Calculation of space-time correlation function on liquid benzene by using MEM
最大エントロピー法による液体ベンゼンの時空相関数の計算
菊地 龍弥 
 ; 中島 健次
; 中島 健次 
 ; 河村 聖子
; 河村 聖子 

 ; 稲村 泰弘
; 稲村 泰弘 

Kikuchi, Tatsuya; Nakajima, Kenji; Kawamura, Seiko; Inamura, Yasuhiro
中性子散乱実験で得られる動的構造因子は、van Hoveの時空相関関数のフーリエ変換で記述される。この時空相関関数は実時間・実空間における関数であり、原子分子のダイナミクスを直接的に表すため、それらの解明に重要である。しかしながら、その計算には広いQ-E範囲でかつ高分解能のデータが必要であり、計算自体は数学的には容易であるにもかかわらずほとんど行われていない。近年、分光器の進化により時空相関関数が計算可能な測定が可能になりつつある。われわれはJ-PARCセンターのAMATERAS分光器により中性子散乱実験を行い高分解能・広範囲のデータの取得を行い、時空相関関数の計算を試みた。サンプルには単純な分子液体であるベンゼンを使用した。実際の時空相関関数の計算では、データのカットオフによる計算結果への影響を抑えるために最大エントロピー法を使用した。その結果、計算に成功し時空相関関数を得ることができた。得られた時空相関関数は、静的な構造研究やダイナミクスの研究とも矛盾がなかった。時空相関関数の計算が可能になったことで、新たなダイナミクスの研究が可能になると考えている。
Dynamic structure factor, 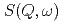 , which can be obtained by neutron scatterings is defined as a Fourier-transformed function from van Hove's space-time correlation function,
, which can be obtained by neutron scatterings is defined as a Fourier-transformed function from van Hove's space-time correlation function, 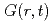 , which is a function in real space and time.
, which is a function in real space and time. 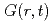 is important for elucidation of relaxation phenomena to express the motion of atoms and molecules directly. However, the calculation of
is important for elucidation of relaxation phenomena to express the motion of atoms and molecules directly. However, the calculation of 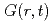 has been hardly performed even though it is so easy mathematically, because it was difficult to measure both in high resolution and wide Q-E range. By the progress of the recent neutron sources and spectrometers, the measurements with wide range and high resolution in Q-E space are becoming easy. We measured high-resolution
has been hardly performed even though it is so easy mathematically, because it was difficult to measure both in high resolution and wide Q-E range. By the progress of the recent neutron sources and spectrometers, the measurements with wide range and high resolution in Q-E space are becoming easy. We measured high-resolution 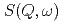 using AMATERAS spectrometer installed at J-PARC and calculated
using AMATERAS spectrometer installed at J-PARC and calculated 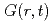 's. We chose benzene and benzene-d6 as the samples, which were simple molecular liquids. We used the maximum entropy method to lower the bias of truncation errors for the calculation of
's. We chose benzene and benzene-d6 as the samples, which were simple molecular liquids. We used the maximum entropy method to lower the bias of truncation errors for the calculation of 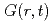 .
.