Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Omer, M.; 静間 俊行*; 羽島 良一*; 小泉 光生
Journal of Applied Physics, 135(18), p.184903_1 - 184903_10, 2024/05
We report on the findings of a quantitative nondestructive analysis of the natural isotopic abundances of hafnium and tungsten elements using nuclear resonance fluorescence. Commercial samples of hafnium and tungsten were irradiated to six quasi-monochromatic  -ray beams generated by laser Compton scattering in the energy range of 2.4-3.2 MeV. Multiple nuclei were simultaneously excited at each of the six
-ray beams generated by laser Compton scattering in the energy range of 2.4-3.2 MeV. Multiple nuclei were simultaneously excited at each of the six  -ray beam energies. A high-purity germanium detector array detected deexcitations of the nuclei. In total,
-ray beam energies. A high-purity germanium detector array detected deexcitations of the nuclei. In total, 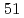 transitions were unprecedentedly employed to estimate the isotopic abundances of heavy elements nondestructively. The estimated abundances of three hafnium isotopes and three tungsten isotopes are consistent with standard known natural abundances within the experimental uncertainties. The deviation from the standard values ranges from 0.18% to 1.36%. This work is a contribution of the Japan Atomic Energy Agency (JAEA) to the International Atomic Energy Agency (IAEA) under the agreement of the coordinated research program (CRP), J02015 (Facilitation of Safe and Secure Trade Using Nuclear Detection Technology - Detection of RN and Other Contraband). This work was a part of a study of the nuclear resonance fluorescence aiming at nuclear security and safeguards applications, being supported by the subsidiary for "promotion of strengthening nuclear security or the like" of the Ministry of Education, Culture, Sports, Science, and Technology (MEXT), Japan.
transitions were unprecedentedly employed to estimate the isotopic abundances of heavy elements nondestructively. The estimated abundances of three hafnium isotopes and three tungsten isotopes are consistent with standard known natural abundances within the experimental uncertainties. The deviation from the standard values ranges from 0.18% to 1.36%. This work is a contribution of the Japan Atomic Energy Agency (JAEA) to the International Atomic Energy Agency (IAEA) under the agreement of the coordinated research program (CRP), J02015 (Facilitation of Safe and Secure Trade Using Nuclear Detection Technology - Detection of RN and Other Contraband). This work was a part of a study of the nuclear resonance fluorescence aiming at nuclear security and safeguards applications, being supported by the subsidiary for "promotion of strengthening nuclear security or the like" of the Ministry of Education, Culture, Sports, Science, and Technology (MEXT), Japan.
 Ta
Ta静間 俊行*; Omer, M.; 羽島 良一*; 小泉 光生
Physical Review C, 109(5), p.054320_1 - 054320_8, 2024/05
Low-lying levels in the odd-mass nucleus  Ta have been populated via nuclear resonance fluorescence using a quasi-monoenergetic, linearly polarized photon beam at the High Intensity
Ta have been populated via nuclear resonance fluorescence using a quasi-monoenergetic, linearly polarized photon beam at the High Intensity  -ray Source (HI
-ray Source (HI S) facility at Duke University. The spin and parity of the levels were determined from the azimuthal intensity asymmetry of resonantly scattered
S) facility at Duke University. The spin and parity of the levels were determined from the azimuthal intensity asymmetry of resonantly scattered  -rays with respect to the polarization plane of the incident photon beam. The electric and magnetic dipole strengths were obtained for excitation energies from 2.2 to 3.2 MeV. The results are discussed in terms of the nuclear scissors mode. This work is a contribution of the Japan Atomic Energy Agency (JAEA) to the International Atomic Energy Agency (IAEA) under the agreement of the coordinated research program (CRP), J02015 (Facilitation of Safe and Secure Trade Using Nuclear Detection Technology - Detection of RN and Other Contraband). This work was a part of a study of the nuclear resonance fluorescence aiming at nuclear security and safeguards applications, being supported by the subsidiary for "promotion of strengthening nuclear security or the like" of the Ministry of Education, Culture, Sports, Science, and Technology (MEXT), Japan.
-rays with respect to the polarization plane of the incident photon beam. The electric and magnetic dipole strengths were obtained for excitation energies from 2.2 to 3.2 MeV. The results are discussed in terms of the nuclear scissors mode. This work is a contribution of the Japan Atomic Energy Agency (JAEA) to the International Atomic Energy Agency (IAEA) under the agreement of the coordinated research program (CRP), J02015 (Facilitation of Safe and Secure Trade Using Nuclear Detection Technology - Detection of RN and Other Contraband). This work was a part of a study of the nuclear resonance fluorescence aiming at nuclear security and safeguards applications, being supported by the subsidiary for "promotion of strengthening nuclear security or the like" of the Ministry of Education, Culture, Sports, Science, and Technology (MEXT), Japan.
