Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
 Zn
Zn
Kitazawa, Takafumi; Ikeda, Yoichi*; Sakakibara, Toshiro*; Matsuo, Akira*; Shimizu, Yusei*; Tokunaga, Yo; Haga, Yoshinori; Kindo, Koichi*; Nambu, Yusuke*; Ikeuchi, Kazuhiko*; et al.
Physical Review B, 108(8), p.085105_1 - 085105_7, 2023/08
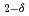 CoGa
CoGa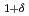 films
filmsKubota, Takahide*; Takano, Daichi*; Kota, Yohei*; Mohanty, S.*; Ito, Keita*; Matsuki, Mitsuhiro*; Hayashida, Masahiro*; Sun, M.*; Takeda, Yukiharu; Saito, Yuji; et al.
Physical Review Materials (Internet), 6(4), p.044405_1 - 044405_12, 2022/04
Times Cited Count:5 Percentile:54.89(Materials Science, Multidisciplinary)Shimizu, Yusei*; Miyake, Atsushi*; Maurya, A.*; Honda, Fuminori*; Nakamura, Ai*; Sato, Yoshiki*; Li, D.*; Homma, Yoshiya*; Yokoyama, Makoto*; Tokunaga, Yo; et al.
Physical Review B, 102(13), p.134411_1 - 134411_11, 2020/10
Times Cited Count:6 Percentile:37.51(Materials Science, Multidisciplinary) Mn
Mn N films with ferrimagnetic compensation
N films with ferrimagnetic compensationIto, Keita*; Yasutomi, Yoko*; Zhu, S.*; Nurmamat, M.*; Tahara, Masaki*; Toko, Kaoru*; Akiyama, Ryota*; Takeda, Yukiharu; Saito, Yuji; Oguchi, Tamio*; et al.
Physical Review B, 101(10), p.104401_1 - 104401_8, 2020/03
Times Cited Count:17 Percentile:73.39(Materials Science, Multidisciplinary)Ieda, Junichi; Barnes, S. E.*; Maekawa, Sadamichi
Journal of the Physical Society of Japan, 87(5), p.053703_1 - 053703_4, 2018/05
Times Cited Count:5 Percentile:41.01(Physics, Multidisciplinary) Sr
Sr CuO
CuO
Matsuda, Masaaki; Fujita, Masaki*; Yamada, Kazuyoshi*; Birgeneau, R. J.*; Endo, Yasuo*; Shirane, Gen*
Physical Review B, 66(17), p.174508_1 - 174508_6, 2002/11
Times Cited Count:11 Percentile:50.63(Materials Science, Multidisciplinary)no abstracts in English

Homma, Tetsuo; Yamamoto, Etsuji; Haga, Yoshinori; Settai, Rikio*; Araki, Shingo*; Inada, Yoshihiko*; Takeuchi, Tetsuya*; Kuwahara, Keitaro*; Amitsuka, Hiroshi*; Sakakibara, T.*; et al.
Physica B; Condensed Matter, 281-282, p.195 - 196, 2000/06
Times Cited Count:2 Percentile:15.63(Physics, Condensed Matter)no abstracts in English
Yamaguchi, Masatake; Kyuno, K.*; Asano, S.*
Nihon Oyo Jiki Gakkai-Shi, 21(7), p.1014 - 1022, 1997/00
no abstracts in English

Yamaguchi, Masatake; *
Journal of Applied Physics, 79(8), p.5952 - 5954, 1996/04
Times Cited Count:16 Percentile:61.97(Physics, Applied)no abstracts in English
Schreiber, J.*; Frait, Z.*; Zeidler, Th.*; Metoki, Naoto; Donner, W.*; Zabel, H.*; Pelzl, J.*
Physical Review B, 51(5), p.2920 - 2929, 1995/02
Times Cited Count:21 Percentile:74.55(Materials Science, Multidisciplinary)no abstracts in English
Ieda, Junichi
no journal, ,
In recent years, attention has been focused on a specific spin state of ferromagnetic ultra-thin film made of a few atomic layers. Elucidation of the underlying mechanism of the perpendicular magnetic anisotropy (PMA) in the ferromagnetic ultra-thin films and its electric field control are crucial for future materials development. Although theoretical explanation has been attempted from various angles, the behavior of the PMA in high electric fields are not yet understood in a unified manner. Is classified into the following three models proposed so far: (Model 1) doping effect to the ferromagnetic ultra-thin film interface: the band filling is changed by doping of ferromagnetic ultra-thin interface leading to the change of the PMA. (Model 2) band splitting effect of ferromagnetic ultra-thin films: In the high electric field, the energy band of ferromagnetic ultra-thin is split leading to the change of the PMA. (Model 3) model Rashba effect in the interface of ferromagnetic ultra-thin films: PMA is expressed by Rashba effect of the interface to compete with exchange splitting of ferromagnetic material, PMA can change through the electric field dependence of the Rashba effect. In this talk, for the third model we have proposed, we will introduce the theory based on the Stoner model of ferromagnetism and the Rashba spin orbit interaction.
