Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Kunimaru, Takanori; Morikawa, Keita; Tachi, Yukio; Kuno, Yoshio*; Hosoya, Shinichi*; Shimoda, Satoko*; Kato, Hiroyasu*; Nakazawa, Toshiyuki*; Ikuse, Hiroyuki*; Kubota, Masako*
JAEA-Data/Code 2012-013, 96 Pages, 2012/07
For the purpose to understand the relationship between characteristic of mass transport and characteristic of fracture, the following experiments were carried out using core sample, which was sampled from the -300 m Stage. This paper compiled the results of these experiment. (1) Diffusion experiments of Cs, Sr, I and uranin in granite samples (2) Sorption experiments of Cs and Sr on crushed granite (3) Measurement of pore physicality by Mercury Intrusion and water saturation
Kuno, Yoshio; Sasamoto, Hiroshi
JAEA-Research 2009-071, 65 Pages, 2010/03
To evaluate colloidal effects on radionuclide (RN) migration through a fractured rock, sensitivity analyses were conducted by considering the properties of groundwater colloids. Distribution coefficient for the mobile colloids Kd (m
(m /kg) and colloid concentration M (kg/m
/kg) and colloid concentration M (kg/m ) are important parameters since the product of them (Kd
) are important parameters since the product of them (Kd M) indicates the colloidal effects on RN migration, which is noticeably enhanced in the case of Kd
M) indicates the colloidal effects on RN migration, which is noticeably enhanced in the case of Kd M
M  1. Furthermore, colloid migration was simulated by taking into account colloid filtration by the fracture surfaces. Filtered colloids tend to increase with increasing the filter coefficient
1. Furthermore, colloid migration was simulated by taking into account colloid filtration by the fracture surfaces. Filtered colloids tend to increase with increasing the filter coefficient  (1/m). Breakthrough of RNs shows a peak curve since RNs sorbed on the filtered colloids increase and mobile RNs decrease with time. RN distribution to the filtered colloids could have a sufficient impact on RN migration by reducing mobile concentration in the fracture.
(1/m). Breakthrough of RNs shows a peak curve since RNs sorbed on the filtered colloids increase and mobile RNs decrease with time. RN distribution to the filtered colloids could have a sufficient impact on RN migration by reducing mobile concentration in the fracture.
Kuno, Yoshio; Morooka, Koichi*; Sasamoto, Hiroshi; Yui, Mikazu
Genshiryoku Bakkuendo Kenkyu, 15(2), p.117 - 129, 2009/03
In the performance assessment of the geological disposal of radioactive wastes, the retardation of radionuclide migration is generally evaluated by using sorption distribution coefficient (Kd). The Kd values would, however, be influenced by the presence of colloidal substance in aqueous phase because these colloids may have the potential abilities to sorb the radionuclides. In this study, Cs-137, bentonite colloids and quartz sands were used for the batch-type sorption tests in order to investigate the influence of colloids on the sorption behavior of radionuclides. The Kds of Cs-137 onto quartz sands (Kd ) and bentonite colloids (Kd
) and bentonite colloids (Kd ) were determined from the distributed amounts in solid phase, colloidal phase and aqueous phase, which were distinguished by the pore size of filters used for the separation of experimental solutions. Distribution behavior of radionuclides in the coexistence of quartz sands and bentonite colloids was able to be evaluated from the Kd
) were determined from the distributed amounts in solid phase, colloidal phase and aqueous phase, which were distinguished by the pore size of filters used for the separation of experimental solutions. Distribution behavior of radionuclides in the coexistence of quartz sands and bentonite colloids was able to be evaluated from the Kd and Kd
and Kd those were obtained from other sorption tests carried out in the separate presence of sands and colloids. To select a suitable filtration method for the separation of the colloidal solutions enables to estimate the influence of colloids on the sorption behavior of radionuclides to solid phase.
those were obtained from other sorption tests carried out in the separate presence of sands and colloids. To select a suitable filtration method for the separation of the colloidal solutions enables to estimate the influence of colloids on the sorption behavior of radionuclides to solid phase.
Kuno, Yoshio; Sasamoto, Hiroshi
Materials Research Society Symposium Proceedings, Vol.1124, p.581 - 586, 2009/00
Column experiments were carried out using an artificial fracture within the granite rock in order to investigate the migration behavior of bentonite colloids. A sufficient fraction of colloids was immobilized within the fractured granite in 10 M NaCl solution. In case of comparatively high ionic concentration, retardation of bentonite colloids is expected in the geological medium.
M NaCl solution. In case of comparatively high ionic concentration, retardation of bentonite colloids is expected in the geological medium.