 -ray elastic scattering
-ray elastic scatteringOmer, M.; 静間 俊行*; 小泉 光生; 羽島 良一*; 橋本 智*; 宮本 修治*
LASTI Annual Report, 24, p.20 - 22, 2023/12
Nondestructive elemental analysis is highly valued in many fields such as archeology, paleontology, space sciences, nuclear security, and nuclear nonproliferation. These fields usually impose estimating the elemental composition of bulk, large, and inhomogeneous samples nondestructively. Common elemental analysis techniques such as X-ray fluorescence (XRF) may fail in such situations due to self-absorption of low energy X-rays within thin layers of the sample. In the present study, we propose a novel nondestructive method that may be useful in distinguishing the elemental composition of a given sample based on the elastic scattering of linearly polarized and high-energy  -rays. Linear polarization of
-rays. Linear polarization of  -rays causes asymmetry of the elastic scattering cross sections with respect to the polarization plane of the incident
-rays causes asymmetry of the elastic scattering cross sections with respect to the polarization plane of the incident  -rays. At specific
-rays. At specific  -ray energies and scattering angles, the asymmetry ratio, R, of the cross sections in two orthogonal planes is characteristic of each element. The measurement of asymmetry ratio of 1.62 MeV linearly polarized
-ray energies and scattering angles, the asymmetry ratio, R, of the cross sections in two orthogonal planes is characteristic of each element. The measurement of asymmetry ratio of 1.62 MeV linearly polarized  -rays at NewSUBARU facility is presented. This work is a contribution of the JAEA to the International Atomic Energy Agency (IAEA) under the agreement of the coordinated research program (CRP), J02015 (Facilitation of Safe and Secure Trade Using Nuclear Detection Technology - Detection of RN and Other Contraband).
-rays at NewSUBARU facility is presented. This work is a contribution of the JAEA to the International Atomic Energy Agency (IAEA) under the agreement of the coordinated research program (CRP), J02015 (Facilitation of Safe and Secure Trade Using Nuclear Detection Technology - Detection of RN and Other Contraband).
Omer, M.; 静間 俊行*; 小泉 光生; 平 義隆*; Zen, H.*; 大垣 英明*; 羽島 良一
UVSOR-50, P. 37, 2023/08
核共鳴蛍光(NRF)を用いた非破壊分析において、試料温度によるドップラー効果による影響を調べることを目的とした研究を開始した。今回は、波長1980nmのファイバーレーザーを加速エネルギー746MeVの電子ビームと衝突させて生成した最大エネルギー5.54MeVのレーザーコンプトンガンマ線を Pb標的に照射し、共鳴散乱ガンマ線を3台の高純度ゲルマニウム検出器を用いて測定した。その結果、レーザーコンプトンガンマ線最大エネルギーよりも高いエネルギーで、複数のガンマ線ピークが観測された。これらのガンマ線は、実験室内の制動放射線によって発生した中性子が測定装置の周囲の物質と反応した後に放出された中性子捕獲即発ガンマ線であると考えられる。そのため、バックグラウンドガンマ線の低減のため、ゲルマニウム検出器の周囲を厚さ10cmの鉛を用いて遮蔽した。その結果、即発ガンマ線のバックグラウンドは抑制され、
Pb標的に照射し、共鳴散乱ガンマ線を3台の高純度ゲルマニウム検出器を用いて測定した。その結果、レーザーコンプトンガンマ線最大エネルギーよりも高いエネルギーで、複数のガンマ線ピークが観測された。これらのガンマ線は、実験室内の制動放射線によって発生した中性子が測定装置の周囲の物質と反応した後に放出された中性子捕獲即発ガンマ線であると考えられる。そのため、バックグラウンドガンマ線の低減のため、ゲルマニウム検出器の周囲を厚さ10cmの鉛を用いて遮蔽した。その結果、即発ガンマ線のバックグラウンドは抑制され、 Pbの共鳴散乱ガンマ線を観測することができた。
Pbの共鳴散乱ガンマ線を観測することができた。
Omer, M.; 静間 俊行*; 羽島 良一*; 小泉 光生
第43回日本核物質管理学会年次大会会議論文集(インターネット), 3 Pages, 2022/11
Gamma-rays originated from laser Compton scattering (LCS) are convenient photon sources for nondestructive interrogation of nuclear materials. LCS can be used with nuclear resonance fluorescence (NRF) and X-ray fluorescence (XRF), the two of which are considered photon-based active interrogation techniques. However, an accurate estimation of the incident LCS  -ray flux is crucial. The
-ray flux is crucial. The  -ray flux is customarily measured using high purity germanium (HPGe) detectors, usually calibrated using standard point-like radioactive
-ray flux is customarily measured using high purity germanium (HPGe) detectors, usually calibrated using standard point-like radioactive  -ray sources. These standard sources are entirely different from LCS beams in terms of detection geometry. Therefore, the calibration process must be corrected to meet the LCS beam conditions. Here, we demonstrate how to implement the required corrections and provide experimental validation of these corrections.