Ieda, Junichi
no journal, ,
A mechanism of perpendicular magnetic anisotropy originating from the Rashba effect at surface/interface of metallic films is overviewed. Electric field control of the magnetic anisotropy and an emergent spinmotive force via electric field dependence of the Rashba effect are also discussed.
Ieda, Junichi; Barnes, S. E.*; Maekawa, Sadamichi
no journal, ,
We develop a simple analytic theory for the existence and electrical control of perpendicular magnetic anisotropy (PMA) based on the Rashba spin-orbit interaction and the single band Stoner model of magnetism. We show the competition between the Rashba spin-orbit fields and the exchange interaction, reflecting electron correlations. This theory can potentially lead to a very large magnetic anisotropy arising from the internal electric fields,  , which exist at, e.g., ferromagnetic/metal and ferromagnetic/oxide insulator interfaces but modified by the addition of an applied electric field
, which exist at, e.g., ferromagnetic/metal and ferromagnetic/oxide insulator interfaces but modified by the addition of an applied electric field  . There is a Rashba splitting of the band structure leading to a quadratic,
. There is a Rashba splitting of the band structure leading to a quadratic,  , contribution to the magnetic anisotropy, contrasting with a linear in
, contribution to the magnetic anisotropy, contrasting with a linear in  doping effect.
doping effect.
Ieda, Junichi
no journal, ,
We show that the Rashba effect at a ferromagnet/nonmagnet interface induces the interfacial magnetic anisotropy. While the Rashba effect itself stabilizes the in-plane magnetic configuration parallel to the interface the competition between the Rashba effect and the ferromagnetic exchange interaction leads to the perpendicular magnetic anisotropy. In this talk, we focus on the possible Rashba effect at the interface between a single layer graphene and a ferromagnetic thin layer and the induced perpendicular magnetic anisotropy.
Ieda, Junichi; Maekawa, Sadamichi
no journal, ,
We study magnetic anisotropy in antiferromagnets (AFMs) with the inversion symmetry breaking (ISB). Magnetic anisotropy determines an energy barrier that separates preferable orientations of staggered magnetization in AFMs, and in its sense, understanding and controlling the magnetic anisotropy energy (MAE) in AFMs are fundamentally important for devising magnetic memory bits that should be reliably robust against any external (thermal, magnetic field, and electric current) noises. It has also been pointed out that a large value of MAE in AFMs is advantageous for the exchange bias field that is routinely used to fix magnetization direction at the AFM/FM interface in current magnetic memory technology. In this work, we employ two representative models for the AFMs and obtain the MAE as a consequence of the cooperation of the Rashba spin-orbit (RSO) and exchange interactions. For the global ISB model the MAE shows a transition depending on the magnitude of the RSO coupling: the easy-plane magnetic anisotropy is favored with the small RSO coupling whereas the perpendicular magnetic anisotropy (PMA) is induced with the large RSO coupling. For the local ISB the PMA is generally results in, which contrasts to the corresponding ferromagnetic case in which the condition for the PMA depends on the band structure and dimensionality. These features are particularly important for stabilizing the direction of the order parameter in AMF nanostructures and for electrical-field control of the MAE via the externally modulated RSO coupling.
Ieda, Junichi; Maekawa, Sadamichi
no journal, ,
Recently spintronics phenomenon based on antiferromagnets has drawn much attention. In 2014, we proposed a mechanism that the Rashba spin-orbital interaction produces magnetic anisotropy due to competition with magnetic exchange interaction in a ferromagnetic thin film. This time the theory is extended to antiferromagnet with the Rashba spin-orbital interaction. Conduction electron spin that hops between the nearest neighbor sites on a lattice with antiferromagnetic order in two sublattice is considered. Two kinds of lattice models which feel an on-site exchange interaction and the Rashba interaction of (a) the same sign for the nearest neighbor hopping, or (b) the different sign for the next nearest neighbor hopping are investigated. Former is a model of the Rashba effect occurring at the interface between the antiferromagnetic thin film and another substance and the latter is for the Rashba effect in the antiferromagnet in which the inversion symmetry locally broken, such as CuMnAs. For each model, the angle dependence of the total energy on the antiferromagnetic order-parameter direction is obtained and the expression of the uniaxial magnetic anisotropy constant is derived. In model (a), it is shown that transition from easy plane anisotropy to perpendicular magnetic anisotropy occurs with increasing Rashba interaction. On the other hand, in model (b), it is shown that Rashba interaction always favors the perpendicular magnetic anisotropy as a result of competition with exchange interaction.
Ieda, Junichi
no journal, ,
no abstracts in English
Ieda, Junichi; Yamamoto, Kei
no journal, ,
no abstracts in English
Ieda, Junichi
no journal, ,