Spin-density wave near the vortex cores in the high-temperature superconductor Bi Sr
Sr CaCu
CaCu O
O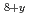
高温超伝導体Bi Sr
Sr CaCu
CaCu O
O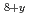 の渦糸コア付近のスピン密度波
の渦糸コア付近のスピン密度波
Mounce, A. M.*; Oh, S.*; Mukhopadhyay, S.*; Halperin, W. P.*; Reyes, A. P.*; Kuhns, P. L.*; 藤田 和博*; 石角 元志; 内田 慎一*
Mounce, A. M.*; Oh, S.*; Mukhopadhyay, S.*; Halperin, W. P.*; Reyes, A. P.*; Kuhns, P. L.*; Fujita, Kazuhiro*; Ishikado, Motoyuki; Uchida, Shinichi*
磁性と超伝導の競合は高温超伝導メカニズムの核心であり、それは磁束コア付近で最も顕著に見られる。渦の磁性を調べるためにわれわれはNMR(核磁気共鳴)スピン格子緩和分光法に基づいた空間分解プローブを開発した。この装置を用いたアプローチによってわれわれはBi Sr
Sr CaCu
CaCu O
O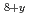 の磁束コアに伴うスピン密度波を発見した。それは走査型トンネル顕微鏡実験で報告された局所状態密度におけるチェッカーボードパターンと類似している。われわれはスピン変調振幅と磁束コアからの減衰長を
の磁束コアに伴うスピン密度波を発見した。それは走査型トンネル顕微鏡実験で報告された局所状態密度におけるチェッカーボードパターンと類似している。われわれはスピン変調振幅と磁束コアからの減衰長を =30Tまで決定した。
=30Tまで決定した。
Competition with magnetism is at the heart of high-temperature superconductivity, most intensely felt near a vortex core. To investigate vortex magnetism we have developed a spatially resolved probe based upon NMR spin-lattice-relaxation spectroscopy. With this approach we have found a spin-density wave associated with the vortex core in Bi Sr
Sr CaCu
CaCu O
O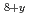 , similar to checkerboard patterns in the local density of electronic states reported from scanning tunneling microscope experiments. We have determined both the spin-modulation amplitude and decay length from the vortex core in fields up to
, similar to checkerboard patterns in the local density of electronic states reported from scanning tunneling microscope experiments. We have determined both the spin-modulation amplitude and decay length from the vortex core in fields up to  = 30 T.
= 30 T.