Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Deng, Y.*; Watanabe, Yukinobu*; Manabe, Seiya*; Liao, W.*; Hashimoto, Masanori*; Abe, Shinichiro; Tampo, Motonobu*; Miyake, Yasuhiro*
IEEE Transactions on Nuclear Science, 71(4), p.912 - 920, 2024/04
With the miniaturization of semiconductors and the decrease in operating voltage, there is a growing interest and discussion in whether the muons in cosmic rays may be the source of single event upsets (SEUs). In the case of neutron-induced SEUs, it was reported that the irradiation side has the impact on SEU cross sections. Here, to investigate the impact of irradiation direction on muon-induced SEUs, we have measured and simulate muon-induced SEUs in 65-nm bulk SRAMs with different muon irradiation directions. It was found that the peak SEU cross section for the package side irradiation is about twice large as that for the board side irradiation. We also revealed that the difference in observed SEU cross sections between the package side and the board side irradiation is caused by differences in energy straggling due to changes in penetration depth depending on the incident direction.
Yomogida, Takumi; Hashimoto, Tadashi; Okumura, Takuma*; Yamada, Shinya*; Tatsuno, Hideyuki*; Noda, Hirofumi*; Hayakawa, Ryota*; Okada, Shinji*; Takatori, Sayuri*; Isobe, Tadaaki*; et al.
Analyst, 149(10), p.2932 - 2941, 2024/03
In this study, we successfully applied a transition-edge sensor (TES) spectrometer as a detector for microbeam X-ray measurements from a synchrotron X-ray light source to determine uranium (U) distribution at the micro-scale and its chemical species in biotite obtained from the U mine. It is difficult to separate the fluorescent X-ray of the U L
 line at 13.615 keV from that of the Rb K
line at 13.615 keV from that of the Rb K line at 13.395 keV in the X-ray fluorescence spectrum with an energy resolution of approximately 220 eV of the conventional silicon drift detector (SDD). Meanwhile, the fluorescent X-rays of U L
line at 13.395 keV in the X-ray fluorescence spectrum with an energy resolution of approximately 220 eV of the conventional silicon drift detector (SDD). Meanwhile, the fluorescent X-rays of U L
 and Rb K
and Rb K were fully separated by TES with 50 eV energy resolution at the energy of around 13 keV. The successful peak separation by TES led to an accurate mapping analysis of trace U in micro-X-ray fluorescence measurements and a decrease in the signal-to-background ratio in micro-X-ray absorption near edge structure spectroscopy.
were fully separated by TES with 50 eV energy resolution at the energy of around 13 keV. The successful peak separation by TES led to an accurate mapping analysis of trace U in micro-X-ray fluorescence measurements and a decrease in the signal-to-background ratio in micro-X-ray absorption near edge structure spectroscopy.
 -ray elastic scattering
-ray elastic scatteringOmer, M.; Shizuma, Toshiyuki*; Koizumi, Mitsuo; Hajima, Ryoichi*; Hashimoto, Satoshi*; Miyamoto, Shuji*
LASTI Annual Report, 24, p.20 - 22, 2023/12
Takasaki, Koji; Yasumune, Takashi; Yamaguchi, Yukako; Hashimoto, Makoto; Maeda, Koji; Kato, Masato
Journal of Nuclear Science and Technology, 60(11), p.1437 - 1446, 2023/11
Times Cited Count:0 Percentile:0.01(Nuclear Science & Technology)The aerodynamic radioactive median diameter (AMAD) is necessary information to assess the internal exposure. On June 6, 2017, at a plutonium handling facility in Oarai site of Japan Atomic Energy Agency (JAEA), during the inspection work of a storage container that contains nuclear fuel materials, accidental contamination occurred and five workers inhaled radioactive materials including plutonium. Some smear papers and an air sampling filter were measured with the imaging plate, and we conservatively estimated minimum AMADs for two cases, plutonium nitrate and plutonium dioxide. As a result of AMAD estimation, even excluding a giant particle of a smear sample, the minimum AMADs of plutonium nitrate from smear papers were 4.3 - 11.3  m and those of plutonium dioxide were 5.6 - 14.1
m and those of plutonium dioxide were 5.6 - 14.1  m. Also, the minimum AMAD of plutonium nitrate from an air sampling filter was 3.0
m. Also, the minimum AMAD of plutonium nitrate from an air sampling filter was 3.0  m and that of plutonium dioxide was 3.9
m and that of plutonium dioxide was 3.9  m.
m.
