Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Tamura, Koji; Nakanishi, Ryuzo; Oba, Hironori; Karino, Takahiro; Shibata, Takuya; Taira, Takunori*; Wakaida, Ikuo
Journal of Nuclear Science and Technology, 8 Pages, 2024/00
Times Cited Count:0 Percentile:0.01(Nuclear Science & Technology)
 atoms (J-PARC E03, E07 and future)
atoms (J-PARC E03, E07 and future)Yamamoto, Takeshi; Fujita, Manami; Gogami, Toshiyuki*; Harada, Takeshi*; Hayakawa, Shuhei*; Hosomi, Kenji; Ichikawa, Yudai; Ishikawa, Yuji*; Kamata, K.*; Kanauchi, H.*; et al.
EPJ Web of Conferences, 271, p.03001_1 - 03001_5, 2022/11
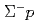 elastic scattering in momentum range 470 to 850 MeV/
elastic scattering in momentum range 470 to 850 MeV/
Miwa, Koji*; Fujita, Manami; Hasegawa, Shoichi; Hosomi, Kenji; Ichikawa, Yudai; Imai, Kenichi*; Nanamura, Takuya; Naruki, Megumi; Sako, Hiroyuki; Sato, Susumu; et al.
Physical Review C, 104(4), p.045204_1 - 045204_20, 2021/10
Times Cited Count:13 Percentile:88.31(Physics, Nuclear)Tamura, Koji; Oba, Hironori; Saeki, Morihisa; Taguchi, Tomitsugu*; Lim, H. H.*; Taira, Takunori*; Wakaida, Ikuo
Journal of Nuclear Science and Technology, 58(4), p.405 - 415, 2021/04
Times Cited Count:12 Percentile:83.57(Nuclear Science & Technology)Radiation dose rate effects on the properties of a compact fiber-optic laser-induced breakdown spectroscopy (LIBS) system with a monolithic Nd:YAG/Cr:YAG composite ceramics were investigated for remote analysis in hazardous environment. To investigate radiation effects on the LIBS signal, properties related to the Nd:YAG laser operation such as oscillation threshold, output energy, oscillation timing, temporal pulse shape, and beam profile were measured as a function of the radiation dose rate from 0 to 10 kGy/hr in view of their influences to the signal. LIBS spectra of zirconium metal were measured under irradiation. Although signal intensity decreased considerably by irradiation, informative spectra were well obtained even at the maximum radiation dose rate. From the comparison of the LIBS-related parameters among the laser properties, signal reduction was mainly ascribed to the pulse energy reduction. Scintillation emission spectra were also measured from the ceramics during the irradiation, where the signal intensity increased linearly with the dose rate. The results show that the developed system.
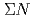 interaction from the
interaction from the 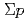 scattering experiment at J-PARC
scattering experiment at J-PARCMiwa, Koji*; Fujita, Manami; Hasegawa, Shoichi; Hosomi, Kenji; Ichikawa, Masaya; Ichikawa, Yudai; Imai, Kenichi*; Nanamura, Takuya; Naruki, Megumi; Sako, Hiroyuki; et al.
Journal of Physics; Conference Series, 1643, p.012174_1 - 012174_6, 2020/12
Times Cited Count:2 Percentile:84.36(Astronomy & Astrophysics)Tamura, Koji*; Toyama, Shinichi
Nihon Genshiryoku Gakkai-Shi ATOMO , 62(5), p.268 - 271, 2020/05
, 62(5), p.268 - 271, 2020/05
The laser cutting technology is expected to be a promising candidate for the decommissioning measure of nuclear facilities, because it has a lot of advantage such as its high controllability and excellent suitability to remote handling by robot arm, etcetera. This report describes the recent result from laser cutting technology development for thick steel materials summarizing the cutting demonstration of 300 mm thick steels and dummy pressure vessel, the analysis of cutting condition of thick steel cutting, the observation of cutting process, remote controlled cutting system, the cutting in pile of steels by the system, and countermeasure for fume produce by cutting process.
