Energetic deuterium and helium irradiation effects on chemical structure of CVD diamond
CVDダイアモンドの化学組成における重水素及びヘリウム照射効果
佐々木 政義*; 森本 泰臣*; 木村 宏美*; 高橋 幸司; 坂本 慶司; 今井 剛; 奥野 健二*
Sasaki, Masayoshi*; Morimoto, Yasutomi*; Kimura, Hiromi*; Takahashi, Koji; Sakamoto, Keishi; Imai, Tsuyoshi; Okuno, Kenji*
核融合炉用ミリ波帯高周波加熱システムのトーラス窓(高周波窓)の窓材として、CVDダイアモンドは標準となっている。トーラス窓は、トリチウム障壁としての役割も担うことから、トリチウムやヘリウム,放射性ダスト環境下にあり、したがって、ダイアモンドの化学構造に対する水素同位体等の影響を解明することは重要である。本研究では、窓と同一グレードのCVDダイアモンド試料( =10.0mm, t=0.21mm)を、アルゴンイオンビームスパッタリング(E
=10.0mm, t=0.21mm)を、アルゴンイオンビームスパッタリング(E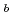 =1keV)による酸素等の不純物除去の後に、重水素及びヘリウムイオンを照射した。照射エネルギーはそれぞれ0.25keV, 0.45keVである。照射サンプルをX線光電子分光(XPS)測定によって調べたところ、C1ピークが低エネルギー側にシフトしていることが観測された。この結果は、ダイアモンドがC-D結合によりアモルファス化したことを示唆している。
=1keV)による酸素等の不純物除去の後に、重水素及びヘリウムイオンを照射した。照射エネルギーはそれぞれ0.25keV, 0.45keVである。照射サンプルをX線光電子分光(XPS)測定によって調べたところ、C1ピークが低エネルギー側にシフトしていることが観測された。この結果は、ダイアモンドがC-D結合によりアモルファス化したことを示唆している。
A CVD diamond has been the reference material of a torus widow for a rf heating system in a fusion reactor. Since the window is in the circumstance of tritium, helium and radio activated dust, it is important to elucidate the effect of ions on chemical structure of the diamond, existing states of tritium and tritium inventory. Polycrystalline CVD diamond disks( =10.0mm, t=0.21mm) used in this study are the same grade as rf windows. After sputtering the surface with 1.0 keV Ar
=10.0mm, t=0.21mm) used in this study are the same grade as rf windows. After sputtering the surface with 1.0 keV Ar to remove oxygen impurity, the sample was irradiated with deuterium (D
to remove oxygen impurity, the sample was irradiated with deuterium (D
 ) or helium ions (He
) or helium ions (He ) at an angle of 0 degrees to the surface normal. The irradiation energies of deuterium and helium are 0.25 keV D
) at an angle of 0 degrees to the surface normal. The irradiation energies of deuterium and helium are 0.25 keV D and 0.45 keV He
and 0.45 keV He , respectively. The structural change of the irradiated sample was measured by X-ray Photoelectron Spectroscopy (XPS) technique. The C1s peak shift toward lower binding energy side was observed when deuterium ions irradiated. This result indicates that the diamond changes to amorphous carbon due to formation of C-D bond.
, respectively. The structural change of the irradiated sample was measured by X-ray Photoelectron Spectroscopy (XPS) technique. The C1s peak shift toward lower binding energy side was observed when deuterium ions irradiated. This result indicates that the diamond changes to amorphous carbon due to formation of C-D bond.