Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Tamura, Hajimu*; Shibata, Kenji*; Takahashi, Naoya; Niwa, Masakazu
JAEA-Testing 2017-001, 52 Pages, 2017/03
It is essential to understand the activity of faults in and around a target area to assess the long-term geosphere stability for geological isolation. Potassium-Argon (K-Ar) dating of fault gouge has been conducted in Tono Geoscience Center as one of the dating technique for faulting. This report includes methods for sample preparation, analyses, and age calculation on the K-Ar dating. This can contribute to an evaluation of calculated K-Ar ages.
 Ar resetting in an ultracataclasite by reactivation of a fossil seismogenic fault along the subducting plate interface in the Mugi M
Ar resetting in an ultracataclasite by reactivation of a fossil seismogenic fault along the subducting plate interface in the Mugi M lange of the Shimanto accretionary complex, southwest Japan
lange of the Shimanto accretionary complex, southwest JapanTonai, Satoshi*; Ito, Shun*; Hashimoto, Yoshitaka*; Tamura, Hajimu; Tomioka, Naotaka*
Journal of Structural Geology, 89, p.19 - 29, 2016/08
Times Cited Count:16 Percentile:48.38(Geosciences, Multidisciplinary)We used the K-Ar ages of clay-sized mineral grains to investigate the timing of activity on the fossil seismogenic Minami-Awa Fault. The K-Ar ages from matrix shale of the m lange range from 85 to 48 Ma and decrease with decreasing amount of detrital mica. In contrast, the K-Ar ages of an ultracataclasite within the fault core are significantly younger, ranging from 29 to 23 Ma, and are unrelated to grain size. This indicates that
lange range from 85 to 48 Ma and decrease with decreasing amount of detrital mica. In contrast, the K-Ar ages of an ultracataclasite within the fault core are significantly younger, ranging from 29 to 23 Ma, and are unrelated to grain size. This indicates that  Ar diffused completely from the ultracataclasite between 29 and 23 Ma. The diffusion of
Ar diffused completely from the ultracataclasite between 29 and 23 Ma. The diffusion of  Ar in the ultracataclasite was probably caused by frictional heating or high-temperature fluid migration that occurred when the fault was reactivated. The results indicate that seismogenic faults that separate tectonic m
Ar in the ultracataclasite was probably caused by frictional heating or high-temperature fluid migration that occurred when the fault was reactivated. The results indicate that seismogenic faults that separate tectonic m lange from coherent strata in accretionary complex may slip, not only during accretion, but also long after accretion.
lange from coherent strata in accretionary complex may slip, not only during accretion, but also long after accretion.
Niwa, Masakazu; Shimada, Koji; Tamura, Hajimu*; Shibata, Kenji*; Sueoka, Shigeru; Yasue, Kenichi; Ishimaru, Tsuneari; Umeda, Koji*
Clays and Clay Minerals, 64(2), p.86 - 107, 2016/04
Times Cited Count:11 Percentile:34.14(Chemistry, Physical)no abstracts in English
Umeda, Koji; Yasue, Kenichi; Kokubu, Yoko; Niwa, Masakazu; Asamori, Koichi; Fujita, Natsuko; Shimizu, Mayuko; Matsubara, Akihiro; Tamura, Hajimu; Yokoyama, Tatsunori; et al.
JAEA-Review 2015-019, 42 Pages, 2015/09
This report is a plan of research and development (R&D) on geosphere stability for long-term isolation of high-level radioactive waste (HLW) in JAEA, in fiscal year 2015. The objectives and contents in fiscal year 2015 are described in detail based on the outline of 7 years plan (fiscal years 2015-2021). Background of this research is clarified with the necessity and the significance for site investigation and safety assessment, and the past progress in this report. In addition, the plan framework is structured into the following categories: (1) Development and systematization of investigation techniques, (2) Development of models for long-term estimation and effective assessment, (3) Development of dating techniques.
Umeda, Koji; Yasue, Kenichi; Kokubu, Yoko; Niwa, Masakazu; Asamori, Koichi; Fujita, Natsuko; Shimizu, Mayuko; Shimada, Akiomi; Matsubara, Akihiro; Tamura, Hajimu; et al.
JAEA-Review 2015-012, 43 Pages, 2015/08
The concept of geological disposal of high-level radioactive waste (HLW) in Japan is based on a multibarrier system which combines a stable geological environment with an engineered barrier system. Potential geological host formations and their surroundings are chosen, in particular, for their long-term stability, taking into account the fact that Japan is located in tectonically active zone. This report is to outline 7 years plan (fiscal years 2015-2021) of research and development (R&D) for geosphere stability for long-term isolation of the HLW in JAEA. Background of this research is clarified with the necessity and the significance, and the past progress in this report. The objectives, outline, contents and schedule during the next 7 years are described in detail. In addition, the plan framework is structured into the following categories: (1) Development and Systematization of investigation techniques, (2) Development of models for long-term estimation and effective assessment, (3) Development of dating techniques.
Yasue, Kenichi; Asamori, Koichi; Niwa, Masakazu; Kokubu, Yoko; Kobori, Kazuo; Makuuchi, Ayumu; Matsubara, Akihiro; Shibata, Kenji; Tamura, Hajimu; Tanabe, Hiroaki; et al.
JAEA-Review 2014-033, 43 Pages, 2014/09
The concept of geological disposal of HLW in Japan is based on a multi-barrier system which combines a stable geological environment with a robust barrier system. Potential geological host formations and their surroundings are chosen, in particular, for their long-term stability, taking into account the fact that Japan is located in a tectonically active zone. This report is a plan of research and development (R&D) on geosphere stability for long-term isolation of HLW in JAEA, in fiscal year 2014. The objectives and contents in fiscal year 2014 are described in detail based on the outline of 5 years plan (fiscal years 2010-2014). In addition, the planned framework is structured into the following categories: (1) Development and systematization of investigation techniques, (2) Development of models for long-term estimation and effective assessment, (3) Development of dating techniques.