Tamura, Koji*; Toyama, Shinichi
Nihon Genshiryoku Gakkai-Shi ATOMO , 61(5), p.413 - 415, 2019/05
, 61(5), p.413 - 415, 2019/05
In decommissioning of nuclear reactors, it is necessary to disassemble the nuclear reactor structure. In addition to the conventional cutting method, the laser method has many advantages such as remote controllability and no need for replacement parts such as blades, which can be a powerful choice. Nuclear reactor structure such as a pressure vessel are made of steel materials with a thickness exceeding 100 mm, and the laser method has poor knowledge and experience in cutting such thick steel materials. Therefore, as a result of trial cutting of steel materials under various cutting conditions with the high power fiber laser which is progressively available nowadays, it has been demonstrated that laser cutting is also possible for thick plates such as those used in nuclear reactors, and cutting of thick steel plates. We also developed the cutting technology using remote control using a robot in order to apply it to the decommissioning of thick steel cutting on the spot.
Wakaida, Ikuo; Oba, Hironori; Miyabe, Masabumi; Akaoka, Katsuaki; Oba, Masaki; Tamura, Koji; Saeki, Morihisa
Kogaku, 48(1), p.13 - 20, 2019/01
By Laser Induced Breakdown Spectroscopy and by related resonance spectroscopy, elemental and isotope analysis of Uranium and Plutonium for nuclear fuel materials and in-situ remote analysis under strong radiation condition for melt downed nuclear fuel debris at damaged core in "Fukushima Daiichi Nuclear Power Station", are introduced and performed as one of the application in atomic energy research field.
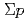 scattering experiment using high intensity pion beams at J-PARC
scattering experiment using high intensity pion beams at J-PARCMiwa, Koji*; Hasegawa, Shoichi; Hayakawa, Shuhei; Hosomi, Kenji; Imai, Kenichi; Kondo, Yasuhiro; Naruki, Megumi; Sako, Hiroyuki; Sato, Susumu; Sugimura, Hitoshi; et al.
JPS Conference Proceedings (Internet), 17, p.041002_1 - 041002_6, 2017/07
Niwa, Masakazu; Shimada, Koji; Tamura, Hajimu*; Shibata, Kenji*; Sueoka, Shigeru; Yasue, Kenichi; Ishimaru, Tsuneari; Umeda, Koji*
Clays and Clay Minerals, 64(2), p.86 - 107, 2016/04
Times Cited Count:11 Percentile:34.14(Chemistry, Physical)no abstracts in English
Umeda, Koji; Yasue, Kenichi; Kokubu, Yoko; Niwa, Masakazu; Asamori, Koichi; Fujita, Natsuko; Shimizu, Mayuko; Matsubara, Akihiro; Tamura, Hajimu; Yokoyama, Tatsunori; et al.
JAEA-Review 2015-019, 42 Pages, 2015/09
This report is a plan of research and development (R&D) on geosphere stability for long-term isolation of high-level radioactive waste (HLW) in JAEA, in fiscal year 2015. The objectives and contents in fiscal year 2015 are described in detail based on the outline of 7 years plan (fiscal years 2015-2021). Background of this research is clarified with the necessity and the significance for site investigation and safety assessment, and the past progress in this report. In addition, the plan framework is structured into the following categories: (1) Development and systematization of investigation techniques, (2) Development of models for long-term estimation and effective assessment, (3) Development of dating techniques.
Umeda, Koji; Yasue, Kenichi; Kokubu, Yoko; Niwa, Masakazu; Asamori, Koichi; Fujita, Natsuko; Shimizu, Mayuko; Shimada, Akiomi; Matsubara, Akihiro; Tamura, Hajimu; et al.
JAEA-Review 2015-012, 43 Pages, 2015/08
The concept of geological disposal of high-level radioactive waste (HLW) in Japan is based on a multibarrier system which combines a stable geological environment with an engineered barrier system. Potential geological host formations and their surroundings are chosen, in particular, for their long-term stability, taking into account the fact that Japan is located in tectonically active zone. This report is to outline 7 years plan (fiscal years 2015-2021) of research and development (R&D) for geosphere stability for long-term isolation of the HLW in JAEA. Background of this research is clarified with the necessity and the significance, and the past progress in this report. The objectives, outline, contents and schedule during the next 7 years are described in detail. In addition, the plan framework is structured into the following categories: (1) Development and Systematization of investigation techniques, (2) Development of models for long-term estimation and effective assessment, (3) Development of dating techniques.
