PZC) and molybdate zirconium gel were carried out under cooperation with the Kazakhstan National Nuclear Energy Center (NNC). As a result, the
) method such as poly-zirconium compound (PZC) and molybdate zirconium gel were carried out under cooperation with the Kazakhstan National Nuclear Energy Center (NNC). As a result, the  Mo adsorption performance of the adsorbents was the same level as conventional data, whereas the
Mo adsorption performance of the adsorbents was the same level as conventional data, whereas the  Tc elution performance of the adsorbents was lower than conventional data. The
Tc elution performance of the adsorbents was lower than conventional data. The  Mo adsorption and
Mo adsorption and  Tc elution performance will be investigated again in future.
Tc elution performance will be investigated again in future.
Inoue, Shuichi; Yamaura, Takayuki; Saito, Takashi; Ishikawa, Kazuyoshi; Kikuchi, Taiji; Sozawa, Shizuo; Tsuchiya, Kunihiko
JAEA-Technology 2009-076, 33 Pages, 2010/03
In Japan Material Testing Reactor (JMTR), a lot of experiments of fuel irradiation with the power ramping tests have been performed by using the shroud irradiation facility and the Boiling Water Capsule (BOCA). The fuel samples used in these tests were welded to re-instrumentation devices such as thermocouples and FP gas pressures. In this development, the mechanical connection method as "mechanical seal structure", that enables the re-use of re-instrumentation devices, was adopted in order to improve the utilization efficiency of the device. The test samples with mechanical seal structure were fabricated and the confirmatory tests such as He leakage test, thermal cycle test, autoclave test, etc. were carried out. The test samples with the mechanical seal structure showed an excellent result in various confirmatory tests, and the prospect are bright for the re-use of re-instrumentation devices with the mechanical seal structure.
Yoshikawa, Akira; Tanigawa, Hisashi; Seki, Yohji; Hirose, Takanori; Tsuru, Daigo; Ezato, Koichiro; Yokoyama, Kenji; Nishi, Hiroshi; Suzuki, Satoshi; Tanzawa, Sadamitsu; et al.
JAEA-Technology 2009-077, 23 Pages, 2010/03
In the side wall of TBM, parallel flow channels are considered. In the cooling channels structure, the flow distribution probably arises from the pressure drop in the channels. The purpose of this study is to clarify the water flow distribution in the side wall and design the cooling channels structure so that structural material of the side wall can be kept under the allowable temperature. The structural material for assumed flow rates and the flow distribution were estimated, and then the cooling channels structure was designed. The design was verified using the mockup made of the vinyl chloride pipe. For the verified design, the mockup made of F82H is manufactured, and the water flow distribution and the pressure drop were measured. It was found that the heat removal capability was sufficient in this design. From these results, the design for the cooling channels structure in the side wall is established so that enough water flow to cool the structural material is kept.
Hanawa, Yoshio; Tsuboi, Kazuaki; Uchida, Munenori*; Suzuki, Ken*; Takahashi, Kunihiro
JAEA-Technology 2009-078, 18 Pages, 2010/03
Beryllium has been used as the neutron reflector in the Japan Materials Testing Reactor (JMTR). A beryllium frame is arranged in the JMTR core and the frame consists of 3 sections (North, East and West). Each section has 7 stories of the beryllium blocks. Each block is connected by the aluminum joints. The capsule or the beryllium plug is located in the inside of the beryllium frame. The first criticality achieved in 1968 and the frame has been replaced 6 times and now the 7th frame is being manufactured. The replacement is planned to be done in the spring of 2010. The design has been modified to decrease the swelling camber and the lifetime has been improved. The manufacturing procedure is severely controlled to assure the quality. The chemical composition must be specified to minimize the swelling and radiation. The machining procedure is highly controlled because beryllium is very brittle. And the environmental control is also important, because the beryllium is a toxic material.
