Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Saito, Takumi*; Nishi, Shusaku*; Amano, Yuki; Beppu, Hikari*; Miyakawa, Kazuya
ACS ES&T Water (Internet), 3(12), p.4103 - 4112, 2023/12
Esser, S. P.*; Rahlff, J.*; Zhao, W.*; Predl, M.*; Plewka, J.*; Sures, K.*; Wimmer, F.*; Lee, J.*; Adam, P. S.*; McGonigle, J.*; et al.
Nature Microbiology (Internet), 8(9), p.1619 - 1633, 2023/09
Times Cited Count:2 Percentile:75.4(Microbiology)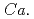 Methanoperedenaceae
MethanoperedenaceaeNishimura, Hiroki*; Kozuka, Mariko*; Fukuda, Akari*; Ishimura, Toyoho*; Amano, Yuki; Beppu, Hikari*; Miyakawa, Kazuya; Suzuki, Yohei*
Environmental Microbiology Reports (Internet), 15(3), p.197 - 205, 2023/06
Times Cited Count:1 Percentile:53.1(Environmental Sciences)The family 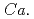 Methanoperedenaceae archaea mediate anaerobic oxidation of methane (AOM). We newly developed a high-pressure laboratory incubation system and investigated groundwater from 214- and 249-m deep boreholes at Horonobe Underground Research Laboratory, Japan, where the high and low abundances of
Methanoperedenaceae archaea mediate anaerobic oxidation of methane (AOM). We newly developed a high-pressure laboratory incubation system and investigated groundwater from 214- and 249-m deep boreholes at Horonobe Underground Research Laboratory, Japan, where the high and low abundances of 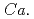 Methanoperedenaceae archaea have been revealed, respectively. We incubated the samples amended with or without amorphous Fe(III) and
Methanoperedenaceae archaea have been revealed, respectively. We incubated the samples amended with or without amorphous Fe(III) and  C-labelled methane at an in-situ pressure of 1.6 MPa. After three to seven-day incubation, AOM activities were not detected from the 249-m sample but from the 214-m sample. The AOM rates were 93.7
C-labelled methane at an in-situ pressure of 1.6 MPa. After three to seven-day incubation, AOM activities were not detected from the 249-m sample but from the 214-m sample. The AOM rates were 93.7 40.6 and 27.7
40.6 and 27.7 37.5 nM/day with and without Fe(III) amendment. Suspended particulates were not visible in the 249-m sample on the filter, while they were abundant and contained amorphous Fe(III) and Fe(III)-bearing phyllosilicates in the 214-m sample. This supports the in-situ activity of Fe(III)-dependent AOM in the deep subsurface borehole.
37.5 nM/day with and without Fe(III) amendment. Suspended particulates were not visible in the 249-m sample on the filter, while they were abundant and contained amorphous Fe(III) and Fe(III)-bearing phyllosilicates in the 214-m sample. This supports the in-situ activity of Fe(III)-dependent AOM in the deep subsurface borehole.
Terashima, Motoki; Endo, Takashi*; Kimuro, Shingo; Beppu, Hikari*; Nemoto, Kazuaki*; Amano, Yuki
Journal of Nuclear Science and Technology, 60(4), p.374 - 384, 2023/04
Times Cited Count:2 Percentile:50.96(Nuclear Science & Technology) archaea
archaeaSchoelmerich, M. C.*; Oubouter, H. T.*; Sachdeva, R.*; Penev, P. I.*; Amano, Yuki; West-Roberts, J.*; Welte, C. U.*; Banfield, J. F.*
Nature Communications (Internet), 13, p.7085_1 - 7085_11, 2022/11
Times Cited Count:6 Percentile:70.43(Multidisciplinary Sciences)Bateman, K.*; Murayama, Shota*; Hanamachi, Yuji*; Wilson, J.*; Seta, Takamasa*; Amano, Yuki; Kubota, Mitsuru*; Ouchi, Yuji*; Tachi, Yukio
Minerals (Internet), 12(7), p.883_1 - 883_20, 2022/07
Times Cited Count:1 Percentile:0.02(Geochemistry & Geophysics)Bateman, K.; Murayama, Shota*; Hanamachi, Yuji*; Wilson, J.*; Seta, Takamasa*; Amano, Yuki; Kubota, Mitsuru*; Ouchi, Yuji*; Tachi, Yukio
Minerals (Internet), 11(9), p.1026_1 - 1026_23, 2021/09
Times Cited Count:2 Percentile:22.02(Geochemistry & Geophysics)Jaffe, A. L.*; Thomas, A. D.*; He, C.*; Keren, R.*; Valentin-Alvarado, L. E.*; Munk, P.*; Bouma-Gregson, K.*; Farag, I. F.*; Amano, Yuki; Sachdeva, R.*; et al.
