Beta-decay measurement of 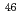 Cr
Cr
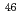 Crのベータ崩壊の測定
Crのベータ崩壊の測定
若林 泰生; 山口 英斉*; 橋本 尚志*; 早川 勢也*; 栗原 佑蔵*; Binh, D.*; Kahl, D.*; 久保野 茂*; 西村 俊二*; 郷農 靖之*; 壽賀 正城*; 藤田 佳孝*
Wakabayashi, Yasuo; Yamaguchi, Hidetoshi*; Hashimoto, Takashi*; Hayakawa, Seiya*; Kurihara, Yuzo*; Binh, D.*; Kahl, D.*; Kubono, Shigeru*; Nishimura, Shunji*; Gono, Yasuyuki*; Suga, Masaki*; Fujita, Yoshitaka*
For the rapid proton capture process (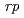 -process) in X-ray bursts and the core-collapse stage of supernovae, proton-rich
-process) in X-ray bursts and the core-collapse stage of supernovae, proton-rich 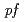 -shell nuclei far from the line of stability play important roles. Studies of the feeding ratios and half-lives of the
-shell nuclei far from the line of stability play important roles. Studies of the feeding ratios and half-lives of the  and electron capture decays of these proton-rich
and electron capture decays of these proton-rich 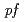 -shell nuclei are of great astrophysical interest not only for nucleosynthesis but also for Fermi and Gamow-Teller transition study. The experiment to measure the half life of
-shell nuclei are of great astrophysical interest not only for nucleosynthesis but also for Fermi and Gamow-Teller transition study. The experiment to measure the half life of  decay of
decay of 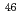 Cr was performed using the low-energy RI beam separator (CRIB) of the Center for Nuclear Study (CNS), University of Tokyo. The
Cr was performed using the low-energy RI beam separator (CRIB) of the Center for Nuclear Study (CNS), University of Tokyo. The 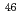 Cr particles were produced by the
Cr particles were produced by the  Ar +
Ar +  C fusion reaction. A natural C foil of 0.56 mg/cm
C fusion reaction. A natural C foil of 0.56 mg/cm was installed as the primary target. The
was installed as the primary target. The  Ar primary beam was accelerated up to 3.6 MeV/nucleon by the RIKEN AVF cyclotron. A double sided Si strip detector (DSSD) of 500-
Ar primary beam was accelerated up to 3.6 MeV/nucleon by the RIKEN AVF cyclotron. A double sided Si strip detector (DSSD) of 500- m thickness was used as a
m thickness was used as a  -ray detector. A Si detector of 1.5-mm thickness was placed just behind the DSSD for a
-ray detector. A Si detector of 1.5-mm thickness was placed just behind the DSSD for a  -ray detector. To measure
-ray detector. To measure  -delayed
-delayed  rays, 3 clover and 1 coaxial Ge detectors were set around the target chamber. The beam was pulsed to measure the half life of the
rays, 3 clover and 1 coaxial Ge detectors were set around the target chamber. The beam was pulsed to measure the half life of the  decay of
decay of 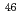 Cr. The
Cr. The  -delayed
-delayed  ray of
ray of 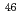 Cr was observed in this experiment. The experimental result will be discussed.
Cr was observed in this experiment. The experimental result will be discussed.