Toyocamycin specifically inhibits auxin signaling mediated by SCF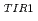 pathway
pathway
トヨカマイシンはSCF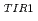 経路のオーキシン情報伝達を阻害する
経路のオーキシン情報伝達を阻害する
林 謙一郎*; 神尾 秀一*; 大野 豊; Townsend, L.*; 野崎 浩*
Hayashi, Kenichiro*; Kamio, Shuichi*; Ono, Yutaka; Townsend, L.*; Nozaki, Hiroshi*
Toyocamycin, a nucleoside-type antibiotic, was identified as auxin signaling inhibitor in a screen of microbial extracts for inhibition of the auxin-inducible reporter gene assay. Toyocamycin specifically inhibited auxin-responsive gene expression, but did not affect other hormone-inducible gene expression. Toyocamycin also blocked auxin-enhanced degradation of the Aux/IAA repressor modulated by the SCF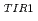 ubiquitin-proteasome pathway without inhibiting proteolytic activity of proteasome. Furthermore, toyocamycin inhibited auxin-induced lateral root formation and epinastic growth of cotyledon in the Arabidopsis thaliana plant. This evidence suggested that toyocamycin would act on the ubiquitination process regulated by SCF
ubiquitin-proteasome pathway without inhibiting proteolytic activity of proteasome. Furthermore, toyocamycin inhibited auxin-induced lateral root formation and epinastic growth of cotyledon in the Arabidopsis thaliana plant. This evidence suggested that toyocamycin would act on the ubiquitination process regulated by SCF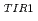 machineries. To address the structural requirements for the specific activity of toyocamycin on auxin signaling, the structure-activity relationships of nine toyocamycin-related compounds, including sangivamycin and tubercidin, were investigated.
machineries. To address the structural requirements for the specific activity of toyocamycin on auxin signaling, the structure-activity relationships of nine toyocamycin-related compounds, including sangivamycin and tubercidin, were investigated.