Strain and magnetic-field characterization of a bronze-route Nb Sn ITER wire; Benchmarking of strain measurement facilities at NIST and University of Twente
Sn ITER wire; Benchmarking of strain measurement facilities at NIST and University of Twente
ITER用ブロンズ法Nb Sn素線の歪み及び磁場特性; NIST及びTwente大学における歪み測定装置のベンチマーク
Sn素線の歪み及び磁場特性; NIST及びTwente大学における歪み測定装置のベンチマーク
Cheggour, N.*; Nijhuis, A.*; Krooshoop, H. J. G.*; Lu, X. F.*; Splett, J.*; Stauffer, T. C.*; Goodrich, L. F.*; Jewell, M. C.*; Devred, A.*; 名原 啓博
Cheggour, N.*; Nijhuis, A.*; Krooshoop, H. J. G.*; Lu, X. F.*; Splett, J.*; Stauffer, T. C.*; Goodrich, L. F.*; Jewell, M. C.*; Devred, A.*; Nabara, Yoshihiro
ITER用ブロンズ法Nb Sn素線の4.2Kにおける臨界電流を、軸方向歪みと磁束密度を関数としてNISTとTwente大学でそれぞれ測定し、ベンチマーク試験を行った。NISTはWalters' spring歪み印加装置を、Twente大学ではPacman歪み印加装置を使って測定した。このITER用ブロンズ法素線は非常に高い可逆限界歪みを持っているので、
Sn素線の4.2Kにおける臨界電流を、軸方向歪みと磁束密度を関数としてNISTとTwente大学でそれぞれ測定し、ベンチマーク試験を行った。NISTはWalters' spring歪み印加装置を、Twente大学ではPacman歪み印加装置を使って測定した。このITER用ブロンズ法素線は非常に高い可逆限界歪みを持っているので、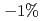 から
から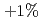 までの広い歪み範囲で測定データの比較が可能である。本稿では、各装置での測定データとそれらの比較を行い、また、測定方法やフィッティング関数のパラメータ決定方法に関しても議論する。
までの広い歪み範囲で測定データの比較が可能である。本稿では、各装置での測定データとそれらの比較を行い、また、測定方法やフィッティング関数のパラメータ決定方法に関しても議論する。
A benchmarking experiment was conducted to compare strain measurement facilities at the National Institute of Standards and Technology (NIST) and the University of Twente. The critical current of a bronze-route Nb Sn ITER wire was measured as a function of axial strain and magnetic field in liquid helium temperature at both institutes. NIST used a Walters' spring strain device and University of Twente used a Pacman apparatus. The ITER bronze-route wire investigated had a very high irreversible strain limit and allowed the comparison of data over a wide range of applied strain from
Sn ITER wire was measured as a function of axial strain and magnetic field in liquid helium temperature at both institutes. NIST used a Walters' spring strain device and University of Twente used a Pacman apparatus. The ITER bronze-route wire investigated had a very high irreversible strain limit and allowed the comparison of data over a wide range of applied strain from 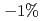 to
to 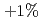 . A full account of the data analysis and comparisons will be presented. Measurement protocols and parameterization procedures will also be discussed.
. A full account of the data analysis and comparisons will be presented. Measurement protocols and parameterization procedures will also be discussed.