Nondestructive detection and assay of nuclear material by laser Compton  -rays from energy-recovery linacs
-rays from energy-recovery linacs
エネルギー回収型リニアックによる大強度 線の発生と放射性核種の非破壊分析への利用
線の発生と放射性核種の非破壊分析への利用
羽島 良一; 菊澤 信宏  ; 早川 岳人; 峰原 英介
; 早川 岳人; 峰原 英介
Hajima, Ryoichi; Kikuzawa, Nobuhiro; Hayakawa, Takehito; Minehara, Eisuke
エネルギー回収型リニアックによる大電流高輝度電子ビームを利用したレーザーコンプトン 線の発生では、従来の光源を大きく上回る
線の発生では、従来の光源を大きく上回る 線フラックス(
線フラックス(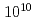 photon/sec/keV)が得られる見込みである。この
photon/sec/keV)が得られる見込みである。この 線ビームを使って、原子核共鳴散乱(NRF)反応を起こすことで、任意の原子核を非破壊で検出することができる。本稿では、
線ビームを使って、原子核共鳴散乱(NRF)反応を起こすことで、任意の原子核を非破壊で検出することができる。本稿では、 線源の概念設計,非破壊検出のモンテカルロシミュレーション結果について述べ、本手法の原子力廃棄物の処理処分への利用を展望する。
線源の概念設計,非破壊検出のモンテカルロシミュレーション結果について述べ、本手法の原子力廃棄物の処理処分への利用を展望する。
Nondestructive assay of nuclear materials is one of the most urgent research issues for the management of nuclear waste. We apply nuclear resonant fluorescence (NRF), a fingerprint of each isotope, to the nondestructive detection. Detection of NRF signals from objectives irradiated by quasi-monochromatic  -rays enables one to make quantitative assay of nuclear materials in a nondestructive manner. In order to obtain high-flux
-rays enables one to make quantitative assay of nuclear materials in a nondestructive manner. In order to obtain high-flux  -rays for the above purpose, we propose to utilize an energy-recovery linac (ERL), which produces a high-brightness electron beam with high-average current. A design study of high-flux
-rays for the above purpose, we propose to utilize an energy-recovery linac (ERL), which produces a high-brightness electron beam with high-average current. A design study of high-flux  -ray source based on an ERL shows that a
-ray source based on an ERL shows that a  -ray flux of
-ray flux of 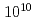 ph/sec/keV is obtained and detection of U-238 of 1 Bq/g in a concrete drum is possible within 1 second. In this paper, we present a design of the assay system and results of Monte Carlo simulations of NRF.
ph/sec/keV is obtained and detection of U-238 of 1 Bq/g in a concrete drum is possible within 1 second. In this paper, we present a design of the assay system and results of Monte Carlo simulations of NRF.