 C level structure by
C level structure by  -ray spectroscopy
-ray spectroscopyHosomi, Kenji; Ma, Y.*; Ajimura, Shuhei*; Aoki, Kanae*; Dairaku, Seishi*; Fu, Y.*; Fujioka, Hiroyuki*; Futatsukawa, Kenta*; Imoto, Wataru*; Kakiguchi, Yutaka*; et al.
Progress of Theoretical and Experimental Physics (Internet), 2015(8), p.081D01_1 - 081D01_8, 2015/08
Times Cited Count:14 Percentile:66.39(Physics, Multidisciplinary)Level structure of the  C hypernucleus was precisely determined by means of
C hypernucleus was precisely determined by means of  -ray spectroscopy. We identified four
-ray spectroscopy. We identified four  -ray transitions via the
-ray transitions via the  C
C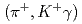 reaction using a germanium detector array, Hyperball2. The spacing of the ground-state doublet
reaction using a germanium detector array, Hyperball2. The spacing of the ground-state doublet 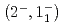 was measured to be
was measured to be 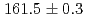 (stat)
(stat)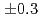 (syst)keV from the direct
(syst)keV from the direct  transition. Excitation energies of the
transition. Excitation energies of the 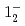 and
and 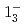 states were measured to be
states were measured to be 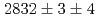 , keV and
, keV and 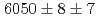 , keV, respectively. The obtained level energies provide definitive references for the reaction spectroscopy of
, keV, respectively. The obtained level energies provide definitive references for the reaction spectroscopy of  hypernuclei.
hypernuclei.
Tamura, Koji; Ozawa, Masaki*
Journal of Nuclear Science and Technology, 52(6), p.872 - 877, 2015/06
Times Cited Count:2 Percentile:17.52(Nuclear Science & Technology)We studied laser isotope separation of cesium (Cs) on the basis of a laser photochemical reaction and two-photon excitation scheme using a narrow line width Ti:sapphire laser to reduce long-term radioactive toxicity of a long-lived fission product. Using resonant laser irradiation to Cs atoms in hydrogen gas, we observed cesium hydride fine particles, and confirmed the formation by calculations using rate equations. Our results show that the process seems promising for efficient Cs isotope separation.
Yasue, Kenichi; Asamori, Koichi; Niwa, Masakazu; Kokubu, Yoko; Kobori, Kazuo; Makuuchi, Ayumu; Matsubara, Akihiro; Shibata, Kenji; Tamura, Hajimu; Tanabe, Hiroaki; et al.
JAEA-Review 2014-033, 43 Pages, 2014/09
The concept of geological disposal of HLW in Japan is based on a multi-barrier system which combines a stable geological environment with a robust barrier system. Potential geological host formations and their surroundings are chosen, in particular, for their long-term stability, taking into account the fact that Japan is located in a tectonically active zone. This report is a plan of research and development (R&D) on geosphere stability for long-term isolation of HLW in JAEA, in fiscal year 2014. The objectives and contents in fiscal year 2014 are described in detail based on the outline of 5 years plan (fiscal years 2010-2014). In addition, the planned framework is structured into the following categories: (1) Development and systematization of investigation techniques, (2) Development of models for long-term estimation and effective assessment, (3) Development of dating techniques.
Yasue, Kenichi; Asamori, Koichi; Niwa, Masakazu; Hanamuro, Takahiro; Kokubu, Yoko; Sueoka, Shigeru; Makuuchi, Ayumu; Ikuta, Masafumi; Matsubara, Akihiro; Tamura, Hajimu; et al.