Hashimoto, Kei*; Shiwaku, Toru*; Aoki, Hiroyuki; Yokoyama, Hideaki*; Mayumi, Koichi*; Ito, Kozo*
Science Advances (Internet), 9(47), p.eadi8505_1 - eadi8505_8, 2023/11
Times Cited Count:5 Percentile:45.8(Multidisciplinary Sciences)Ikeda, Yoichi*; Umemoto, Yoshihiko*; Matsumura, Daiju; Tsuji, Takuya; Hashimoto, Yuki*; Kitazawa, Takafumi*; Fujita, Masaki*
Materials Transactions, 64(9), p.2254 - 2260, 2023/09
Times Cited Count:0 Percentile:0(Materials Science, Multidisciplinary)Abe, Shinichiro; Hashimoto, Masanori*; Liao, W.*; Kato, Takashi*; Asai, Hiroaki*; Shimbo, Kenichi*; Matsuyama, Hideya*; Sato, Tatsuhiko; Kobayashi, Kazutoshi*; Watanabe, Yukinobu*
IEEE Transactions on Nuclear Science, 70(8, Part 1), p.1652 - 1657, 2023/08
Times Cited Count:0 Percentile:0.01(Engineering, Electrical & Electronic)Single event upsets (SEUs) caused by neutrons is a reliability problem for microelectronic devices in the terrestrial environment. Acceleration tests using white neutron beam provide realistic soft error rates (SERs), but only a few facilities can provide white neutron beam in the world. If single-source irradiation applicable to diverse neutron source can be utilized for the evaluation of the SER in the terrestrial environment, it contributes to solve the shortage of beam time. In this study, we investigated the feasibility of the SER estimation in the terrestrial environment by any one of these measured data with the SEU cross sections obtained by PHITS simulation. It was found that the SERs estimated by our proposed method are within a factor of 2.7 of that estimated by the Weibull function. We also investigated the effect of simplification which reduce the computational cost in simulation to the SER estimation.
Ishitsuka, Etsuo; Ho, H. Q.; Kitagawa, Kanta*; Fukuda, Takahito*; Ito, Ryo*; Nemoto, Masaya*; Kusunoki, Hayato*; Nomura, Takuro*; Nagase, Sota*; Hashimoto, Haruki*; et al.
JAEA-Technology 2023-013, 19 Pages, 2023/06
Eight people from five universities participated in the 2022 summer holiday practical training with the theme of "Technical development on HTTR". The participants practiced the feasibility study for nuclear battery, the burn-up analysis of HTTR core, the feasibility study for  Cf production, the analysis of behavior on loss of forced cooling test, and the thermal-hydraulic analysis near reactor pressure vessel. In the questionnaire after this training, there were impressions such as that it was useful as a work experience, that some students found it useful for their own research, and that discussion with other university students was a good experience. These impressions suggest that this training was generally evaluated as good.
Cf production, the analysis of behavior on loss of forced cooling test, and the thermal-hydraulic analysis near reactor pressure vessel. In the questionnaire after this training, there were impressions such as that it was useful as a work experience, that some students found it useful for their own research, and that discussion with other university students was a good experience. These impressions suggest that this training was generally evaluated as good.
 probed by anisotropic low-energy excitations
probed by anisotropic low-energy excitationsIshihara, Kota*; Roppongi, Masaki*; Kobayashi, Masayuki*; Imamura, Kumpei*; Mizukami, Yuta*; Sakai, Hironori; Opletal, P.; Tokiwa, Yoshifumi; Haga, Yoshinori; Hashimoto, Kenichiro*; et al.