-ray sources. These standard sources are entirely different from LCS beams in terms of detection geometry. Therefore, the calibration process must be corrected to meet the LCS beam conditions. Here, we demonstrate how to implement the required corrections and provide experimental validation of these corrections.
Omer, M.; 静間 俊行*; 羽島 良一*; 小泉 光生
Radiation Physics and Chemistry, 198, p.110241_1 - 110241_7, 2022/09
被引用回数:2 パーセンタイル:48.47(Chemistry, Physical)In beam geometries where a directed  -ray beam hits the surface of a coaxial high purity germanium detector (HPGe), the detector efficiency is sensitive to the position where
-ray beam hits the surface of a coaxial high purity germanium detector (HPGe), the detector efficiency is sensitive to the position where  -rays initially hit the detector surface because the structure of the detector is nonuniform. This may cause inaccuracy of the detector efficiency when measured using standard sources that are point-like sources emitting
-rays initially hit the detector surface because the structure of the detector is nonuniform. This may cause inaccuracy of the detector efficiency when measured using standard sources that are point-like sources emitting  -rays isotropically. Obtaining a precise estimation of the full energy peak efficiency of the coaxial HPGe detector in the beam geometry for on-axis and off-axis measurements requires a Monte Carlo simulation. We performed a Monte Carlo simulation that calculates the detector efficiency in the beam geometry. The effects of the off-axis distance and
-rays isotropically. Obtaining a precise estimation of the full energy peak efficiency of the coaxial HPGe detector in the beam geometry for on-axis and off-axis measurements requires a Monte Carlo simulation. We performed a Monte Carlo simulation that calculates the detector efficiency in the beam geometry. The effects of the off-axis distance and  -ray beam size on the efficiency are quantitatively analyzed. We found that the intrinsic efficiency in the beam geometry is maximized when the beam hits the detector at specific off-axis distances. Our Monte Carlo calculations have been supported by a nuclear resonance fluorescence experiment using laser Compton scattering
-ray beam size on the efficiency are quantitatively analyzed. We found that the intrinsic efficiency in the beam geometry is maximized when the beam hits the detector at specific off-axis distances. Our Monte Carlo calculations have been supported by a nuclear resonance fluorescence experiment using laser Compton scattering  -ray beam.
-ray beam.
 -ray beam
-ray beamOmer, M.; 静間 俊行*; 羽島 良一*
Nuclear Instruments and Methods in Physics Research A, 951, p.162998_1 - 162998_6, 2020/01
被引用回数:1 パーセンタイル:12.95(Instruments & Instrumentation)Compton scattering of a single-energy  -ray results in a one-to-one relationship between the incident and scattered photon energies. This relationship is altered when the incident beam has a definite energy distribution because of the broadening occurring in the energy distribution upon Compton scattering. This broadening causes a change in the spectral density of the Compton-scattered spectra. To restore the spectral density, the energy distribution of the scattered radiation must be manifested as a function of the scattering kinematics. Here, we propose a simple analytic way to calculate the energy spread of the scattered photons in terms of the geometry of the scattering process and the energy spread of the incident photon beam. The predictions of the model agree with measurements of Compton scattering of quasi-monochromatic
-ray results in a one-to-one relationship between the incident and scattered photon energies. This relationship is altered when the incident beam has a definite energy distribution because of the broadening occurring in the energy distribution upon Compton scattering. This broadening causes a change in the spectral density of the Compton-scattered spectra. To restore the spectral density, the energy distribution of the scattered radiation must be manifested as a function of the scattering kinematics. Here, we propose a simple analytic way to calculate the energy spread of the scattered photons in terms of the geometry of the scattering process and the energy spread of the incident photon beam. The predictions of the model agree with measurements of Compton scattering of quasi-monochromatic  -ray beams, carried out at the High Intensity
-ray beams, carried out at the High Intensity  -ray Source (HI
-ray Source (HI S) facility, Duke University. As a benchmark of our method, we measured the intensity profile of energy-distributed
S) facility, Duke University. As a benchmark of our method, we measured the intensity profile of energy-distributed  -ray beams by direct measurements as well as by Compton scattering. We found that only when the spectral density of the scattered radiation is restored, the measured intensity profile agrees with the actual profile of the incident beam. The proposed method can continuously measure the flux of an energy-distributed
-ray beams by direct measurements as well as by Compton scattering. We found that only when the spectral density of the scattered radiation is restored, the measured intensity profile agrees with the actual profile of the incident beam. The proposed method can continuously measure the flux of an energy-distributed  -ray beams in the real time and on a bin-by-bin basis. Such online monitoring of
-ray beams in the real time and on a bin-by-bin basis. Such online monitoring of  -ray beams is indispensable for in-beam measurements and applications. This work was supported by the subsidiary for promotion of strengthening nuclear security or the like of the Ministry of Education, Culture, Sports, Science, and Technology (MEXT), Japan.