mBio, 12(4), p.e00521-21_1 - e00521-21_21, 2021/08
Times Cited Count:22 Percentile:90.08(Microbiology)Bateman, K.; Amano, Yuki; Kubota, Mitsuru*; Ouchi, Yuji*; Tachi, Yukio
Minerals (Internet), 11(6), p.588_1 - 588_19, 2021/06
Times Cited Count:4 Percentile:43.25(Geochemistry & Geophysics)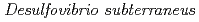 sp. nov., a mesophilic sulfate-reducing deltaproteobacterium isolated from a deep siliceous mudstone formation
sp. nov., a mesophilic sulfate-reducing deltaproteobacterium isolated from a deep siliceous mudstone formationUeno, Akio*; Tamazawa, Satoshi*; Tamamura, Shuji*; Murakami, Takuma*; Kiyama, Tamotsu*; Inomata, Hidenori*; Amano, Yuki; Miyakawa, Kazuya; Tamaki, Hideyuki*; Naganuma, Takeshi*; et al.
International Journal of Systematic and Evolutionary Microbiology, 71(2), p.004683_1 - 004683_10, 2021/02
Times Cited Count:8 Percentile:60.22(Microbiology)A novel mesophilic sulfate-reducing bacterium, designated strain HN2 , was isolated from groundwater sampled from the subsurface Miocene Wakkanai Formation located in Horonobe, Hokkaido, Japan. The cells were Gram-negative rods, with motility conferred by a single polar flagellum. The isolate expressed desulfoviridin, but no catalase or oxidase activities was detected. Strain HN2
, was isolated from groundwater sampled from the subsurface Miocene Wakkanai Formation located in Horonobe, Hokkaido, Japan. The cells were Gram-negative rods, with motility conferred by a single polar flagellum. The isolate expressed desulfoviridin, but no catalase or oxidase activities was detected. Strain HN2 grew in a temperature range of 5-43
grew in a temperature range of 5-43  C (optimum, 35
C (optimum, 35  C) and in a pH range of 6.5-7.5 (optimum, pH 7.0-7.3). It used sulfate, thiosulfate, dimethyl sulfoxide, anthraquinone-2,6-disulfonate, Fe
C) and in a pH range of 6.5-7.5 (optimum, pH 7.0-7.3). It used sulfate, thiosulfate, dimethyl sulfoxide, anthraquinone-2,6-disulfonate, Fe , and manganese oxide as electron acceptors, but not elemental sulfur, nitrite, or nitrate. The bacterium showed very weak growth with sulfite as the electron acceptor. The strain fermented pyruvate and cysteine in the absence of sulfate, but not malate or succinate. The bacterium did not require NaCl, but tolerated up to 4% NaCl (w/v). Strain HN2
, and manganese oxide as electron acceptors, but not elemental sulfur, nitrite, or nitrate. The bacterium showed very weak growth with sulfite as the electron acceptor. The strain fermented pyruvate and cysteine in the absence of sulfate, but not malate or succinate. The bacterium did not require NaCl, but tolerated up to 4% NaCl (w/v). Strain HN2 did not require vitamins. The G+C content of the genomic DNA was 56.66 mol%. A 16S rRNA gene sequence analysis showed that the closest recognized relative of strain HN2
did not require vitamins. The G+C content of the genomic DNA was 56.66 mol%. A 16S rRNA gene sequence analysis showed that the closest recognized relative of strain HN2 is
is 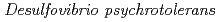 JS1
JS1 (97.0% similarity). The average nucleotide identity (ANI) value between strain HN2
(97.0% similarity). The average nucleotide identity (ANI) value between strain HN2 and D.