JAEA-Research 2013-047, 109 Pages, 2014/03
This annual report documents the progress of R&D in the 3rd fiscal year during the JAEA 2nd Midterm Plan (FY 2010 - 2014) to provide the scientific base for assessing geosphere stability for long-term isolation of the high-level radioactive waste. The planned framework is structured into the following categories: (1) development and systematization of investigation techniques for selecting suitable sites in geosphere stability, (2) development, application and verification of prediction models for evaluating the changes of geological environment in thermal, hydraulic, mechanical and geochemical conditions for a long period of time, and (3) development of new dating techniques for providing information about geologic history and the timing of geologic events. In this paper, the current status of R&D activities with previous scientific and technological progress is summarized.
Takemoto, Noriyuki; Sugaya, Naoto; Otsuka, Kaoru; Hanakawa, Hiroki; Onuma, Yuichi; Hosokawa, Jinsaku; Hori, Naohiko; Kaminaga, Masanori; Tamura, Kazuo*; Hotta, Koji*; et al.
JAEA-Technology 2013-013, 44 Pages, 2013/06
A real-time simulator for operating both a reactor and irradiation facilities of a materials testing reactor, Simulator of Materials Testing Reactors, was developed for understanding reactor behavior and upskilling in order to utilize for a nuclear human resource development and to promote partnership with developing countries which have a plan to introduce nuclear power plant. The simulator is designed based on the JMTR (Japan Materials Testing Reactor) and it simulates operation, irradiation tests and various kinds of anticipated operational transients and accident conditions caused by the reactor and irradiation facilities. The development of the simulator was sponsored by the Japanese government as one of the specialized projects of advanced research infrastructure in order to promote basic as well as applied researches. This report summarizes the simulation model, hardware specification and operation procedure of the simulator.
Tamura, Koji
Optics & Laser Technology, 44(6), p.1818 - 1822, 2012/09
Times Cited Count:0 Percentile:0(Optics)A narrow linewidth pulse and a broadband pulse were simultaneously operated in the master oscillator power amplifier (MOPA) of a self-seeded Ti:sapphire laser, and their intensity ratio was varied by increasing the incident pump energy. It was explained that the broadband pulse from the independent free-running oscillation was preferentially amplified in the MOPA chain and replaced the narrow linewidth pulse. The explanation was confirmed by comparing the behavior with a bandpass filter inserted at the exit of the oscillator. The behaviors were well simulated by numerical calculations. From the results, a method to produce both narrow linewidth and broadband pulses was proposed with a ratio depending on the pump energy.
Tamura, Koji
Japanese Journal of Applied Physics, 50(6), p.066301_1 - 066301_6, 2011/06
Times Cited Count:0 Percentile:0(Physics, Applied)The atomic beam of rubidium was isotope selectively photoionized by the irradiation of the fundamental output of Ti:sapphire laser. The produced rubidium ions were extracted and collimated with electrodes as a laser ion source. The ion images of  Rb and
Rb and 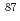 Rb were observed at a phosphor screen of MCP. The ion energy corresponded to the potential of the laser irradiated position between the electrodes. The ion source can be one of the isotope selective tools for surface engineering.
Rb were observed at a phosphor screen of MCP. The ion energy corresponded to the potential of the laser irradiated position between the electrodes. The ion source can be one of the isotope selective tools for surface engineering.
Tamura, Koji
Japanese Journal of Applied Physics, 48(4), p.046003_1 - 046003_4, 2009/04
Times Cited Count:2 Percentile:9.94(Physics, Applied)In order to demonstrate the applicability of the developed self-seeded pulsed Ti:sapphire laser oscillator with a pair of diffraction gratings to the laser isotope separation, two-step photoionization of rubidium (Rb) using the oscillator output at 780 nm (Rb D line) and the UV laser (the third harmonics of the Nd:YAG laser) was measured. Ion signals correspond to
line) and the UV laser (the third harmonics of the Nd:YAG laser) was measured. Ion signals correspond to  Rb and
Rb and 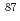 Rb isotopes were selectively observed at the first excitation frequency corresponding to their resonance lines. The results shows that Rb atoms were selectively photoionized with high yields of selectivity, and that the developed laser geometry was useful for the laser isotope separation.
Rb isotopes were selectively observed at the first excitation frequency corresponding to their resonance lines. The results shows that Rb atoms were selectively photoionized with high yields of selectivity, and that the developed laser geometry was useful for the laser isotope separation.