治療用重粒子イオンビームの放射線化学反応
Radiation chemical reactions in water radiolysis with therapeutic heavy ion beams
山下 真一
Yamashita, Shinichi
放射線医学総合研究所のHIMAC(Heavy Ion Medical Accelerator in Chiba)から供給される高エネルギー重粒子線による水の放射線分解について、生成物収率とトラック構造・ダイナミクスとの相関という観点から調べてきた。捕捉剤による転換を利用することで、広い範囲のLETのイオンビームに対して水和電子・OHラジカル・過酸化水素といった主要生成物の収率を測定してきた。メチルビオローゲン(MV)-ギ酸水溶液系では、近似的に水分解ラジカルの収率の総和と見なせるMVカチオンラジカルの収率を測り、その時間挙動からトラック内ダイナミクスについても検討した。また、モンテカルロ計算による測定結果の再現や、蛍光プローブを利用した高感度OHラジカル検出手法の開発についても簡潔に触れる。
Water radiolysis with heavy-ion beams of energies up to 28 GeV provided from HIMAC (Heavy Ion Medical Accelerator in Chiba), NIRS (National Institute of Radiological Sciences) has been investigated from the viewpoint of correlation of products yields with track structure and its dynamics. For wide variety of heavy-ion beams in terms of LET, velocity, charge, etc., primary yields of major products in water radiolysis, 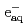 ,
,  OH and H
OH and H O
O , have been measured by employing scavenging method to convert transient water radicals into stable and easily detectable species. Temporal behavior of approximate sum of water radicals has also been experimentally measured by a scavenging method with methyl viologen cation and formate anion. A Monte-Carlo simulation code of water radiolysis developed by a group of Universit
, have been measured by employing scavenging method to convert transient water radicals into stable and easily detectable species. Temporal behavior of approximate sum of water radicals has also been experimentally measured by a scavenging method with methyl viologen cation and formate anion. A Monte-Carlo simulation code of water radiolysis developed by a group of Universit de Sherbrooke, Canada was complementally used in discussion of microscopic track structure and its dynamics. In addition, a fluorescent probe, 7-hydroxyl-coumarin-3-carboxylic acid, was utilized in sensitive
de Sherbrooke, Canada was complementally used in discussion of microscopic track structure and its dynamics. In addition, a fluorescent probe, 7-hydroxyl-coumarin-3-carboxylic acid, was utilized in sensitive  OH detection with HPLC connected fluorometry.
OH detection with HPLC connected fluorometry.