Production of no-carrier-added  Lu via the
Lu via the  Yb(n,
Yb(n, )
) Yb
Yb
 Lu process
Lu process
 Yb(n,
Yb(n, )
) Yb
Yb
 Lu反応による無担体
Lu反応による無担体 Luの製造研究
Luの製造研究
橋本 和幸; 松岡 弘充; 内田 昇二*
Hashimoto, Kazuyuki; Matsuoka, Hiromitsu; Uchida, Shoji*
 線放出核種である
線放出核種である Luは、がん治療用の核種として有望である。半減期が6.73日,
Luは、がん治療用の核種として有望である。半減期が6.73日, 線の最大エネルギーが498keVで、組織中の
線の最大エネルギーが498keVで、組織中の 線の飛程が短い。さらに、画像化に適した208及び113keVの
線の飛程が短い。さらに、画像化に適した208及び113keVの 線を放出する。Lu-177は、通常
線を放出する。Lu-177は、通常 Lu(n,
Lu(n, )
) Lu反応を利用して高収率・高比放射能で製造される。しかしながら、標識抗体などを利用する放射免疫治療の分野ではより高い比放射能のRIが望まれている。そこで、無担体の
Lu反応を利用して高収率・高比放射能で製造される。しかしながら、標識抗体などを利用する放射免疫治療の分野ではより高い比放射能のRIが望まれている。そこで、無担体の Luを製造するために、
Luを製造するために、 Yb(n,
Yb(n, )
) Yb
Yb 
 Lu反応を利用した製造研究を行った。本製造法では、マクロ量のYbターゲットから無担体の
Lu反応を利用した製造研究を行った。本製造法では、マクロ量のYbターゲットから無担体の Luを分離する段階が最も重要である。本研究では、逆相イオン対カラムクロマトグラフィーを用いて、その分離条件を検討した。その結果、5mgのYb
Luを分離する段階が最も重要である。本研究では、逆相イオン対カラムクロマトグラフィーを用いて、その分離条件を検討した。その結果、5mgのYb O
O を用いた場合、80%の分離収率で無担体の
を用いた場合、80%の分離収率で無担体の Luを得ることができた。
Luを得ることができた。
The 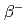 emitter
emitter  Lu is a promising therapeutic radioisotope for the treatment of cancer. It has a half-life of 6.73 days and maximum
Lu is a promising therapeutic radioisotope for the treatment of cancer. It has a half-life of 6.73 days and maximum 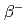 energy of 498 keV, resulting in a short range of radiation in tissue. The decay is accompanied by the emission of low energy
energy of 498 keV, resulting in a short range of radiation in tissue. The decay is accompanied by the emission of low energy  -radiation with
-radiation with 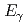 = 208 keV (11.0%) and 113 keV (6.4%) suitable for simultaneous imaging. Lutetium-177 can be usually produced at nuclear reactors with high yield and high specific radioactivity by the
= 208 keV (11.0%) and 113 keV (6.4%) suitable for simultaneous imaging. Lutetium-177 can be usually produced at nuclear reactors with high yield and high specific radioactivity by the  Lu(n,
Lu(n, )
) Lu reaction. However, radioisotopes with higher specific radioactivity are required in the field of radioimmunotherapy using labeled monoclonal antibodies. Thus, an alternative production route, namely the
Lu reaction. However, radioisotopes with higher specific radioactivity are required in the field of radioimmunotherapy using labeled monoclonal antibodies. Thus, an alternative production route, namely the  Yb(n,
Yb(n, )
) Yb
Yb 
 Lu process was studied to produce no-carrier-added (nca)
Lu process was studied to produce no-carrier-added (nca)  Lu in this work. The radiochemical separation of the nca
Lu in this work. The radiochemical separation of the nca  Lu from the macroscopic ytterbium target was investigated by means of reversed-phase ion-pair HPLC. The nca
Lu from the macroscopic ytterbium target was investigated by means of reversed-phase ion-pair HPLC. The nca  Lu was obtained in radiochemical pure form with a separation yield of 80%.
Lu was obtained in radiochemical pure form with a separation yield of 80%.