Characteristics of the first H-mode discharges in KSTAR
KSTARにおける最初のHモード放電の特性
Yoon, S. W.*; Ahn, J.-W.*; Jeon, Y. M.*; 鈴木 隆博; Hahn, S. H.*; Ko, W. H.*; Lee, K. D.*; Chung, J. I.*; Nam, Y. U.*; Kim, J.*; Hong, S. H.*; Kim, H.-S.*; Kim, W. C.*; Oh, Y. K.*; Kwak, J. G.*; Park, Y. S.*; Sabbagh, S. A.*; Humphreys, D. A.*; Na, Y. S.*; Kim, K. M.*; Yun, G. S.*; Hyatt, A. W.*; Gohil, P.*; Bae, Y. S.*; Yang, H. L.*; Park, H. K.*; Kwon, M.*; Lee, G. S.*; KSTAR Team*
Yoon, S. W.*; Ahn, J.-W.*; Jeon, Y. M.*; Suzuki, Takahiro; Hahn, S. H.*; Ko, W. H.*; Lee, K. D.*; Chung, J. I.*; Nam, Y. U.*; Kim, J.*; Hong, S. H.*; Kim, H.-S.*; Kim, W. C.*; Oh, Y. K.*; Kwak, J. G.*; Park, Y. S.*; Sabbagh, S. A.*; Humphreys, D. A.*; Na, Y. S.*; Kim, K. M.*; Yun, G. S.*; Hyatt, A. W.*; Gohil, P.*; Bae, Y. S.*; Yang, H. L.*; Park, H. K.*; Kwon, M.*; Lee, G. S.*; KSTAR Team*
中性粒子ビーム(NB)と電子サイクロトロン(EC)加熱を組合せることでKSTARトカマクにおいてELMを有する典型的なHモード放電を得た。2Tのトロイダル磁場では、Hモード遷移に必要な閾パワーは最小で1.1MWであり密度は1.4 10
10 m
m であった。この密度以下では閾パワーは増加した。閉じ込め時間はスケーリング則より1.4-1.6倍高いが、NBの損失を考慮するとスケーリング則に近づく。Hモード時には電子温度とイオン温度がペデスタル部で明確に上昇したが、中心部のイオン温度は大きくは変化しなかった。他方、トロイダル回転はHモード時に全領域で増加した。ELM周波数は30-50HzでELM時の蓄積エネルギーの変化割合は5%以下であった。NBとEC加熱を組合せた場合には、大振幅のELM間に小振幅のELMが観測された。
であった。この密度以下では閾パワーは増加した。閉じ込め時間はスケーリング則より1.4-1.6倍高いが、NBの損失を考慮するとスケーリング則に近づく。Hモード時には電子温度とイオン温度がペデスタル部で明確に上昇したが、中心部のイオン温度は大きくは変化しなかった。他方、トロイダル回転はHモード時に全領域で増加した。ELM周波数は30-50HzでELM時の蓄積エネルギーの変化割合は5%以下であった。NBとEC加熱を組合せた場合には、大振幅のELM間に小振幅のELMが観測された。
Typical ELMy H-mode discharges have been achieved on the KSTAR tokamak with the combined auxiliary heating of NBI and ECRH. The minimum external heating power required is about 1.1 MW at a line-averaged density higher than 1.4 10
10 m
m and a toroidal field of 2 T. There is a clear indication of the increase of the L-H threshold power at densities lower than
and a toroidal field of 2 T. There is a clear indication of the increase of the L-H threshold power at densities lower than 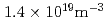 . The initial analysis of energy confinement time (
. The initial analysis of energy confinement time (
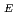 ) predicted that
) predicted that 
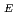 was higher than the prediction of multi-machine scaling laws by a factor 1.4-1.6. However, when the contribution of fast ion confinement to the total energy was taken into account,
was higher than the prediction of multi-machine scaling laws by a factor 1.4-1.6. However, when the contribution of fast ion confinement to the total energy was taken into account, 
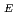 better agreed with the scaling results. A clear increase of electron and ion temperature in the pedestal was observed in the H-mode phase but the core ion temperature did not change significantly. On the other hand, the toroidal rotation also increased over all radii in the H-mode phase. The measured ELM frequency was from 30-50 Hz and the drop of total energy appeared to be less than 5%. Between large ELM spikes, small/grassy ELMs were also identified when mixed heating of NBI and ECRH was applied.
better agreed with the scaling results. A clear increase of electron and ion temperature in the pedestal was observed in the H-mode phase but the core ion temperature did not change significantly. On the other hand, the toroidal rotation also increased over all radii in the H-mode phase. The measured ELM frequency was from 30-50 Hz and the drop of total energy appeared to be less than 5%. Between large ELM spikes, small/grassy ELMs were also identified when mixed heating of NBI and ECRH was applied.