Quantum chemical study of atomic structure evolution of Co /C
/C (x
(x  2.8) composites
2.8) composites
Co /C
/C (x
(x  2.8)混合物の原子的構造の進展に関する量子化学的研究
2.8)混合物の原子的構造の進展に関する量子化学的研究
Avramov, P.; 楢本 洋*; 境 誠司; 鳴海 一雅; Lavrentiev, V.*; 前田 佳均
Avramov, P.; Naramoto, Hiroshi*; Sakai, Seiji; Narumi, Kazumasa; Lavrentiev, V.*; Maeda, Yoshihito
CoとC からなる新奇化合物Co
からなる新奇化合物Co /C
/C (x
(x  2.8)の局所的な原子配置を、Co
2.8)の局所的な原子配置を、Co (C
(C )
) (n=1, 2, m=2, 3)について、B3LYP/6-31G
(n=1, 2, m=2, 3)について、B3LYP/6-31G 法を用いた第一原理計算によって研究した。n=1の異性体については、スピン状態S=1/2の場合がエネルギー的に安定で、それに対して、n=2の異性体はスピン状態S=1のときにより安定だった。また、n=1, 2のいずれの場合も
法を用いた第一原理計算によって研究した。n=1の異性体については、スピン状態S=1/2の場合がエネルギー的に安定で、それに対して、n=2の異性体はスピン状態S=1のときにより安定だった。また、n=1, 2のいずれの場合も
 型(C
型(C の6員環間に2座で配位)のCoの配位がエネルギー的に安定だった。
の6員環間に2座で配位)のCoの配位がエネルギー的に安定だった。
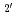 型の配位(6員環-5員環間に2座で配位)、さらに
型の配位(6員環-5員環間に2座で配位)、さらに
 型の配位(5員環に5座で配位)は、Co原子がC
型の配位(5員環に5座で配位)は、Co原子がC ケージ上をマイグレートする際に中間体になりえ、さらに、Co
ケージ上をマイグレートする際に中間体になりえ、さらに、Co /C
/C は、最終的にCoダイマーの形成によって平衡状態の原子配置に近づくことを明らかにした。
は、最終的にCoダイマーの形成によって平衡状態の原子配置に近づくことを明らかにした。
The main features of the local atomic structure of novel Co /C
/C (x
(x  2.8) complex mixtures were studied using the
2.8) complex mixtures were studied using the  B3LYP/6-31G
B3LYP/6-31G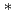 method for a set of low and high energy Co
method for a set of low and high energy Co (C
(C )
) (n = 1, 2, m = 2, 3) clusters in low and intermediate spin states. For the n = 1 isomers the spin state S = 1/2 is energetically preferable whereas the low energy isomers of n = 2 have an intermediate spin state of S = 1. The
(n = 1, 2, m = 2, 3) clusters in low and intermediate spin states. For the n = 1 isomers the spin state S = 1/2 is energetically preferable whereas the low energy isomers of n = 2 have an intermediate spin state of S = 1. The 
 (6-6 edge of C
(6-6 edge of C ) type of cobalt ion coordination is preferable for both n = 1 and n = 2 cases. The
) type of cobalt ion coordination is preferable for both n = 1 and n = 2 cases. The 
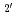 (coordination with 6-5 edge) and even the
(coordination with 6-5 edge) and even the 
 (C
(C fragment) types can serve as low and high energy intermediates for the cobalt ion's migration around the C
fragment) types can serve as low and high energy intermediates for the cobalt ion's migration around the C cage. Formation of cobalt dimers can be the final stage of evolution of Co
cage. Formation of cobalt dimers can be the final stage of evolution of Co /C
/C atomic structure approaching the equilibrium atomic geometry.
atomic structure approaching the equilibrium atomic geometry.