-ray beams is indispensable for in-beam measurements and applications. This work was supported by the subsidiary for promotion of strengthening nuclear security or the like of the Ministry of Education, Culture, Sports, Science, and Technology (MEXT), Japan.
 -rays elastic scattering by Monte Carlo simulation
-rays elastic scattering by Monte Carlo simulationOmer, M.; 羽島 良一*
New Journal of Physics (Internet), 21(11), p.113006_1 - 113006_10, 2019/11
被引用回数:5 パーセンタイル:41.86(Physics, Multidisciplinary)Nuclear resonance fluorescence (NRF) is a promising technique for nondestructive assay (NDA) of nuclear materials. Its strength is improved when polarized  -ray beams are used as probes because the polarized
-ray beams are used as probes because the polarized  -rays provide an asymmetry in the intensity of the scattered photons. Nonetheless, NRF interaction takes place with other interactions such as elastic scattering of
-rays provide an asymmetry in the intensity of the scattered photons. Nonetheless, NRF interaction takes place with other interactions such as elastic scattering of  -rays. These interactions are unavoidable background which may limit the sensitivity of the NRF technique. Therefore, estimating polarization effects of elastic scattering is a significant factor in assessing the NRF method. Here, we implement a new Monte Carlo simulation to account for polarization effects of the elastic scattering. The simulation is based on explicit expressions driven in the Stokes parameters formalism. The scattering amplitudes of Rayleigh, nuclear Thomson, and Delbr
-rays. These interactions are unavoidable background which may limit the sensitivity of the NRF technique. Therefore, estimating polarization effects of elastic scattering is a significant factor in assessing the NRF method. Here, we implement a new Monte Carlo simulation to account for polarization effects of the elastic scattering. The simulation is based on explicit expressions driven in the Stokes parameters formalism. The scattering amplitudes of Rayleigh, nuclear Thomson, and Delbr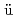 ck scattering processes have been superimposed into a two-orthogonal set of complex amplitudes. This set is then exploited to construct the core of the simulation in a way such that the simulation could handle arbitrary polarization states of the incoming beam and correspondingly generate polarization states for the outgoing beam. This work was supported by the subsidiary for promotion of strengthening nuclear security or the like of the Ministry of Education, Culture, Sports, Science, and Technology (MEXT), Japan.
ck scattering processes have been superimposed into a two-orthogonal set of complex amplitudes. This set is then exploited to construct the core of the simulation in a way such that the simulation could handle arbitrary polarization states of the incoming beam and correspondingly generate polarization states for the outgoing beam. This work was supported by the subsidiary for promotion of strengthening nuclear security or the like of the Ministry of Education, Culture, Sports, Science, and Technology (MEXT), Japan.
Omer, M.; 静間 俊行*; 羽島 良一*; 小泉 光生
日本核物質管理学会第40回年次大会プロシーディングス集, p.59 - 62, 2019/11
Nuclear resonance fluorescence (NRF) is a phenomenon that a nuclide-specific  -ray is resonantly absorbed and re-emitted. This method is considered useful for the nondestructive detection of nuclear materials. In order to demonstrate how accurate the NRF method is able to measure the isotopic abundance, we performed NRF experiments on natural tungsten as a surrogate of nuclear materials at the High Intensity
-ray is resonantly absorbed and re-emitted. This method is considered useful for the nondestructive detection of nuclear materials. In order to demonstrate how accurate the NRF method is able to measure the isotopic abundance, we performed NRF experiments on natural tungsten as a surrogate of nuclear materials at the High Intensity  -ray Source (HI
-ray Source (HI S) facility, Duke University. Our results show that the relative deviations between the reference and measured abundances are less than
S) facility, Duke University. Our results show that the relative deviations between the reference and measured abundances are less than  4%. This work was supported by the subsidiary for promotion of strengthening nuclear security or the like of the Ministry of Education, Culture, Sports, Science, and Technology (MEXT), Japan.
4%. This work was supported by the subsidiary for promotion of strengthening nuclear security or the like of the Ministry of Education, Culture, Sports, Science, and Technology (MEXT), Japan.
