Magnetic-field-induced enhancement of nuclear spin-lattice relaxation rates in the heavy-fermion superconductor CeCoIn using
using  Co nuclear magnetic resonance
Co nuclear magnetic resonance
重い電子系超伝導体CeCoIn における磁場誘起した
における磁場誘起した Co核の核磁気共鳴核スピン緩和率の増大
Co核の核磁気共鳴核スピン緩和率の増大
酒井 宏典 

 ; Brown, S. E.*; Baek, S.-H.*; Ronning, F.*; Bauer, E. D.*; Thompson, J. D.*
; Brown, S. E.*; Baek, S.-H.*; Ronning, F.*; Bauer, E. D.*; Thompson, J. D.*
Sakai, Hironori; Brown, S. E.*; Baek, S.-H.*; Ronning, F.*; Bauer, E. D.*; Thompson, J. D.*
重い電子系超伝導体CeCoIn において、
において、 Co核の核スピン緩和率を磁場をc軸にかけて測定した。上部臨界磁場
Co核の核スピン緩和率を磁場をc軸にかけて測定した。上部臨界磁場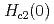 直上の極低温の通常状態において、核スピン緩和率の増大を観測した。核スピン緩和率は、直接、動的帯磁率を反映する物理量であり、反強磁性不安定性が
直上の極低温の通常状態において、核スピン緩和率の増大を観測した。核スピン緩和率は、直接、動的帯磁率を反映する物理量であり、反強磁性不安定性が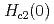 近傍にあることを直接証明している。核スピン緩和率の磁場依存性・温度依存性は、反強磁性スピン揺らぎの自己無撞着理論によってよく再現することができ、得られたパラメータを用いて、比熱や熱膨張の測定結果を上手く説明することができる。
近傍にあることを直接証明している。核スピン緩和率の磁場依存性・温度依存性は、反強磁性スピン揺らぎの自己無撞着理論によってよく再現することができ、得られたパラメータを用いて、比熱や熱膨張の測定結果を上手く説明することができる。
 Co nuclear spin lattice relaxation has been measured for the heavy-fermion superconductor CeCoIn
Co nuclear spin lattice relaxation has been measured for the heavy-fermion superconductor CeCoIn in a range of applied fields directed parallel to the
in a range of applied fields directed parallel to the  -axis. An enhanced normal state relaxation rate, observed at low temperatures and fields just above
-axis. An enhanced normal state relaxation rate, observed at low temperatures and fields just above 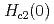 , is taken as a direct measure of the dynamical susceptibility and provides microscopic evidence for an antiferromagnetic instability. The results are well-described using the self-consistent renormalized theory for two-dimensional antiferromagnetic spin fluctuations, and parameters obtained in the analysis are applied to previously reported specific heat and thermal expansion data with good agreement.
, is taken as a direct measure of the dynamical susceptibility and provides microscopic evidence for an antiferromagnetic instability. The results are well-described using the self-consistent renormalized theory for two-dimensional antiferromagnetic spin fluctuations, and parameters obtained in the analysis are applied to previously reported specific heat and thermal expansion data with good agreement.