Low temperature hetero-epitaxy of ferromagnetic silicide on Ge substrates for spin-transistor application
強磁性体シリサイド/Geの低温エピタキシャル成長とスピントランジスタ
安藤 裕一郎*; 上田 公二*; 熊野 守*; 佐道 泰造*; 鳴海 一雅; 前田 佳均; 宮尾 正信*
Ando, Yuichiro*; Ueda, Koji*; Kumano, Mamoru*; Sado, Taizo*; Narumi, Kazumasa; Maeda, Yoshihito; Miyao, Masanobu*
スピン偏極強磁性体シリサイドDO3型Fe Siは、格子定数(0.565nm)がGeの格子定数(0.565nm)とほぼ一致しており、Ge基板上におけるFe
Siは、格子定数(0.565nm)がGeの格子定数(0.565nm)とほぼ一致しており、Ge基板上におけるFe Si層の高品位エピタキシャル成長が可能と期待される。本研究では、分子線エピタキシャル成長法を用いて、Fe/Si組成比及び成長温度がFe
Si層の高品位エピタキシャル成長が可能と期待される。本研究では、分子線エピタキシャル成長法を用いて、Fe/Si組成比及び成長温度がFe Si/Geの結晶性に与える効果を系統的に検討した。その結果、Fe/Si組成比を化学量論比(Fe:Si=3:1)とし、成長温度を低温化(
Si/Geの結晶性に与える効果を系統的に検討した。その結果、Fe/Si組成比を化学量論比(Fe:Si=3:1)とし、成長温度を低温化( 300
300 C)することで、結晶性が高く(ラザフォード後方散乱法による最小散乱収率
C)することで、結晶性が高く(ラザフォード後方散乱法による最小散乱収率
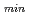 : 2
: 2 3%)かつ界面が原子レベルで平坦なFe
3%)かつ界面が原子レベルで平坦なFe Si/Ge積層構造を実現した。さらに、この積層構造は、400
Si/Ge積層構造を実現した。さらに、この積層構造は、400 Cまでの熱処理プロセスでは劣化しないことを確認した。
Cまでの熱処理プロセスでは劣化しないことを確認した。
Ferromagnetic silicide Fe Si (Currie temperature: 840 K) has three phases (A2, B2, and DO3), where the DO3-type is an ordered phase and calculated to be spin-polarized at the Fermi level. In addition, the lattice constant (0.565 nm) of Fe
Si (Currie temperature: 840 K) has three phases (A2, B2, and DO3), where the DO3-type is an ordered phase and calculated to be spin-polarized at the Fermi level. In addition, the lattice constant (0.565 nm) of Fe Si is almost completely equal to that (0.565 nm) of Ge. Therefore, atomically controlled epitaxial growth of Fe
Si is almost completely equal to that (0.565 nm) of Ge. Therefore, atomically controlled epitaxial growth of Fe Si is expected on Ge. This will be a powerful tool to realize Ge channel spin transistors with ultrahigh speed operation and ultralow power consumption. This paper reviews our recent progress in novel epitaxial growth of Fe
Si is expected on Ge. This will be a powerful tool to realize Ge channel spin transistors with ultrahigh speed operation and ultralow power consumption. This paper reviews our recent progress in novel epitaxial growth of Fe Si on Ge for spintronics application.
Si on Ge for spintronics application.