X-ray Raman scattering study on the valence transition in EuPd Si
Si
X線Raman散乱によるEuPd Si
Si の価数転移の研究
の価数転移の研究
稲見 俊哉; 石井 賢司; Jarrige, I.*; 吉田 雅洋*; 光田 暁弘*
Inami, Toshiya; Ishii, Kenji; Jarrige, I.*; Yoshida, Masahiro*; Mitsuda, Akihiro*
ランタノイドの 吸収端や
吸収端や 吸収端でのX線吸収分光は、
吸収端でのX線吸収分光は、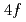 電子の価数や空間対称性、混成を研究するうえで有用な手法である。一方、この手法の欠点は軟X線の固体への侵入長が非常に短いことである。X線Raman散乱法(XRS)はX線吸収スペクトルを得るための代わりの方法である。高エネルギーの入射X線はそのエネルギーの一部をさまざまな励起に与えることができ、得られたエネルギー損失スペクトルは吸収スペクトルに対応する。高エネルギーX線の長い侵入長はこの手法をバルク敏感にしており、極限環境への適用も容易である。この手法は軽元素に長い間適用されてきたが、近年発見された大きな運動量遷移での鋭いプリエッジ構造により、XRSはランタノイドやアクチノイドといった重元素の電子構造の研究に有用な新しい手法として認識されるようになった。ここでは、このXRSの
電子の価数や空間対称性、混成を研究するうえで有用な手法である。一方、この手法の欠点は軟X線の固体への侵入長が非常に短いことである。X線Raman散乱法(XRS)はX線吸収スペクトルを得るための代わりの方法である。高エネルギーの入射X線はそのエネルギーの一部をさまざまな励起に与えることができ、得られたエネルギー損失スペクトルは吸収スペクトルに対応する。高エネルギーX線の長い侵入長はこの手法をバルク敏感にしており、極限環境への適用も容易である。この手法は軽元素に長い間適用されてきたが、近年発見された大きな運動量遷移での鋭いプリエッジ構造により、XRSはランタノイドやアクチノイドといった重元素の電子構造の研究に有用な新しい手法として認識されるようになった。ここでは、このXRSの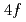 混合原子価状態への適用の可能性について研究した。試料としては、150Kで大きく鋭い価数転移を示すEuPd
混合原子価状態への適用の可能性について研究した。試料としては、150Kで大きく鋭い価数転移を示すEuPd Si
Si を用いた。得られたXRSスペクトルは明確なEuの
を用いた。得られたXRSスペクトルは明確なEuの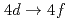 と
と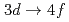 吸収構造を示した。しかし、予想に反して、スペクトルの温度変化は全く観測されなかった。
吸収構造を示した。しかし、予想に反して、スペクトルの温度変化は全く観測されなかった。
X-ray absorption spectroscopy at the lanthanoid  - and
- and  -edges is a versatile tool for investigating valency, spatial symmetry and hybridization of the
-edges is a versatile tool for investigating valency, spatial symmetry and hybridization of the 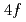 electrons. A disadvantage of this technique, however, is the very short penetration length of soft X-rays in solid materials. X-ray Raman scattering (XRS) is an alternative method to obtain absorption spectra. High energy incident X-rays transfer a part of their energy to various excitations and the obtained energy-loss spectrum corresponds to an absorption spectrum. Because of the high penetration depth of hard X-rays, this technique is truly bulk sensitive. Here we report on a feasibility study of XRS experiments applied to a mixed-valent f-electron system. The test sample was EuPd
electrons. A disadvantage of this technique, however, is the very short penetration length of soft X-rays in solid materials. X-ray Raman scattering (XRS) is an alternative method to obtain absorption spectra. High energy incident X-rays transfer a part of their energy to various excitations and the obtained energy-loss spectrum corresponds to an absorption spectrum. Because of the high penetration depth of hard X-rays, this technique is truly bulk sensitive. Here we report on a feasibility study of XRS experiments applied to a mixed-valent f-electron system. The test sample was EuPd Si
Si , which exhibits a sharp and large valence transition around 150 K. The obtained XRS spectra showed clear absorption features at the
, which exhibits a sharp and large valence transition around 150 K. The obtained XRS spectra showed clear absorption features at the  - and
- and  -edges. However, we did not detect any difference between the spectra at 10 K and 200 K.
-edges. However, we did not detect any difference between the spectra at 10 K and 200 K.