Kuno, Yoshio; Sasamoto, Hiroshi
JAEA-Research 2008-016, 21 Pages, 2008/03
In this study, the influence of chemical difference between in-situ condition and atmospheric condition on inorganic colloids was evaluated by carrying out the characterization of groundwater colloids in the Horonobe area. Remarkable amount of suspended substance including mainly Ca was observed in the groundwater collected from the HDB-10 borehole. Additional laboratory experiments were therefore conducted using this groundwater to investigate the impact on the groundwater composition and the colloidal properties by exposing to the atmosphere. Not only precipitation but also suspended particles composed mainly of CaCO were generated under the atmospheric condition. From the prediction using the DLVO theory, however, the suspended particles are not expected to have a dispersive stability in this groundwater. Formation of suspended particles seems to be a transient behavior caused by the change of chemical conditions and these particles would not exist in in-situ groundwater.
were generated under the atmospheric condition. From the prediction using the DLVO theory, however, the suspended particles are not expected to have a dispersive stability in this groundwater. Formation of suspended particles seems to be a transient behavior caused by the change of chemical conditions and these particles would not exist in in-situ groundwater.
Umeda, Koji; Oi, Takao; Osawa, Hideaki; Oyama, Takuya; Oda, Chie; Kamei, Gento; Kuji, Masayoshi*; Kurosawa, Hideki; Kobayashi, Yasushi; Sasaki, Yasuo; et al.
JAEA-Review 2007-050, 82 Pages, 2007/12
This report shows the annual report which shows the summarized results and topic outline of each project on geological disposal technology in the fiscal year of 2006.
Ueta, Shinzo*; Kuno, Yoshio*
JNC TJ8400 2003-066, 34 Pages, 2004/02
Methods of management of database which was based on understanding of phenomena, reliable, and closely related with performance assessment were studied on parallel with researches for individual model improvement by means of literature survey, column experiment, and analysis code development. For future management of JNC-TDB was discussed with the latest literatures. Collaboration with outer organization was considered necessary especially on authorization of the TDB. One of the outer organizations could be found in geo-thermal research field. For future management of JNC-SDB, sorption ithotherm of Np on bentonite was tested, and the consistency of the data in SDB was found. A semi-quantitative evaluation method of the reliability of the data was developed and tested with the sorption of Pu and Ni on bentonite. The result shows moderateness of the method and some literature data was considered unreliable by the evaluation. From the literature survey of ir/reversibility of nuclide sorption on colloid showed that apparent irreversibility may often be caused by slow kinetics. Additionally, some general recommendation on the system to be studied was discussed. The column experiment of Sr migration facilitated by colloid through porous media was carried out and analysed by COLFRAC-MRL code. The code was developed to simulate the colloid facilitated migration through porous media.
Ueta, Shinzo*; Kuno, Yoshio*
JNC TJ8400 2003-065, 204 Pages, 2004/02
Methods of management of database which was based on understanding of phenomena, reliable, and closely related with performance assessment were studied on parallel with researches for individual model improvement by means of literature survey, column experiment, and analysis code development. For future management of JNC-TDB was discussed with the latest literatures. Collaboration with outer organization was considered necessary especially on authorization of the TDB. One of the outer organizations could be found in geo-thermal research field. For future management of JNC-SDB, sorption ithotherm of Np on bentonite was tested, and the consistency of the data in SDB was found. A semi-quantitative evaluation method of the reliability of the data was developed and tested with the sorption of Pu and Ni on bentonite. The result shows moderateness of the method and some literature data was considered unreliable by the evaluation. From the literature survey of ir/reversibility of nuclide sorption on colloid showed that apparent irreversibility may often be caused by slow kinetics. Additionally, some general recommendation on the system to be studied was discussed. The column experiment of Sr migration facilitated by colloid through porous media was carried out and analysed by COLFRAC-MRL code. The code was developed to simulate the colloid facilitated migration through porous media.
Kurosawa, Susumi; Ueta, Shinzo*; Yui, Mikazu; Kato, Hiroyasu*; Hayashi, Kenichi*; *; Yoshikawa, Hideki
Nihon Genshiryoku Gakkai Wabun Rombunshi, 2(4), p.460 - 468, 2003/12
None
Kurosawa, Susumi; Kuno, Yoshio*; Morooka, Koichi; Ueta, Shinzo*
JNC TN8430 2003-006, 39 Pages, 2003/03
The transport behavior of colloids through the compacted sand-bentonite mixture was investigated by the column experiments. Colloidal gold was used to simulate the mobile colloids because gold colloid was stabilized easily. The sand-bentonite mixtures were prepared by mixing 30wt.% silica sand with the bentonite (Na-type and Ca-type) and were compacted at the dry density of 1.6g/cm . The colloidal particles in the 3.5% NaCl solution migrated through the compacted sand- Na bentonite mixture at 8kgf/cm
. The colloidal particles in the 3.5% NaCl solution migrated through the compacted sand- Na bentonite mixture at 8kgf/cm of injection pressure. However colloidal migration was not observed after injection pressure of the colloidal solution was lowered below the swelling pressure. And the selective flow path of colloids in the compacted sand-bentonite mixture was observed after the experiment. On the other hand, colloids in the pure water were filtered by the compacted sand- Ca bentonite mixture.
of injection pressure. However colloidal migration was not observed after injection pressure of the colloidal solution was lowered below the swelling pressure. And the selective flow path of colloids in the compacted sand-bentonite mixture was observed after the experiment. On the other hand, colloids in the pure water were filtered by the compacted sand- Ca bentonite mixture.
