Equilibrium evaporation behavior of polonium and its homologue tellurium in liquid lead-bismuth eutectic
Ohno, Shuji 
 ; Kurata, Yuji; Miyahara, Shinya
; Kurata, Yuji; Miyahara, Shinya 
 ; Katsura, Ryoei*; Yoshida, Shigeru*
; Katsura, Ryoei*; Yoshida, Shigeru*
Experimental study using the transpiration method investigated equilibrium evaporation behavior of radionuclide polonium ( Po) generated and accumulated in liquid lead-bismuth eutectic (LBE) cooled nuclear systems. The experiment consisted of two series of tests: preliminary evaporation tests for homologue element tellurium (Te) in LBE, and evaporation tests for
Po) generated and accumulated in liquid lead-bismuth eutectic (LBE) cooled nuclear systems. The experiment consisted of two series of tests: preliminary evaporation tests for homologue element tellurium (Te) in LBE, and evaporation tests for  Po-accumulated LBE in which test specimens were prepared by neutron irradiation. The evaporation tests of Te in LBE provided the suggestion that Te would exist in a chemical form of PbTe as well as the information for confirming the validity of technique and conditions of Po test. From the evaporation tests of
Po-accumulated LBE in which test specimens were prepared by neutron irradiation. The evaporation tests of Te in LBE provided the suggestion that Te would exist in a chemical form of PbTe as well as the information for confirming the validity of technique and conditions of Po test. From the evaporation tests of  Po in LBE, we obtained fundamental data and empirical equations such as
Po in LBE, we obtained fundamental data and empirical equations such as  Po vapor concentration in the gas phase,
Po vapor concentration in the gas phase,  Po partial vapor pressure, thermodynamic activity coefficients, and gas-liquid equilibrium partition coefficients of
Po partial vapor pressure, thermodynamic activity coefficients, and gas-liquid equilibrium partition coefficients of  Po in LBE in the temperature range from 450
Po in LBE in the temperature range from 450 C to 750
C to 750 C. Additionally, radioactivity concentration of
C. Additionally, radioactivity concentration of  Po and
Po and 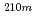 Bi vapor in a cover gas region of a typical LBE-cooled nuclear system was estimated based on the obtained experimental results, and the importance of
Bi vapor in a cover gas region of a typical LBE-cooled nuclear system was estimated based on the obtained experimental results, and the importance of  Po evaporation behavior was demonstrated.
Po evaporation behavior was demonstrated.