 Al; Its low-lying multiplet structure
Al; Its low-lying multiplet structure静間 俊行*; Omer, M.; 羽島 良一*; 清水 則孝*; 宇都野 穣
Physical Review C, 100(1), p.014307_1 - 014307_6, 2019/07
被引用回数:7 パーセンタイル:58.41(Physics, Nuclear)Nuclear resonance fluorescence (NRF) is a promising technique for the nondestructive assay (NDA) of nuclear materials. One of the features of the NRF is the angular distribution of the emitted photons in response to a linearly polarized incident beam. Here we irradiate the calibration standard of  Al to linearly polarized beam. The spin and parity of the 3.004-MeV level in
Al to linearly polarized beam. The spin and parity of the 3.004-MeV level in  Al have been determined by measuring the angular correlation function of radiation emitted from levels populated by resonant absorption of polarized photons. The nuclear resonance fluorescence experiments were carried out at the High Intensity
Al have been determined by measuring the angular correlation function of radiation emitted from levels populated by resonant absorption of polarized photons. The nuclear resonance fluorescence experiments were carried out at the High Intensity  -ray Source (HI
-ray Source (HI S) facility at Duke University using quasi-monoenergetic linearly polarized photon beams. The spin and parity of levels in
S) facility at Duke University using quasi-monoenergetic linearly polarized photon beams. The spin and parity of levels in  Al were deduced from a comparison of the measured angular distribution ratios and azimuthal intensity asymmetries with theoretical predictions. The observed resonance properties were compared with shell model calculations using the universal sd interaction. The Monte Carlo shell model calculations were also performed to investigate low-energy structure of
Al were deduced from a comparison of the measured angular distribution ratios and azimuthal intensity asymmetries with theoretical predictions. The observed resonance properties were compared with shell model calculations using the universal sd interaction. The Monte Carlo shell model calculations were also performed to investigate low-energy structure of  Al. This work was supported by the subsidiary for promotion of strengthening nuclear security or the like of the Ministry of Education, Culture, Sports, Science, and Technology (MEXT), Japan.
Al. This work was supported by the subsidiary for promotion of strengthening nuclear security or the like of the Ministry of Education, Culture, Sports, Science, and Technology (MEXT), Japan.
 -rays
-raysOmer, M.; 羽島 良一*
JAEA-Data/Code 2018-007, 32 Pages, 2018/06
原子核蛍光共鳴散乱(NRF)は、核物質の非破壊検査(NDA)において有用な技術である。NRFは同位体に固有のエネルギーをもったガンマ線と物質の相互作用であることから、同位体を識別したNDAを実現できる。しかしながら、NRFと競合する他の光核相互作用が存在し、そのため、NRFによるNDAの測定性能が制限される可能性がある。競合する相互作用のうち原子核によるガンマ線の弾性散乱(デルブリュック散乱)は、これまでのモンテカルロコードでは考慮されていなかった。日本原子力研究開発機構では、平成27年度からNRFに基づくNDAシステムの開発プログラムを開始し、その一環としてガンマ線の弾性散乱がNRF測定に及ぼす影響を評価するために、Geant4にガンマ線の弾性散乱を追加するためのコードを新規に開発した。今回刊行するJAEA-データ/コードレポートでは、シミュレーションコードの詳細な説明と、コード入力に用いたガンマ線弾性散乱断面積、および、コードの検証と妥当性確認に用いた計算結果を示す。このレポートを公開することで、当該コードの信頼性向上に必要なユーザーからのフィードバックの機会が得られる。本研究は文部科学省の核セキュリティ強化等推進事業費補助金の支援を受けた。
 ck scattering in GEANT4
ck scattering in GEANT4Omer, M.; 羽島 良一*