and D. 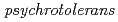 JS1
JS1 was 79.8%. Based on the phenotypic and molecular genetic evidence, the isolate is assigned to the new species
was 79.8%. Based on the phenotypic and molecular genetic evidence, the isolate is assigned to the new species 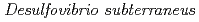 sp. nov. The type strain is HN2
sp. nov. The type strain is HN2 (=DSM 101010
(=DSM 101010 =NBRC 112213
=NBRC 112213 ).
).
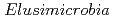 are metabolically diverse compared to gut microbiome
are metabolically diverse compared to gut microbiome 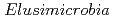 and some have a novel nitrogenase paralog
and some have a novel nitrogenase paralogM heust, R.*; Castelle, C. J.*; Matheus Carnevali, P. B.*; Farag, I. F.*; He, C.*; Chen, L.-X.*; Amano, Yuki; Hug, L. A.*; Banfield, J. F.*
heust, R.*; Castelle, C. J.*; Matheus Carnevali, P. B.*; Farag, I. F.*; He, C.*; Chen, L.-X.*; Amano, Yuki; Hug, L. A.*; Banfield, J. F.*
ISME Journal, 14(12), p.2907 - 2922, 2020/12
Times Cited Count:40 Percentile:94.4(Ecology)Fukuda, Kenji; Watanabe, Yusuke; Murakami, Hiroaki; Amano, Yuki; Aosai, Daisuke*; Hara, Naohiro*
JAEA-Data/Code 2020-012, 80 Pages, 2020/10
Japan Atomic Energy Agency has been investigating groundwater chemistry to understand the influence of excavation and maintenance of underground facilities as part of the Mizunami Underground Research Laboratory (MIU) Project in Mizunami, Gifu, Japan. In this report, we compiled data of groundwater chemistry and microbiology obtained at the MIU in the fiscal year 2019. In terms of ensuring traceability of data, basic information (e.g. sampling location, sampling time, sampling method and analytical method) and methodology for quality control are described.
Fukuda, Kenji; Watanabe, Yusuke; Murakami, Hiroaki; Amano, Yuki; Aosai, Daisuke*; Kumamoto, Yoshiharu*; Iwatsuki, Teruki
JAEA-Data/Code 2019-019, 74 Pages, 2020/03
Japan Atomic Energy Agency has been investigating groundwater chemistry to understand the influence of excavation and maintenance of underground facilities as part of the Mizunami Underground Research Laboratory (MIU) Project in Mizunami, Gifu, Japan. In this report, we compiled data of groundwater chemistry and microbiology obtained at the MIU in the fiscal year 2018. In terms of ensuring traceability of data, basic information (e.g. sampling location, sampling time, sampling method and analytical method) and methodology for quality control are described.
Al-Shayeb, B.*; Sachdeva, R.*; Chen, L.-X.*; Ward, F.*; Munk, P.*; Devoto, A.*; Castelle, C. J.*; Olm, M. R.*; Bouma-Gregson, K.*; Amano, Yuki; et al.