Nature Communications (Internet), 14, p.2966_1 - 2966_7, 2023/05
Times Cited Count:9 Percentile:93.15(Multidisciplinary Sciences)The superconducting symmetry of the heavy fermion uranium-based superconductor UTe is investigated using low temperature penetration depth measurements. The anisotropic low-energy quasiparticle excitations indicates multiple superconducting components in a chiral complex form. The most consistent is a chiral non-unitary state.
is investigated using low temperature penetration depth measurements. The anisotropic low-energy quasiparticle excitations indicates multiple superconducting components in a chiral complex form. The most consistent is a chiral non-unitary state.

Ishihara, Kota*; Kobayashi, Masayuki*; Imamura, Kumpei*; Konczykowski, M.*; Sakai, Hironori; Opletal, P.; Tokiwa, Yoshifumi; Haga, Yoshinori; Hashimoto, Kenichiro*; Shibauchi, Takasada*
Physical Review Research (Internet), 5(2), p.L022002_1 - L022002_6, 2023/04
Lower superconducting critical fields 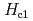 of UTe
of UTe have been determined. Orthorhombic UTe
have been determined. Orthorhombic UTe has magnetic easy axis along the
has magnetic easy axis along the  -axis. We found
-axis. We found 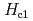 perpendicular to
perpendicular to  showed anomalous enhancement. By comparing with anisotropy of upper critical fields, effect of magnetic fluctuations on superconductivity is suggested.
showed anomalous enhancement. By comparing with anisotropy of upper critical fields, effect of magnetic fluctuations on superconductivity is suggested.
 -edge for Ce in bauxites using transition-edge sensors; Implications for Ti-rich geological samples
-edge for Ce in bauxites using transition-edge sensors; Implications for Ti-rich geological samplesLi, W.*; Yamada, Shinya*; Hashimoto, Tadashi; Okumura, Takuma*; Hayakawa, Ryota*; Nitta, Kiyofumi*; Sekizawa, Oki*; Suga, Hiroki*; Uruga, Tomoya*; Ichinohe, Yuto*; et al.
Analytica Chimica Acta, 1240, p.340755_1 - 340755_9, 2023/02
Times Cited Count:4 Percentile:29.37(Chemistry, Analytical)no abstracts in English
Watanabe, Seiya*; Kawahara, Jun*; Aoki, Takayuki*; Sugihara, Kenta; Takase, Shinsuke*; Moriguchi, Shuji*; Hashimoto, Hirotada*
Engineering Applications of Computational Fluid Mechanics, 17(1), p.2211143_1 - 2211143_23, 2023/00
Times Cited Count:1 Percentile:56.82(Engineering, Multidisciplinary)In tsunami inundations or slope disasters of heavy rain, a lot of floating debris or driftwood logs are included in the flows. The damage to structures from solid body impacts is more severe than the damage from the water pressure. In order to study free-surface flows that include floating debris, developing a high-accurate simulation code of free-surface flows with high performance for large-scale computations is desired. We propose the single-phase free-surface flow model based on the cumulant lattice Boltzmann method coupled with a particle-based rigid body simulation. The discrete element method calculates the contact interaction between solids. An octree-based AMR (Adaptive Mesh Refinement) method is introduced to improve computational accuracy and time-to-solution. High-resolution grids are assigned near the free surfaces and solid boundaries. We conducted two kinds of tsunami flow experiments in the 15 and 70 m water tanks at Hachinohe Institute of Technology and Kobe University to validate the accuracy of the proposed model. The simulation results have shown good agreement with the experiments for the drifting speed, the number of trapped wood pieces, and the stacked angles.
Sato, Tatsuhiko; Iwamoto, Yosuke; Hashimoto, Shintaro; Ogawa, Tatsuhiko; Furuta, Takuya; Abe, Shinichiro; Kai, Takeshi; Matsuya, Yusuke; Matsuda, Norihiro; Hirata, Yuho; et al.