Nuclear Instruments and Methods in Physics Research B, 405, p.43 - 49, 2017/08
被引用回数:8 パーセンタイル:60.68(Instruments & Instrumentation)原子核あるいは原子による 線の弾性散乱は、
線の弾性散乱は、 線と物質の相互作用に関連付けられ、レイリー散乱、核トムソン散乱及びデルブリュック散乱がある。
線と物質の相互作用に関連付けられ、レイリー散乱、核トムソン散乱及びデルブリュック散乱がある。 線の弾性散乱を模擬するモンテカルロシミュレーションコードのほとんどは、現状では弾性散乱の全体像をカバーしていなく、レイリー散乱の寄与のみを取り扱い、核トムソン散乱及びデルブリュック散乱は無視されている。われわれは弾性散乱を模擬(シミュレート)するために、最も一般的なオープンソースのGeant4に、レイリー散乱に加えて、核トムソン散乱及びデルブリュック散乱を取込んだコードを開発した。この際のシミュレーションでは、これまでのフォームファクタ近似に基づくデータに代り、二次散乱行列に基づく微分散乱断面積を使っている。また、これらの3つの散乱プロセスの重ね合わせは、散乱振幅の複素数表示を考慮して慎重に行わった。このシミュレーションは、
線の弾性散乱を模擬するモンテカルロシミュレーションコードのほとんどは、現状では弾性散乱の全体像をカバーしていなく、レイリー散乱の寄与のみを取り扱い、核トムソン散乱及びデルブリュック散乱は無視されている。われわれは弾性散乱を模擬(シミュレート)するために、最も一般的なオープンソースのGeant4に、レイリー散乱に加えて、核トムソン散乱及びデルブリュック散乱を取込んだコードを開発した。この際のシミュレーションでは、これまでのフォームファクタ近似に基づくデータに代り、二次散乱行列に基づく微分散乱断面積を使っている。また、これらの3つの散乱プロセスの重ね合わせは、散乱振幅の複素数表示を考慮して慎重に行わった。このシミュレーションは、 線エネルギー範囲0.01
線エネルギー範囲0.01 E
E 3MeVと1
3MeVと1 Z
Z 99の原子番号を持つすべての元素をカバーしている。さらに、われわれは、以前の実験で測定された微分断面積とシミュレーションから得られる微分断面積とを比較することによって、シミュレーションを検証した。この検証では、シミュレーションの結果は、実験の測定値と良い一致を示している。実験とシミュレーションとの違いは、
99の原子番号を持つすべての元素をカバーしている。さらに、われわれは、以前の実験で測定された微分断面積とシミュレーションから得られる微分断面積とを比較することによって、シミュレーションを検証した。この検証では、シミュレーションの結果は、実験の測定値と良い一致を示している。実験とシミュレーションとの違いは、 線エネルギーが2.754MeVで、ウランで21%、鉛で24%、タンタルで3%、及びセリウムで8%であった。高Z.(ウランや鉛)における比較的大きな差は、デルブリュック散乱振幅に対するクーロン補正により説明できる。
線エネルギーが2.754MeVで、ウランで21%、鉛で24%、タンタルで3%、及びセリウムで8%であった。高Z.(ウランや鉛)における比較的大きな差は、デルブリュック散乱振幅に対するクーロン補正により説明できる。
 -ray polarization in NRF-based nondestructive assay of nuclear materials
-ray polarization in NRF-based nondestructive assay of nuclear materialsOmer, M.; 羽島 良一*; 静間 俊行*; 小泉 光生
Proceedings of INMM 58th Annual Meeting (Internet), 7 Pages, 2017/07
核共鳴蛍光(NRF)は、核の電気双極子励起および/または磁気双極子励起が起こるプロセスである。これらの励起はそれぞれの原子核の固有のシグネチャであるため、NRFは核物質の非破壊検知出と分析・測定のための実用的なツールを提供する。偏極 線ビームを使用すると、原子核の励起の性質を区別することは容易である。散乱角90
線ビームを使用すると、原子核の励起の性質を区別することは容易である。散乱角90 では、電気双極子励起は偏光面に対して垂直に放射されるが、磁気双極子励起は入射ビーム偏光と同じ平面内で放射される。対照的に、原子との他の
では、電気双極子励起は偏光面に対して垂直に放射されるが、磁気双極子励起は入射ビーム偏光と同じ平面内で放射される。対照的に、原子との他の 線相互作用は、入射ビームの偏光に関して異なる応答を示すことがある。例えば、弾性散乱は入射ビームの偏光方向において他の方向より約60%低い放射強度を与えることが期待される。光子エネルギーに基づいてNRFと弾性散乱とを分離することができないので、この事実は、NRF技術の感度に大きな影響を及ぼす。我々は、2.04MeVのエネルギーを有する100%直線偏光
線相互作用は、入射ビームの偏光に関して異なる応答を示すことがある。例えば、弾性散乱は入射ビームの偏光方向において他の方向より約60%低い放射強度を与えることが期待される。光子エネルギーに基づいてNRFと弾性散乱とを分離することができないので、この事実は、NRF技術の感度に大きな影響を及ぼす。我々は、2.04MeVのエネルギーを有する100%直線偏光 線を用いて行った
線を用いて行った Uにおける光子散乱実験の結果について、弾性散乱が入射ビームの偏光にどのように応答するかを実証する。したがって、我々は、NRF測定における入射光子の偏光の影響を解決することができる。
Uにおける光子散乱実験の結果について、弾性散乱が入射ビームの偏光にどのように応答するかを実証する。したがって、我々は、NRF測定における入射光子の偏光の影響を解決することができる。
瀬谷 道夫; 羽島 良一*; 呉田 昌俊
Proceedings of INMM 58th Annual Meeting (Internet), 10 Pages, 2017/07
港湾で扱われる貨物コンテナは容積が大きく重量物も運べるため、核物質が隠されて持ち込まれる危険性が高い。核セキュリティを強化する上では、重遮へい物中の規制外核物質の確実な検知、及び、重遮へい物体の安全な解体により中から核物質を取出すことが不可欠である。このための対応として、確実な核物質検知システムの導入、検知物の正確な内部構造把握、及び核物質性状把握(核兵器か否か、爆発物の混入等)が要求され、これらの情報を使うことにより検知物の安全な解体と核物質の取出しが可能となる。この発表では、X線スキャン装置と単色線利用NRFベース非破壊検知装置の組合せを確実な核物質検知システム及び内部検査システムとして、また、取出された核物質部分に関する内部検査機能を持つものとして、小型中性子線源(D-T中性子源)を用いるアクティブNDA装置を提案する。
瀬谷 道夫; 羽島 良一*; 呉田 昌俊
第37回核物質管理学会日本支部年次大会論文集(CD-ROM), 10 Pages, 2017/02
