Ion induced luminescence from sapphire irradiated with swift cluster ion beams; Energy dependence of incident cluster beams
高速炭素クラスターイオンのサファイアへの照射誘起発光過程; 入射クラスターイオンのエネルギー依存性
柴田 裕実*; 齋藤 勇一; 千葉 敦也; 山田 圭介; 田口 光正; 鳴海 一雅
Shibata, Hiromi*; Saito, Yuichi; Chiba, Atsuya; Yamada, Keisuke; Taguchi, Mitsumasa; Narumi, Kazumasa
Luminescent spectra from sapphire ( -Al
-Al O
O ) induced by 0.5
) induced by 0.5 1.5 MeV/atom (42
1.5 MeV/atom (42 126 keV/u) C
126 keV/u) C
 C
C ion irradiation were measured in the wavelength range of 250-800 nm as a function of ion fluence at room temperature. As a result, the luminescence yields increase as the cluster sizes increase for every incident energy range, but the ratios R
ion irradiation were measured in the wavelength range of 250-800 nm as a function of ion fluence at room temperature. As a result, the luminescence yields increase as the cluster sizes increase for every incident energy range, but the ratios R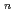 (R
(R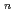 = I(n) /nI(1), where n is number of cluster ion, I(n) is the yield for C
= I(n) /nI(1), where n is number of cluster ion, I(n) is the yield for C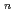
 cluster ion and I(1) is the yield for C
cluster ion and I(1) is the yield for C
 ion) become less than unity in the energy range of 0.5 and 1.0 MeV/atom. The experimental results show the same tendency as the calculation of stopping power theory and exist between unity and the value for the united atom of the cluster ion. This suggests that luminescence caused by irradiation defects directly relates the stopping power of incident cluster ion.
ion) become less than unity in the energy range of 0.5 and 1.0 MeV/atom. The experimental results show the same tendency as the calculation of stopping power theory and exist between unity and the value for the united atom of the cluster ion. This suggests that luminescence caused by irradiation defects directly relates the stopping power of incident cluster ion.