Yasue, Kenichi; Asamori, Koichi; Niwa, Masakazu; Hanamuro, Takahiro; Kokubu, Yoko; Sueoka, Shigeru; Makuuchi, Ayumu; Ikuta, Masafumi; Matsubara, Akihiro; Tamura, Hajimu; et al.
JAEA-Research 2013-047, 109 Pages, 2014/03
This annual report documents the progress of R&D in the 3rd fiscal year during the JAEA 2nd Midterm Plan (FY 2010 - 2014) to provide the scientific base for assessing geosphere stability for long-term isolation of the high-level radioactive waste. The planned framework is structured into the following categories: (1) development and systematization of investigation techniques for selecting suitable sites in geosphere stability, (2) development, application and verification of prediction models for evaluating the changes of geological environment in thermal, hydraulic, mechanical and geochemical conditions for a long period of time, and (3) development of new dating techniques for providing information about geologic history and the timing of geologic events. In this paper, the current status of R&D activities with previous scientific and technological progress is summarized.
Tamura, Hajimu; Sato, Keiko*
Chishitsu Gijutsu, (3), p.21 - 25, 2013/09
K-Ar age of fault is sometimes exclusive fact age of fault activity though the age of fault activity is determined on stratigraphy and ages by different dating methods. This note describes application of K-Ar dating to fault sample. Pseudotachylyte and Authigenic illite in fault gauge are major target material of dating. Sample preparation and determination of age are difficult for both of them and the geochronology is still in development stage. Dating examples of Pseudotachylyte says that sample separation is important to select part which was equilibrate to atomosphere in generation by spot analysis like laser fusion  Ar-
Ar-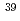 Ar dating, as illite examples that sample preparation to obtain fine - about 1 micrometer or less - grain and sample determination by inspection with electron microscope or XRD analysis are important.
Ar dating, as illite examples that sample preparation to obtain fine - about 1 micrometer or less - grain and sample determination by inspection with electron microscope or XRD analysis are important.
Suzuki, Chihiro*; Kato, Takako*; Sato, Kuninori*; Tamura, Naoki*; Kato, Daiji*; Sudo, Shigeru*; Yamamoto, Norimasa*; Tanuma, Hajime*; Ohashi, Hayato*; Suda, Shintaro*; et al.
Journal of Physics; Conference Series, 163, p.012019_1 - 012019_4, 2009/06
Times Cited Count:11 Percentile:94.18(Physics, Multidisciplinary)We have measured EUV spectra from highly charged tin ions in low density plasmas produced in the Large Helical Device (LHD). The well known dense spectral structure around 13.5 nm is measured when the plasma is rapidly cooled and approaching radioactive collapse, while the sparse spectrum with several unidentified discrete lines from 13.8-14.6 nm is observed if the plasma is cooled more slowly. The dominant charge states in the former case are Sn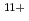 -Sn
-Sn . The latter case may be explained by considering the spectral lines from charge states higher than Sn
. The latter case may be explained by considering the spectral lines from charge states higher than Sn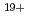 .
.
Adachi, Hajime; Tamura, Koji; Ogura, Koichi; Shibata, Takemasa
Japanese Journal of Applied Physics, 38(12A), p.6887 - 6889, 1999/12
Times Cited Count:4 Percentile:23.76(Physics, Applied)no abstracts in English
Tamura, Koji; Adachi, Hajime*; Ogura, Koichi; Oba, Hironori; Shibata, Takemasa
Japanese Journal of Applied Physics, Part 1, 38(11), p.6512 - 6516, 1999/11
Times Cited Count:12 Percentile:50.91(Physics, Applied)no abstracts in English
Tamura, Koji; Adachi, Hajime; Shibata, Takemasa
Japanese Journal of Applied Physics, Part 1, 38(5A), p.2973 - 2977, 1999/05
Times Cited Count:6 Percentile:32.51(Physics, Applied)no abstracts in English
Tamura, Koji; ; Adachi, Hajime; Oba, Hironori; Shibata, Takemasa
Japanese Journal of Applied Physics, Part 1, 38(4A), p.2122 - 2123, 1999/04
Times Cited Count:9 Percentile:42.94(Physics, Applied)no abstracts in English
Adachi, Hajime; Tamura, Koji; ; Ogura, Koichi; Oba, Hironori; Shibata, Takemasa
JAERI-Research 99-029, 19 Pages, 1999/03
no abstracts in English
Tamura, Koji; ; Adachi, Hajime; Oba, Hironori; Shibata, Takemasa
JAERI-Research 98-073, 10 Pages, 1998/12
no abstracts in English
Tamura, Koji; ; Adachi, Hajime; Shibata, Takemasa; Oba, Hironori
Japanese Journal of Applied Physics, Part 1, 37(12A), p.6651 - 6654, 1998/12
Times Cited Count:0 Percentile:0(Physics, Applied)no abstracts in English
Adachi, Hajime; Tamura, Koji; ; Shibata, Takemasa
JAERI-Tech 98-029, 32 Pages, 1998/08
no abstracts in English
; Tamura, Koji; Adachi, Hajime; Oba, Hironori; *; Shibata, Takemasa
JAERI-Tech 98-020, 17 Pages, 1998/06
no abstracts in English
Adachi, Hajime; Tamura, Koji; ; Shibata, Takemasa
JAERI-Research 98-030, 29 Pages, 1998/06
no abstracts in English
Tamura, Koji; Adachi, Hajime; Shibata, Takemasa
JAERI-Research 98-020, 13 Pages, 1998/03
no abstracts in English