Journal of Nuclear Science and Technology, 9 Pages, 2023/00
Times Cited Count:8 Percentile:99.12(Nuclear Science & Technology)The Particle and Heavy Ion Transport code System (PHITS) is a general-purpose Monte Carlo radiation transport code that can simulate the behavior of most particle species with energies up to 1 TeV (per nucleon for ions). Its new version, PHITS3.31, was recently developed and released to the public. In the new version, the compatibility with high-energy nuclear data libraries and the algorithm of the track-structure modes have been improved. In this paper, we summarize the upgraded features of PHITS3.31 with respect to the physics models, utility functions, and application software introduced since the release of PHITS3.02 in 2017.
Oka, Hiroshi*; Tanno, Takashi; Yano, Yasuhide; Otsuka, Satoshi; Kaito, Takeji; Hashimoto, Naoyuki*
Journal of Nuclear Materials, 572, p.154032_1 - 154032_8, 2022/12
Times Cited Count:3 Percentile:66.21(Materials Science, Multidisciplinary)9Cr oxide dispersion strengthened steels with slightly different nitrogen concentrations (0.0034 - 0.029 wt%) were prepared and their creep property at 973 K was investigated with microstructural characterization before and after the creep test. The creep strength decreased significantly as the nitrogen concentration increased. Microstructural observation revealed that, in the higher nitrogen concentration specimen, coarse Y-rich inclusions were found along the boundary between transformed ferrite region and residual ferrite region. The solubility difference of nitrogen in  and
and  phase would induce the localized increment of nitrogen concentration in the boundary region during the austenitizing process, resulting in the thermodynamic destabilization and subsequent coarsening of the dispersed oxide particles. The rows of creep voids were found near the rupture part of the crept specimen, suggesting that the coarse inclusions were the starting point of creep void formation and the subsequent premature fracture.
phase would induce the localized increment of nitrogen concentration in the boundary region during the austenitizing process, resulting in the thermodynamic destabilization and subsequent coarsening of the dispersed oxide particles. The rows of creep voids were found near the rupture part of the crept specimen, suggesting that the coarse inclusions were the starting point of creep void formation and the subsequent premature fracture.
 photoproduction on the proton at
photoproduction on the proton at 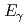 = 1.3-2.4 GeV
= 1.3-2.4 GeVHashimoto, Toshikazu*; Tsuchikawa, Yusuke; LEPS BGOegg Collaboration*; 58 of others*
Physical Review C, 106(3), p.035201_1 - 035201_15, 2022/09
Times Cited Count:3 Percentile:64.25(Physics, Nuclear)Fukaya, Yuji; Okita, Shoichiro; Kanda, Shun*; Goto, Masaki*; Nakajima, Kunihiro*; Sakon, Atsushi*; Sano, Tadafumi*; Hashimoto, Kengo*; Takahashi, Yoshiyuki*; Unesaki, Hironobu*
KURNS Progress Report 2021, P. 101, 2022/07
The Japan Atomic Energy Agency (JAEA) started the Research and Development (R&D) to improve nuclear prediction techniques for High Temperature Gas-cooled Reactors (HTGRs) in 2018. The objectives are to intro-duce the generalized bias factor method to avoid full mock-up experiment for the first commercial HTGR and to improve neutron instrumentation system by virtue of the particular characteristics due to a graphite moderation system. For this end, we composed B7/4"G2/8"p8EU(3)+3/8"p38EU in the B-rack of Kyoto University Critical Assembly (KUCA) in 2021.
Sakon, Atsushi*; Hashimoto, Kengo*; Sano, Tadafumi*; Nakajima, Kunihiro*; Kanda, Shun*; Goto, Masaki*; Fukaya, Yuji; Okita, Shoichiro; Fujimoto, Nozomu*; Takahashi, Yoshiyuki*
KURNS Progress Report 2021, P. 100, 2022/07
The R&D of reactor noise analysis to obtain HTGR nuclear characteristics have been performed with Kyoto University Critical Assembly (KUCA). In the last study, a neutron detector located about 55 cm away of fuel assembly measured the auto power spectral density. However, the prompt neutron decay constants obtained by this detector was different from that of other detectors. The objective of this study is experimental study of reactor noise analysis by the power spectrum method using neutron detector placed outside reactor core.