港湾で扱われる貨物コンテナは容積が大きく重量物も運べるため、核物質が隠されて持ち込まれる危険性が高い。核セキュリティを強化する上では、重遮へい物中の規制外核物質の確実な検知、及び、重遮へい物体の安全な解体により中から核物質を取出すことが不可欠である。このための対応として、(1)確実な核物質検知システムの導入、(2)検知物の正確な内部構造把握、及び(3)核物質性状把握(核兵器か否か、爆発物の混入等)が要求され、これらの情報を使うことにより検知物の安全な解体と核物質の取出しが可能となる。この発表では、(1)については、X線スキャン装置と単色 線利用NRFベース非破壊検知装置の組合せを提案する。後者の装置は重遮へい体に対しては、(2)及び(3)の機能も有している。また、取出された核物質部分に関する(2)及び(3)の機能を持つものとして、小型中性子線源(D-T中性子源)を用いるアクティブNDA装置を提案する。
線利用NRFベース非破壊検知装置の組合せを提案する。後者の装置は重遮へい体に対しては、(2)及び(3)の機能も有している。また、取出された核物質部分に関する(2)及び(3)の機能を持つものとして、小型中性子線源(D-T中性子源)を用いるアクティブNDA装置を提案する。
 -ray beams
-ray beams早川 岳人; 宮本 修治*; 羽島 良一; 静間 俊行; 天野 壮*; 橋本 智*; 三澤 毅*
Journal of Nuclear Science and Technology, 53(12), p.2064 - 2071, 2016/12
被引用回数:6 パーセンタイル:48.81(Nuclear Science & Technology)準単色の 線による光核反応を用いた選択的な同位体変換法を提案する。この手法は、
線による光核反応を用いた選択的な同位体変換法を提案する。この手法は、 Zr,
Zr,  Pd、ないし
Pd、ないし Seのような長寿命核分裂生成物(LLFP)の粒子閾値が、同じ元素の他の安定同位体の粒子閾値より低いという事実に基づく。そのため、この手法では、ターゲット物質がLLFP以外に安定同位体を含んでいたとしても、新しくLLFPが生成されないという傑出した特徴を有する。レーザーコンプトン散乱
Seのような長寿命核分裂生成物(LLFP)の粒子閾値が、同じ元素の他の安定同位体の粒子閾値より低いという事実に基づく。そのため、この手法では、ターゲット物質がLLFP以外に安定同位体を含んでいたとしても、新しくLLFPが生成されないという傑出した特徴を有する。レーザーコンプトン散乱 線と原子炉の中性子捕獲反応
線と原子炉の中性子捕獲反応 線がこの手法に適した
線がこの手法に適した 線源である。
線源である。
 Ta in the region of the scissors mode
Ta in the region of the scissors modeAngell, C.; 羽島 良一; 静間 俊行; Ludewigt, B.*; Quiter, B. J.*
Physical Review Letters, 117(14), p.142501_1 - 142501_5, 2016/09
被引用回数:7 パーセンタイル:48.53(Physics, Multidisciplinary)In recent measurements of the scissors mode in radiative decay experiments, transition strengths were observed that were double that expected from theory and systematics well established from measurements on the radiative excitation channel, that is, using nuclear resonance fluorescence (NRF). Additional strength as measured with NRF can only present itself as heretofore unobserved branching or fragmentation of the scissors mode. Such a possibility was investigated in a transmission NRF measurement on the deformed, odd-mass  Ta, using a quasi-monoenergetic
Ta, using a quasi-monoenergetic  -ray beam at two beam energies, and additionally informing applications using transmission NRF to assay or detect odd-mass fissile isotopes. An anomalously large branching,
-ray beam at two beam energies, and additionally informing applications using transmission NRF to assay or detect odd-mass fissile isotopes. An anomalously large branching,  70%, of small resonances to excited states was discovered. In contrast, previous studies using NRF of the scissors-mode strength in odd-mass nuclei assumed no branching existed. This branching, if present at all energies, combined with the observed highly-fragmented elastic strength would reconcile the scissors-mode strength observed in NRF measurements with the expectations for enhanced scissors-mode strength from radiative decay experiments.
70%, of small resonances to excited states was discovered. In contrast, previous studies using NRF of the scissors-mode strength in odd-mass nuclei assumed no branching existed. This branching, if present at all energies, combined with the observed highly-fragmented elastic strength would reconcile the scissors-mode strength observed in NRF measurements with the expectations for enhanced scissors-mode strength from radiative decay experiments.