Kuno, Yoshio*; Ueta, Shinzo*
JNC TJ8400 2003-025, 47 Pages, 2003/02
Groundwater colloids may act as carriers for sorbing radionuclides released from a radioactive waste repository. To evaluate the influence of colloids to nuclide transport, it is necessary to obtain the characteristic data of groundwater colloids (e.g. colloid concentration, the distribution coefficient for sorption of nuclides on colloids) in the deep geological media and to prepare the simulation code of nuclide transport with colloids. In this study, the groundwater sample was collected from the gallery of the mine in crystalline rock media to investigate the population of the natural colloids. The concentration, size distribution and chemical compositions of colloids were measured by using filtration method. Colloidal particles consist mainly of silicate minerals and Ca-rich particles. The dissolved organic materials were not detected in the groundwater. The properties of colloids seem to depend on the host rock type and the groundwater chemistry. To simulate the in-situ condition of groundwater, chemical conditions were controlled by varying the partial pressure of CO and the colloid generation in each groundwater was investigated. The numerical model (COLFRAC) is developed in Ohio state university that incorporates the mechanism of colloid-facilitated nuclide transport in fractured porous media. Both equilibrium and kinetic sorption of nuclides onto colloidal materials can be considered in this calculation code. The guidance to learn how to use this code was conducted and the user's manual was prepared.
and the colloid generation in each groundwater was investigated. The numerical model (COLFRAC) is developed in Ohio state university that incorporates the mechanism of colloid-facilitated nuclide transport in fractured porous media. Both equilibrium and kinetic sorption of nuclides onto colloidal materials can be considered in this calculation code. The guidance to learn how to use this code was conducted and the user's manual was prepared.
Kuno, Yoshio*; Ueta, Shinzo*
JNC TJ8400 2003-024, 129 Pages, 2003/02
Groundwater colloids may act as carriers for sorbing radionuclides released from a radioactive waste repository. To evaluate the influence of colloids to nuclide transport, it is necessary to obtain the characteristic data of groundwater colloids (e.g. colloid concentration, the distribution coefficient for sorption of nuclides on colloids) in the deep geological media and to prepare the simulation code of nuclide transport with colloids. In this study, the groundwater sample was collected from the gallery of the mine in crystalline rock media to investigate the population of the natural colloids. The concentration, size distribution and chemical compositions of colloids were measured by using filtration method. Colloidal particles consist mainly of silicate minerals and Ca-rich particles. The dissolved organic materials were not detected in the groundwater. The properties of colloids seem to depend on the host rock type and the groundwater chemistry. To simulate the in-situ condition of groundwater, chemical conditions were controlled by varying the partial pressure of CO and the colloid generation in each groundwater was investigated. The numerical model (COLFRAC) is developed in Ohio state university that incorporates the mechanism of colloid-facilitated nuclide transport in fractured porous media. Both equilibrium and kinetic sorption of nuclides onto colloidal materials can be considered in this calculation code. The guidance to learn how to use this code was conducted and the user's manual was prepared.
and the colloid generation in each groundwater was investigated. The numerical model (COLFRAC) is developed in Ohio state university that incorporates the mechanism of colloid-facilitated nuclide transport in fractured porous media. Both equilibrium and kinetic sorption of nuclides onto colloidal materials can be considered in this calculation code. The guidance to learn how to use this code was conducted and the user's manual was prepared.