Nature, 578(7795), p.425 - 431, 2020/02
Times Cited Count:223 Percentile:99.47(Multidisciplinary Sciences)Saito, Yoshimoto*; Hirano, Shinichi*; Nagaoka, Toru*; Amano, Yuki
Ecological Genetics and Genomics, 12, p.100042_1 - 100042_9, 2019/10
Culture-independent molecular techniques enable us to analyze microflora in various environments. Many uncultured prokaryotes have been detected by the molecular methods from extreme environments, including anaerobic, no light, high-pressure, and high temperature. Recently, microbial eukaryotes were also detected in deep-sea environments, suggesting that microbial eukaryotes can adapt to a wider range of environments than previously thought. Here, we performed a culture-independent analysis of eukaryotes from approximately -250 m depth in the Horonobe Underground Research Laboratory at Horonobe, Japan. Our results indicate that fungi are the dominant eukaryotic flora in deep sedimentary rocks of Horonobe. We detected a wide range of species, including Zygomycete, Basidiomycete, and Ascomycete fungi from the rocks. This study is the first report of eukaryotic diversity in deep subsurface sedimentary rocks.
Fukuda, Kenji; Watanabe, Yusuke; Murakami, Hiroaki; Amano, Yuki; Hayashida, Kazuki*; Aosai, Daisuke*; Kumamoto, Yoshiharu*; Iwatsuki, Teruki
JAEA-Data/Code 2018-021, 76 Pages, 2019/03
Japan Atomic Energy Agency has been investigating groundwater chemistry to understand the influence of excavation and maintenance of underground facilities as part of the Mizunami Underground Research Laboratory (MIU) Project in Mizunami, Gifu, Japan. In this report, we compiled data of groundwater chemistry and microbiology obtained at the MIU in the fiscal year 2017. In terms of ensuring traceability of data, basic information (e.g. sampling location, sampling time, sampling method and analytical method) and methodology for quality control are described.
Matheus Carnevali, P. B.*; Schulz, F.*; Castelle, C. J.*; Kantor, R. S.*; Shih, P.*; Sharon, I.*; Santini, J.*; Olm, M. R.*; Amano, Yuki; Thomas, B. C.*; et al.
Nature Communications (Internet), 10, p.463_1 - 463_15, 2019/01
Times Cited Count:35 Percentile:86.27(Multidisciplinary Sciences)Kimuro, Shingo*; Kirishima, Akira*; Nagao, Seiya*; Saito, Takumi*; Amano, Yuki; Miyakawa, Kazuya; Akiyama, Daisuke*; Sato, Nobuaki*
Journal of Nuclear Science and Technology, 55(5), p.503 - 515, 2018/05
Times Cited Count:7 Percentile:57.59(Nuclear Science & Technology)no abstracts in English
Hayashida, Kazuki; Kato, Toshihiro*; Kubota, Mitsuru*; Murakami, Hiroaki; Amano, Yuki; Iwatsuki, Teruki
Chikyu Kagaku, 52(1), p.55 - 71, 2018/03
In this study, the simulated experimental drift was constructed in the granite of 500 m depth at Mizunami Underground Research Laboratory, and the hydrochemical process after the drift closure was observed. The groundwater chemistry around the drift changed with the change of the groundwater flow in the fractures when the gallery was constructed. The redox potential increased due to the infiltration of oxygen from the drift into the rock. After closing the drift, the redox potential of the groundwater plunged due to microbial activity, while the groundwater became alkalized conditon due to the influence of cement material such as shotcrete. The amount of cement material consumed for this alkalization was small, and it was considered that its influence would last long in accordance with the amount of cement used.
Ino, Kohei*; Hernsdorf, A. W.*; Konno, Yuta*; Kozuka, Mariko*; Yanagawa, Katsunori*; Kato, Shingo*; Sunamura, Michinari*; Hirota, Akinari*; Togo, Yoko*; Ito, Kazumasa*; et al.
ISME Journal, 12(1), p.31 - 47, 2018/01
Times Cited Count:49 Percentile:91.37(Ecology)In this study, we found the dominance ofanaerobic methane-oxidizing archaea in groundwater enriched in sulfate and methane from a 300-m deep underground borehole in granitic rock.