Omer, M.; 羽島 良一*; Angell, C.*; 静間 俊行*; 早川 岳人*; 瀬谷 道夫; 小泉 光生
Proceedings of INMM 57th Annual Meeting (Internet), 9 Pages, 2016/07
核種の核共鳴蛍光反応過程で放出される核種固有の 線は、核物質の非破壊検知及び測定の非常に良い方法を提供する。われわれは、
線は、核物質の非破壊検知及び測定の非常に良い方法を提供する。われわれは、 線非破壊検知及び測定に関連する技術を開発している。核共鳴蛍光反応をシミュレートするモンテ・カルロコードは非破壊測定装置の設計及び評価において不可欠なものである。われわれは、そのため、Geant4コードをベースとするシミュレーションコードNRFGeant4を開発している。核共鳴蛍光反応実験においては、一般に高濃度測定対象物が使われる。この場合は核共鳴蛍光反応
線非破壊検知及び測定に関連する技術を開発している。核共鳴蛍光反応をシミュレートするモンテ・カルロコードは非破壊測定装置の設計及び評価において不可欠なものである。われわれは、そのため、Geant4コードをベースとするシミュレーションコードNRFGeant4を開発している。核共鳴蛍光反応実験においては、一般に高濃度測定対象物が使われる。この場合は核共鳴蛍光反応 線が強く、測定しやすいためである。それに対して実際の状況では、測定したい(興味のある)核種が小さい組成比でしか含まれていないことがある。このような状況では、核共鳴蛍光反応
線が強く、測定しやすいためである。それに対して実際の状況では、測定したい(興味のある)核種が小さい組成比でしか含まれていないことがある。このような状況では、核共鳴蛍光反応 線の測定が、他の反応(例として、(核共鳴反応と同じような)弾性散乱)からの影響を受けて困難となる。例えば、典型的な核燃料のペレットは90%程度の
線の測定が、他の反応(例として、(核共鳴反応と同じような)弾性散乱)からの影響を受けて困難となる。例えば、典型的な核燃料のペレットは90%程度の Uを母材として含むが、測定対象として興味のある
Uを母材として含むが、測定対象として興味のある Puは約1%以下の割合でしか含まれていない。このような場合、
Puは約1%以下の割合でしか含まれていない。このような場合、 Puからの核共鳴蛍光
Puからの核共鳴蛍光 線の測定においては、
線の測定においては、 Uの弾性散乱からの強い
Uの弾性散乱からの強い 線バックグランドが発生することとなる。それゆえ、母材の弾性散乱(
線バックグランドが発生することとなる。それゆえ、母材の弾性散乱( 線)強度を評価することは、測定しようとする(興味のある)核種の正確な測定においては不可欠なこととなる。現段階においては、弾性散乱の満足のゆく評価は(ある計算を除いて)できていない。われわれのこの研究では、弾性散乱事象を取込むように、シミュレーションコードの高度化を行っている。
線)強度を評価することは、測定しようとする(興味のある)核種の正確な測定においては不可欠なこととなる。現段階においては、弾性散乱の満足のゆく評価は(ある計算を除いて)できていない。われわれのこの研究では、弾性散乱事象を取込むように、シミュレーションコードの高度化を行っている。
羽島 良一; 藤原 守
Physical Review Accelerators and Beams (Internet), 19(2), p.020702_1 - 020702_9, 2016/02
被引用回数:7 パーセンタイル:48.70(Physics, Nuclear)共振型X線自由電子レーザーを用いて、狭帯域のGeV光子( 線)を発生する方法を提案する。コンプトン散乱の物理から、発生する光子は、エネルギー幅0.1%の狭帯域となる。本
線)を発生する方法を提案する。コンプトン散乱の物理から、発生する光子は、エネルギー幅0.1%の狭帯域となる。本 線光源のフラックス,スペクトル,偏極,エネルギー可変性などについて議論する。
線光源のフラックス,スペクトル,偏極,エネルギー可変性などについて議論する。
羽島 良一; 照沼 信浩*
Isotope News, (741), p.16 - 20, 2016/01
高エネルギー電子とレーザーの衝突散乱によるX線,  線の発生は、レーザー・コンプトン散乱と呼ばれる。発生されるX線,
線の発生は、レーザー・コンプトン散乱と呼ばれる。発生されるX線,  線は、準単色,エネルギー可変,偏極可変の特長をもつことから、医学用イメージングや核物質の非破壊測定など多くの分野で利用が期待されている。本報告では、エネルギー回収型リニアック(コンパクトERL)におけるレーザー・コンプトン散乱X線の発生について、装置の概要、X線の測定、イメージングの予備実験の結果について述べる。
線は、準単色,エネルギー可変,偏極可変の特長をもつことから、医学用イメージングや核物質の非破壊測定など多くの分野で利用が期待されている。本報告では、エネルギー回収型リニアック(コンパクトERL)におけるレーザー・コンプトン散乱X線の発生について、装置の概要、X線の測定、イメージングの予備実験の結果について述べる。