Magnetic and dielectric properties of 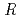 Fe
Fe O
O ,
, 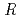 Fe
Fe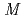 O
O , and
, and 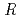 GaCuO
GaCuO (
(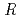 =Yb and Lu,
=Yb and Lu, 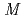 =Co and Cu)
=Co and Cu)
Yoshii, Kenji 
 ; Ikeda, Naoshi*; Matsuo, Yoji*; Horibe, Yoichi*; Mori, Shigeo*
; Ikeda, Naoshi*; Matsuo, Yoji*; Horibe, Yoichi*; Mori, Shigeo*
The magnetic and dielectric properties have been investigated for the isostructural oxides of  Fe
Fe O
O ,
,  Fe
Fe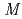 O
O , and
, and  GaCuO
GaCuO (
( =Yb and Lu,
=Yb and Lu, 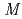 =Co and Cu). The magnetization measurements for
=Co and Cu). The magnetization measurements for  Fe
Fe O
O showed ferrimagnetic ordering at
showed ferrimagnetic ordering at  250 K. This system also exhibited large dielectric constants of
250 K. This system also exhibited large dielectric constants of  10,000-30,000 at around room temperature, which is attributable to the charge-ordering-induced ferroelectricity, as was proposed in our recent report. The magnetic transition temperatures are lowered to
10,000-30,000 at around room temperature, which is attributable to the charge-ordering-induced ferroelectricity, as was proposed in our recent report. The magnetic transition temperatures are lowered to  45-90 K for
45-90 K for  Fe
Fe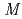 O
O . Magnetic ordering is not found for
. Magnetic ordering is not found for  GaCuO
GaCuO . AC magnetic susceptibility measurements indicate that magnetic ordering becomes short-ranged by the substitution at the Fe site. The overall characteristic behavior of the magnetic properties is explained in terms of the change of a spin value as well as the dilution of magnetic interactions. Although the AC dielectric measurements show the existence of polar regions in each material, the dielectric constants below 300 K become smaller in the order of
. AC magnetic susceptibility measurements indicate that magnetic ordering becomes short-ranged by the substitution at the Fe site. The overall characteristic behavior of the magnetic properties is explained in terms of the change of a spin value as well as the dilution of magnetic interactions. Although the AC dielectric measurements show the existence of polar regions in each material, the dielectric constants below 300 K become smaller in the order of  Fe
Fe O
O ,
,  FeCoO
FeCoO ,
,  FeCuO
FeCuO , and
, and  GaCuO
GaCuO . From the analysis of the dielectric dispersion, the distribution of the fluctuation time of polar regions is wider in
. From the analysis of the dielectric dispersion, the distribution of the fluctuation time of polar regions is wider in  FeCoO
FeCoO ,
,  FeCuO
FeCuO , and
, and  CuGaO
CuGaO than in
than in  Fe
Fe O
O ; a coherent motion of polar regions is suppressed in the substituted systems. By comparison to the results from the magnetic measurements, the dielectric properties are discussed in connection with a charge transfer between the transition-metal 3
; a coherent motion of polar regions is suppressed in the substituted systems. By comparison to the results from the magnetic measurements, the dielectric properties are discussed in connection with a charge transfer between the transition-metal 3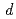 orbitals, consistently with the proposed novel mechanism of the ferroelectricity in
orbitals, consistently with the proposed novel mechanism of the ferroelectricity in  Fe
Fe O
O .
.