Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Li, M.*; Nagashio, Kosuke*; Ishikawa, Takehiko*; Mizuno, Akitoshi*; Adachi, Masayoshi*; Watanabe, Masahito*; Yoda, Shinichi*; Kuribayashi, Kazuhiko*; Katayama, Yoshinori
Acta Materialia, 56(11), p.2514 - 2525, 2008/06
Times Cited Count:23 Percentile:71.49(Materials Science, Multidisciplinary)Co-61.8 at.% Si (CoSe-CoSi ) eutectic alloys were solidified on an electromagnetic levitator (EML) and an electrostatic levitator (ESL) at different undercooling levels. The results indicated that there is only a single recalescence event at low undercooling with the CoSi intermetallic compound as primary phase, which is independent of processing facilities, on either an EML or an ESL. The microstructure, however, is strongly dependent on the processing facility. On high undercooling, double recalescence takes place regardless of levitation condition. In situ X-ray diffraction of alloys solidified on the EML demonstrates that the CoSi
) eutectic alloys were solidified on an electromagnetic levitator (EML) and an electrostatic levitator (ESL) at different undercooling levels. The results indicated that there is only a single recalescence event at low undercooling with the CoSi intermetallic compound as primary phase, which is independent of processing facilities, on either an EML or an ESL. The microstructure, however, is strongly dependent on the processing facility. On high undercooling, double recalescence takes place regardless of levitation condition. In situ X-ray diffraction of alloys solidified on the EML demonstrates that the CoSi compound becomes the primary phase upon the first recalescence, and the CoSi intermetallic phase crystallizes during the second recalescence. In addition to phase identification, real-time diffraction patterns can also provide additional evidence of the fragmentation of the primary phase.
compound becomes the primary phase upon the first recalescence, and the CoSi intermetallic phase crystallizes during the second recalescence. In addition to phase identification, real-time diffraction patterns can also provide additional evidence of the fragmentation of the primary phase.
Nagashio, Kosuke*; Adachi, Masayoshi*; Higuchi, Kensuke*; Mizuno, Akitoshi*; Watanabe, Masahito*; Kuribayashi, Kazuhiko*; Katayama, Yoshinori
Journal of Applied Physics, 100(3), p.033524_1 - 033524_6, 2006/08
Times Cited Count:14 Percentile:47.03(Physics, Applied)Grain refined microstructure is often obtained spontaneously in the solidification of metals and semiconductors from the undercooled melt without any external forces. Although it has been reported that the grain refinement is mainly caused by the fragmentation of the dendrites, the dynamic process of the fragmentation of dendrites has not been fully understood because the microstructure after the solidification has been analyzed. Here, we present a time-resolved 2- dimensional X-ray diffraction experiment on the solidification of Si from the undercooled melt. The number of diffraction spots observed at low undercoolings (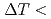 100K) did not increase at the plateau stage, while the diffraction pattern at medium undercoolings (100K
100K) did not increase at the plateau stage, while the diffraction pattern at medium undercoolings (100K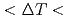 200K) changed from the spots with the tail to rings with the lapse of time. Both this result and high speed video imaging suggested that the high-order arms of the dendrites mostly detached from the main stems because nucleation could not be expected at the melting point after recalescence. The several spots observed at low undercoolings drastically changed to rings at high undercoolings (
200K) changed from the spots with the tail to rings with the lapse of time. Both this result and high speed video imaging suggested that the high-order arms of the dendrites mostly detached from the main stems because nucleation could not be expected at the melting point after recalescence. The several spots observed at low undercoolings drastically changed to rings at high undercoolings (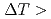 200K), which indicated the complete fragmentation of dendrite main stem as well as high-order arms. This complete fragmentation resulted in the grain refined microstructure.
200K), which indicated the complete fragmentation of dendrite main stem as well as high-order arms. This complete fragmentation resulted in the grain refined microstructure.
*; *; *; *; Nakajima, Kunihiko*; Sugihara, Masayoshi; Yamamoto, Shin; Iida, Hiromasa; Fujisawa, Noboru; Mizoguchi, Tadanori*; et al.
JAERI-M 87-137, 72 Pages, 1987/09
no abstracts in English
Watanabe, Makoto*; Higashi, Hideo*; Sasaki, Minako*; Adachi, Masayoshi*; Otsuka, Makoto*; Fukuyama, Hiroyuki*; Nishi, Tsuyoshi; Yamano, Hidemasa
no journal, ,
This reports results of density measurement of molten iron and nickel that are main components of stainless steel 316 of cladding of control rod as part of thermophysical properties studies of molten control rod material in BWR.
Watanabe, Makoto*; Higashi, Hideo*; Sasaki, Minako*; Adachi, Masayoshi*; Otsuka, Makoto*; Fukuyama, Hiroyuki*; Nishi, Tsuyoshi; Yamano, Hidemasa
no journal, ,
In this study, as a first step, density of the stainless steel 316 (SUS316), pure Fe and Ni were measured. For all samples, the densities are expressed with a linear function of temperature.
