Identification of PprM; A Modulator of the PprI-dependent DNA damage response in 
Oba, Hirofumi; Sato, Katsuya; Sghaier, H.; Yanagisawa, Tadashi*; Narumi, Issei
 possesses a DNA damage response mechanism that acts via the PprI protein to induce RecA and PprA proteins, both of which are necessary in conferring extreme radioresistance. In an effort to further delineate the nature of the DNA damage response mechanism in
possesses a DNA damage response mechanism that acts via the PprI protein to induce RecA and PprA proteins, both of which are necessary in conferring extreme radioresistance. In an effort to further delineate the nature of the DNA damage response mechanism in  , we set out to identify novel components of the PprI-dependent signal transduction pathway in response to radiation stress. Here we demonstrate the discovery of a novel regulatory protein, PprM (a modulator of the PprI-dependent DNA damage response), which is a homolog of cold shock protein (Csp). Disruption of the
, we set out to identify novel components of the PprI-dependent signal transduction pathway in response to radiation stress. Here we demonstrate the discovery of a novel regulatory protein, PprM (a modulator of the PprI-dependent DNA damage response), which is a homolog of cold shock protein (Csp). Disruption of the 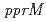 gene rendered
gene rendered  significantly sensitive to
significantly sensitive to  -rays. PprM regulates the induction of PprA but not that of RecA. PprM belongs in a distinct clade of a subfamily together with Csp homologs from
-rays. PprM regulates the induction of PprA but not that of RecA. PprM belongs in a distinct clade of a subfamily together with Csp homologs from  and
and 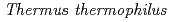 . Purified PprM is present as a homodimer under physiological conditions, as the case with
. Purified PprM is present as a homodimer under physiological conditions, as the case with  CspD. The
CspD. The 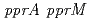 double-disruptant strain exhibited higher sensitivity than the
double-disruptant strain exhibited higher sensitivity than the  or
or 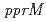 single disruptant strains, suggesting that PprM regulates other hitherto unknown protein(s) important for radioresistance besides PprA. This study strongly suggests that PprM is involved in the radiation response mediated by PprI in
single disruptant strains, suggesting that PprM regulates other hitherto unknown protein(s) important for radioresistance besides PprA. This study strongly suggests that PprM is involved in the radiation response mediated by PprI in  .
.