Development of less toxic polymer gel dosimeter for radiation therapy of cancer
Yamashita, Shinichi; Hiroki, Akihiro; Nagasawa, Naotsugu; Taguchi, Mitsumasa
We developed a polymer gel dosimeter with low toxicity by employing a cellulose derivative, hydroxypropyl cellulose, as a base matrix, 2-hydroxyethyl-methacrylate as a polymerizing monomer, polyethylene glycol ester dimethacrylate as a crosslinker, and tetrakis (hydroxymethyl)phosphonium chloride as an oxygen scavenger. The gel dosimeter was irradiated with  Co
Co 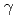 -rays at dose rate of 3-8 Gy/h, resulting in visual change from transparent to white cloud-like state. The irradiated dosimeters were analyzed by UV-vis spectrometry and measurement of haze, which is defined as the ratio of diffractive transmission to sum of diffractive and parallel transmissions. There is no obvious difference in UV-vis spectra among the dosimeters with different compositions. No peak but a broad and downward curve was observed in wavelength from 300 to 800 nm. This would be attributed to scattering by microgel of polymerized solutes or to chemical bonds produced during the polymerization. Haze almost monotonically increases with increasing
-rays at dose rate of 3-8 Gy/h, resulting in visual change from transparent to white cloud-like state. The irradiated dosimeters were analyzed by UV-vis spectrometry and measurement of haze, which is defined as the ratio of diffractive transmission to sum of diffractive and parallel transmissions. There is no obvious difference in UV-vis spectra among the dosimeters with different compositions. No peak but a broad and downward curve was observed in wavelength from 300 to 800 nm. This would be attributed to scattering by microgel of polymerized solutes or to chemical bonds produced during the polymerization. Haze almost monotonically increases with increasing 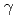 -dose although difference at low dose region (smaller than 1 Gy) was difficult to be quantitatively identified.
-dose although difference at low dose region (smaller than 1 Gy) was difficult to be quantitatively identified.