 measurement of UO
measurement of UO
 concentration in molten NaCl-2CsCl by differential pulse voltammetry
concentration in molten NaCl-2CsCl by differential pulse voltammetry
Nagai, Takayuki 
 ; Uehara, Akihiro*; Fujii, Toshiyuki*; Shirai, Osamu*; Yamana, Hajimu*
; Uehara, Akihiro*; Fujii, Toshiyuki*; Shirai, Osamu*; Yamana, Hajimu*
In order to assess the applicability of Differential Pulse Voltammetry technique to the  measurement of UO
measurement of UO
 concentration in the oxide electro-winning process, DPV measurements for UO
concentration in the oxide electro-winning process, DPV measurements for UO Cl
Cl in molten NaCl-2CsCl were studied. DPV measurement of UO
in molten NaCl-2CsCl were studied. DPV measurement of UO
 in NaCl-2CsCl at 923 K, with a set of optimized parameters (potential sweep rate -0.1 V/s, pulse cycle 0.1 s, pulse width 10 ms, and pulse potential height 50 mV), showed a clear current peak at -0.9 V vs. Cl
in NaCl-2CsCl at 923 K, with a set of optimized parameters (potential sweep rate -0.1 V/s, pulse cycle 0.1 s, pulse width 10 ms, and pulse potential height 50 mV), showed a clear current peak at -0.9 V vs. Cl /Cl
/Cl , and it was attributed to the reduction of UO
, and it was attributed to the reduction of UO
 to UO
to UO
 . The relation between the current peak height and the analytical concentration of the UO
. The relation between the current peak height and the analytical concentration of the UO
 showed good proportionality in the concentration region up to 0.06 mol/
showed good proportionality in the concentration region up to 0.06 mol/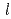 , and the applicability of UO
, and the applicability of UO
 concentration measurement by DPV was confirmed up to 0.4 mol/
concentration measurement by DPV was confirmed up to 0.4 mol/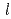 . In order to assess the interference by the coexisting fission product elements to the measurement of UO
. In order to assess the interference by the coexisting fission product elements to the measurement of UO
 concentration, DPV measurements of UO
concentration, DPV measurements of UO
 concentration in molten NaCl-2CsCl containing PdCl
concentration in molten NaCl-2CsCl containing PdCl , NdCl
, NdCl , SmCl
, SmCl , and CeCl
, and CeCl were performed also. Even before removing Pd, the current peak at -0.9 V vs. Cl
were performed also. Even before removing Pd, the current peak at -0.9 V vs. Cl /Cl
/Cl by the reduction of UO
by the reduction of UO
 to UO
to UO
 was found to be distinguishable from the reduction currents of Pd
was found to be distinguishable from the reduction currents of Pd to Pd at -0.7 V vs. Cl
to Pd at -0.7 V vs. Cl /Cl
/Cl . As a result, the applicability of DPV measurement technique to the
. As a result, the applicability of DPV measurement technique to the  monitoring of UO
monitoring of UO
 concentration in oxide electro-winning method is proposed.
concentration in oxide electro-winning method is proposed.