Kanamori, Masashi
JAEA-Technology 2009-079, 44 Pages, 2010/07
In 2001, we summarized the circumstances surrounding termination of the JCO criticality accident based on testimony in the Mito District Court on December 17, 2001. JCO was the company for uranium fuels production in Japan. That document was assembled based on actual testimony in the belief that a description of the work involved in termination of the accident would be useful in some way for preventing nuclear disasters in the future. This year is the tenth year of the JCO criticality accident. To mark this occasion we have decided to translate the record of what occurred at the accident site into English so that more people can draw lessons from this accident.
Inaba, Yoshitomo; Sakamoto, Taichi; Yamaura, Takayuki
JAEA-Technology 2009-080, 22 Pages, 2010/02
The power transient tests for the fuels of light water reactors are to be carried out in the Japan Materials Testing Reactor (JMTR) using capsule-type test facilities, and the integrity of the fuels is to be investigated by the tests. Prior to the irradiation tests of the fuels, the out-of-pile test facility, which had an electric heater pin instead of a test fuel pin, was designed and fabricated to simulate the capsules used in the power transient tests. Using this facility, necessary tests for the planning of the test methods were carried out. In the present report, the outline of the out-of-pile test facility, the test plan and the tests simulating natural convection capsule were described. As a result of the tests, it was found that the power of the heater pin with a diameter of 9.5 mm can achieve to 600 W/cm without transition from nucleate boiling to film boiling under BWR and PWR coolant pressure conditions.
Kawamura, Hideki*; Ando, Kenichi*; Noda, Masaru*; Tanaka, Tatsuya*; Matsuda, Takeshi*; Fujii, Haruhiko*; Hashimoto, Shuji*; Ueda, Tadashi*; Matsui, Hiroya; Takeuchi, Shinji; et al.
JAEA-Technology 2009-081, 182 Pages, 2010/03
Grouting has practical importance for the reduction of groundwater inflow into excavations during construction of underground facilities. Considering the performance assessment of a radioactive waste repository, the performance of the engineered barrier system could be adversely affected by a high pH plume generated from grout. Therefore, a quantitative estimation of the effectiveness of grouting and grout material is essential. This study has been performed in the Mizunami URL being excavated in crystalline rock as a part of the Project for Grouting Technology Development for the Radioactive Waste Repository funded by METI, Japan. The aims were to evaluate the applicability of existing grouting technology and to develop methodology to determine the distribution of grout and change in hydraulic properties of the grouted rock volume. The target rock is the volume of rock around a planned refuge niche where the pre-excavation grouting was performed at 200-m depth from ground surface. After excavation of the refuge niche, ten boreholes were drilled and different kinds of investigations were carried out during and after drilling. The results were integrated and groundwater flow analysis of pre and post excavation grouting conditions were carried out to estimate quantitatively the effect of pre-excavation grouting. The results suggest that current pre-excavation grouting technology is effective for reduction of groundwater inflow into excavations and that hydraulic conductivity of the surrounding rock can be reduced by more than one order of magnitude.
 SO
SO , I
, I and H
and H O by 3-dimensional visualization
O by 3-dimensional visualizationNakajima, Hayato*; Imai, Yoshiyuki; Kubo, Shinji
JAEA-Technology 2009-082, 35 Pages, 2010/08
Concerning the thermochemical water-splitting Iodine-Sulfur process, understanding of solution compositions on 2 liquid phase separation is essential for making good choices of operating conditions and for accurate estimations of thermal efficiency. The compositions of 4-component system composed of HI, H SO
SO , I
, I and H
and H O were examined experimentally and were analysed by a 3-dimensional visualization technique. A chemical titration method was adapted to determine the mole fractions of the solutions at 293 K and 363 K, and the fraction were represented by scattered points in an equilateral tetrahedron. Two valuable features were found from a visualized shape viewed as an aggregate of the points, which were difficult to find out by 2-dimensional presentations.
O were examined experimentally and were analysed by a 3-dimensional visualization technique. A chemical titration method was adapted to determine the mole fractions of the solutions at 293 K and 363 K, and the fraction were represented by scattered points in an equilateral tetrahedron. Two valuable features were found from a visualized shape viewed as an aggregate of the points, which were difficult to find out by 2-dimensional presentations.