Furuta, Takuya; Koba, Yusuke*; Hashimoto, Shintaro; Chang, W.*; Yonai, Shunsuke*; Matsumoto, Shinnosuke*; Ishikawa, Akihisa*; Sato, Tatsuhiko
Physics in Medicine & Biology, 67(14), p.145002_1 - 145002_15, 2022/07
Times Cited Count:3 Percentile:44.25(Engineering, Biomedical)Carbon ion radiotherapy has an advantage over conventional radiotherapy such that its superior dose concentration on the tumor helps to reduce unwanted dose to surrounding normal tissues. Nevertheless, a little dose to normal tissues, which is a potential risk of secondary cancer, is still unavoidable. The Monte Carlo simulation is a good candidate for the tool to assess secondary cancer risk, including the contributions of secondary particles produced by nuclear reactions. We therefore developed a new dose reconstruction system implementing PHITS as the engine. In this system, the PHITS input is automatically created from the DICOM data sets recorded in the treatment planning. The developed system was validated by comparing to experimental dose distribution in water and treatment plan on an anthropomorphic phantom. This system will be used for retrospective studies using the patient data in National Institute for Quantum and Science and Technology.
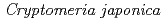 plantation
plantationAbe, Yukiko*; Liang, N.*; Teramoto, Munemasa*; Koarashi, Jun; Atarashi-Andoh, Mariko; Hashimoto, Shoji*; Tange, Takeshi*
Geoderma Regional (Internet), 29, p.e00529_1 - e00529_11, 2022/06
Times Cited Count:1 Percentile:14.82(Soil Science)This study aimed to clarify the causes of spatial variation in soil respiration rate on volcanic ash soil. From January 2013 to August 2019, soil respiration rates were measured at 40 measuring points periodically at a 35-year-old 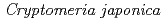 plantation in Tokyo, Japan. In August 2019, the carbon content of the litter layer, total carbon content of soil organic matter (SOM), carbon content of the low-density fraction (LF-C) of SOM, fine root biomass, and bulk density of soil were measured at all measuring points. Results of the multiple regression analysis showed that the model with only the LF-C as an explanatory variable had the highest capability for predicting the respiration rate at a soil temperature of 20
plantation in Tokyo, Japan. In August 2019, the carbon content of the litter layer, total carbon content of soil organic matter (SOM), carbon content of the low-density fraction (LF-C) of SOM, fine root biomass, and bulk density of soil were measured at all measuring points. Results of the multiple regression analysis showed that the model with only the LF-C as an explanatory variable had the highest capability for predicting the respiration rate at a soil temperature of 20 C, indicating that LF-C, which is considered to be readily available to soil microorganisms, can be the main factor responsible for the spatial variation in soil respiration rate.
C, indicating that LF-C, which is considered to be readily available to soil microorganisms, can be the main factor responsible for the spatial variation in soil respiration rate.
Murase, Kiyoka*; Kataoka, Ryuho*; Nishiyama, Takanori*; Nishimura, Koji*; Hashimoto, Taishi*; Tanaka, Yoshimasa*; Kadokura, Akira*; Tomikawa, Yoshihiro*; Tsutsumi, Masaki*; Ogawa, Yasunobu*; et al.
Journal of Space Weather and Space Climate (Internet), 12, p.18_1 - 18_16, 2022/06
Times Cited Count:1 Percentile:20.65(Astronomy & Astrophysics)We identified two energetic electron precipitation (EEP) events during the growth phase of moderate substorms and estimated the mesospheric ionization rate for an EEP event for which the most comprehensive dataset from ground-based and space-born instruments was available. The mesospheric ionization signature reached below 70 km altitude and continued for ~15 min until the substorm onset, as observed by the PANSY radar and imaging riometer at Syowa Station in the Antarctic region. We also used energetic electron flux observed by the Arase and POES 15 satellites as the input for the air-shower simulation code PHITS to quantitatively estimate the mesospheric ionization rate. Combining the cutting-edge observations and simulations, we shed new light on the space weather impact of the EEP events during geomagnetically quiet times, which is important to understand the possible link between the space environment and climate.