; ; Nagasaki, Shinya*
Genshiryoku Bakkuendo Kenkyu, 8(2), p.195 - 203, 2002/03
None
Kuno, Yoshio; Chinju, Hirofumi; Kamei, Gento; Nagasaki, Shinya*; Tanaka, Satoru*
JNC TY8400 2001-007, 62 Pages, 2002/02
None
; Kamei, Gento
2001 MRS Fall Meeting, 0 Pages, 2002/00
None
Kuno, Yoshio; Kamei, Gento; Otani, Hiroyuki*
Materials Research Society Symposium Proceedings, Vol.713, 0 Pages, 2002/00
None
; ; Shibata, Masahiro; Yoshida, Yasushi*; Yui, Mikazu
JNC TN7420 2000-003, 25 Pages, 2000/07
None
Shibutani, Tomoki; Kohara, Yukitoshi*; Oda, Chie; Kubota, Mitsuru*; ; Shibata, Masahiro
JNC TN8400 99-066, 75 Pages, 1999/11
The physico-chemical characteristics of purified Na-smectite and protonation/deprotonation behavior of smectite surface in different concentrations of NaCl solutions were studied to identify the reaction mechanism of smectite-water interaction for performance assessment of HLW geological disposal system. The Na-smectite was purified from Kunipia F (obtained from Kunimine Industries Co. Ltd. Japan). In this smectite, small amount of quartz was detected as an impurity by X-ray diffraction. As a result of XRD and chemical analysis of the smectite, it was found that exchangeable sites in smectite inter-layer were occupied by Na+. Cation exchange capacity (CEC) was measured as 1.108meq g by using ammonium acetate. The N
by using ammonium acetate. The N -BET surface area of smectite was 50
-BET surface area of smectite was 50 58m
58m g
g . Protonation/deprotonation behavior of smectite was studied for 0.01, 0.1 and 0.5M NaCl by using titration and back titration method. Total amount of H
. Protonation/deprotonation behavior of smectite was studied for 0.01, 0.1 and 0.5M NaCl by using titration and back titration method. Total amount of H consumption increased with decreasing pH for all NaCl concentrations, and the titration curves in these solutions showed similar trend in the pH range of 6-11. On the other hand, total amount of H
consumption increased with decreasing pH for all NaCl concentrations, and the titration curves in these solutions showed similar trend in the pH range of 6-11. On the other hand, total amount of H consumption increased with decreasing NaCl concentration in the pH range of 2-6. The dominant sorption mechanism of H
consumption increased with decreasing NaCl concentration in the pH range of 2-6. The dominant sorption mechanism of H on smectite was different between pH
on smectite was different between pH 6 and pH
6 and pH 6, and it can be considered that H
6, and it can be considered that H was sorbed on the same site as Na
was sorbed on the same site as Na for pH
for pH 6 and different site from Na
6 and different site from Na for pH
for pH 6. The prediction of protonation/deprotonation behavior of smectite for 0.01, 0.1 and 0.5M NaCl was carried out based on ion exchange and surface complexation models. The sorption sites were assumed as inter-layer and crystal edge site. The site concentrations for ion exchange and surface complexation were calculated from CEC. The reaction constants were consequently calculated by fitting of experimental results as follows. ...
6. The prediction of protonation/deprotonation behavior of smectite for 0.01, 0.1 and 0.5M NaCl was carried out based on ion exchange and surface complexation models. The sorption sites were assumed as inter-layer and crystal edge site. The site concentrations for ion exchange and surface complexation were calculated from CEC. The reaction constants were consequently calculated by fitting of experimental results as follows. ...
; Yui, Mikazu; *
JNC TN8400 99-080, 19 Pages, 1999/07
Filtration behavior of organic substance through a compacted bentonite was investigated. Na-type bentonite containing 30wt% of quartz sand was compacted in a column and the dry density was adjusted to be 1.6 g/cm . Polyacrylic acid solution (including three types of polyacrynclic acid, average molecular weight 2,100, 15,000 and 450,000) was prepared and was passed through the compacted bentonite. Molecular weight distributions of polyacrylic acid in the effluent solution were analysed by GPC (Gel Permeation Chromatography). A batch type experiment was also carried out in order to examine a sorption behavior of these organic substances onto the surfaces of grains of the bentonite. The results indicated that the smaller size polyacrylic acid (molecular weight
. Polyacrylic acid solution (including three types of polyacrynclic acid, average molecular weight 2,100, 15,000 and 450,000) was prepared and was passed through the compacted bentonite. Molecular weight distributions of polyacrylic acid in the effluent solution were analysed by GPC (Gel Permeation Chromatography). A batch type experiment was also carried out in order to examine a sorption behavior of these organic substances onto the surfaces of grains of the bentonite. The results indicated that the smaller size polyacrylic acid (molecular weight  100,000) was passed through the compacted bentonite. On the other hand, the larger size polyacrylic acid (molecular weight
100,000) was passed through the compacted bentonite. On the other hand, the larger size polyacrylic acid (molecular weight 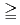 100,000) was mostly filtrated by the compacted bentonite. The batch type sorption tests clarified that the polyacrylic acid did not sorb onto the surfaces of minerals constituting the bentonite. Therefore it was suggested that the larger size molecules (
100,000) was mostly filtrated by the compacted bentonite. The batch type sorption tests clarified that the polyacrylic acid did not sorb onto the surfaces of minerals constituting the bentonite. Therefore it was suggested that the larger size molecules (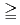 100,000) of organic substances could be predominantly filtrated by the microstructure of the compacted bentonite.
100,000) of organic substances could be predominantly filtrated by the microstructure of the compacted bentonite.