Superconductivity in f-electron systems controlled by crystalline electric fields
f電子系の結晶場によって制御される超伝導
久保 勝規  ; 堀田 貴嗣
; 堀田 貴嗣
Kubo, Katsunori; Hotta, Takashi
CeTIn (T=Co, Rh, and Ir)の超伝導をコントロールするパラメータとその機構を解明するために、
(T=Co, Rh, and Ir)の超伝導をコントロールするパラメータとその機構を解明するために、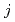 -
-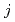 結合描像に基づいた軌道縮退のある
結合描像に基づいた軌道縮退のある 電子モデルに対して揺らぎ交換近似を適用した。本研究では、全角運動量
電子モデルに対して揺らぎ交換近似を適用した。本研究では、全角運動量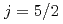 の状態すべてを考慮する。これらの状態は正方晶の結晶場のもとで1つの
の状態すべてを考慮する。これらの状態は正方晶の結晶場のもとで1つの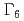 二重項と2つの
二重項と2つの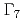 二重項にわかれる。結晶場パラメータを適当に選ぶことによって、結晶場分裂の大きさを固定したまま
二重項にわかれる。結晶場パラメータを適当に選ぶことによって、結晶場分裂の大きさを固定したまま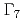 の波動関数を変化させることができる。結晶場分裂の大きさを一定にする限りフェルミ面はほとんど変化しないが、基底状態は
の波動関数を変化させることができる。結晶場分裂の大きさを一定にする限りフェルミ面はほとんど変化しないが、基底状態は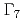 の波動関数に依存して、常磁性,反強磁性,超伝導状態に変化する。よって、フェルミ面の形状やキャリアー密度のほかに、軌道自由度のある系では結晶場の波動関数も超伝導の出現をコントロールする重要な要素になることがわかった。この理論によってCeTIn
の波動関数に依存して、常磁性,反強磁性,超伝導状態に変化する。よって、フェルミ面の形状やキャリアー密度のほかに、軌道自由度のある系では結晶場の波動関数も超伝導の出現をコントロールする重要な要素になることがわかった。この理論によってCeTIn の超伝導転移温度の変化が自然に説明できることも紹介する。
の超伝導転移温度の変化が自然に説明できることも紹介する。
To elucidate the mechanism and controlling parameter of the superconductivity in CeTIn (T=Co, Rh, and Ir), we study an
(T=Co, Rh, and Ir), we study an  -electron model based on a
-electron model based on a 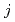 -
-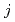 coupling scheme on a square lattice. In this study, we consider electrons with total angular momentum
coupling scheme on a square lattice. In this study, we consider electrons with total angular momentum 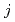 =5/2. These states split into one
=5/2. These states split into one 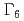 and two
and two 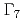 doublets under a tetragonal CEF. By choosing appropriate CEF potential, we can control the CEF wave-functions without changing the level splitting. Although the Fermi surface does not change so much as long as the splitting is fixed, the ground state changes depending on the CEF wave-function among paramagnetic, antiferromagnetic, and
doublets under a tetragonal CEF. By choosing appropriate CEF potential, we can control the CEF wave-functions without changing the level splitting. Although the Fermi surface does not change so much as long as the splitting is fixed, the ground state changes depending on the CEF wave-function among paramagnetic, antiferromagnetic, and  -wave superconducting states. Thus, in addition to the Fermi-surface topology and the carrier density, the wave-function of the CEF state is an important ingredient to control the appearance of superconductivity in such systems. We will discuss possible relevance of our scenarioto the superconductivity in CeTIn
-wave superconducting states. Thus, in addition to the Fermi-surface topology and the carrier density, the wave-function of the CEF state is an important ingredient to control the appearance of superconductivity in such systems. We will discuss possible relevance of our scenarioto the superconductivity in CeTIn .
.