 C by in-situ observation and quench method with electromagnetic levitation
C by in-situ observation and quench method with electromagnetic levitationFukuyama, Hiroyuki*; Higashi, Hideo*; Otsuka, Makoto*; Adachi, Masayoshi*; Yamano, Hidemasa
no journal, ,
The purpose of this study is to investigate the eutectic reaction mechanism of the control rod material (boron carbide (B C)) and the structural material of a reactor vessel (stainless steel: SUS316L (SS)) during a core disruptive accident in a sodium-cooled fast reactor. This paper describes a solidification pathway of SUS316L containing 9-11mass% B
C)) and the structural material of a reactor vessel (stainless steel: SUS316L (SS)) during a core disruptive accident in a sodium-cooled fast reactor. This paper describes a solidification pathway of SUS316L containing 9-11mass% B C by in-situ observation and quench method with electromagnetic levitation.
C by in-situ observation and quench method with electromagnetic levitation.
 C using ultrahigh-temperature thermal analysis based on blackbody radiation
C using ultrahigh-temperature thermal analysis based on blackbody radiationHigashi, Hideo*; Fukuyama, Hiroyuki*; Otsuka, Makoto*; Adachi, Masayoshi*; Yamano, Hidemasa
no journal, ,
The purpose of this study is to investigate the eutectic reaction mechanism of the control rod material (boron carbide (B C)) and the structural material of a reactor vessel (stainless steel: SUS316L (SS)) during a core disruptive accident in a sodium-cooled fast reactor. This paper describes a melting behavior analysis of SUS316L containing 9-11mass% B
C)) and the structural material of a reactor vessel (stainless steel: SUS316L (SS)) during a core disruptive accident in a sodium-cooled fast reactor. This paper describes a melting behavior analysis of SUS316L containing 9-11mass% B C using ultrahigh-temperature thermal analysis based on blackbody radiation.
C using ultrahigh-temperature thermal analysis based on blackbody radiation.
 C by a combination of ultra-high temperature thermal analysis and microstructural observation
C by a combination of ultra-high temperature thermal analysis and microstructural observationFukuyama, Hiroyuki*; Higashi, Hideo*; Adachi, Masayoshi*; Otsuka, Makoto*; Yamano, Hidemasa
no journal, ,
A BN crucible with blackbody cavity containing the sample (14, 17mass%B C-SS) was set in the furnace and then heated in an Ar gas atmosphere. The samples were electromagnetically levitated and completely melted, then the temperature was gradually lowered to below the liquidus temperature or below the eutectic temperature, and then quenched. The surfaces and cross sections of the solidified samples were observed by SEM-EDX, and the phases were identified by an X-ray diffractometer.
C-SS) was set in the furnace and then heated in an Ar gas atmosphere. The samples were electromagnetically levitated and completely melted, then the temperature was gradually lowered to below the liquidus temperature or below the eutectic temperature, and then quenched. The surfaces and cross sections of the solidified samples were observed by SEM-EDX, and the phases were identified by an X-ray diffractometer.
 C using ultrahigh-temperature thermal analysis based on blackbody radiation
C using ultrahigh-temperature thermal analysis based on blackbody radiationHigashi, Hideo*; Fukuyama, Hiroyuki*; Otsuka, Makoto*; Adachi, Masayoshi*; Yamano, Hidemasa
no journal, ,
The purpose of this study is to investigate the eutectic reaction mechanism of the control rod material (boron carbide (B C)) and the structural material of a reactor vessel (stainless steel: SUS316L (SS)) during a core disruptive accident in a sodium-cooled fast reactor. This paper describes a melting behavior analysis of SUS316L containing 14, 17mass% B
C)) and the structural material of a reactor vessel (stainless steel: SUS316L (SS)) during a core disruptive accident in a sodium-cooled fast reactor. This paper describes a melting behavior analysis of SUS316L containing 14, 17mass% B C using ultrahigh-temperature thermal analysis based on blackbody radiation.
C using ultrahigh-temperature thermal analysis based on blackbody radiation.
 C by in-situ observation and quench method with electromagnetic levitation
C by in-situ observation and quench method with electromagnetic levitationFukuyama, Hiroyuki*; Higashi, Hideo*; Otsuka, Makoto*; Adachi, Masayoshi*; Yamano, Hidemasa
no journal, ,
The purpose of this study is to investigate the eutectic reaction mechanism of the control rod material (boron carbide (B C)) and the structural material of a reactor vessel (stainless steel: SUS316L (SS)) during a core disruptive accident in a sodium-cooled fast reactor. This paper describes a solidification pathway of SUS316L containing 14, 17mass% B
C)) and the structural material of a reactor vessel (stainless steel: SUS316L (SS)) during a core disruptive accident in a sodium-cooled fast reactor. This paper describes a solidification pathway of SUS316L containing 14, 17mass% B C by in-situ observation and quench method with electromagnetic levitation.
C by in-situ observation and quench method with electromagnetic levitation.