Observation of intermolecular N-I interaction during the growth of a 4-cyano-4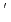 -iodobiphenyl molecular crystal on GeS(001)
-iodobiphenyl molecular crystal on GeS(001)
GeS(001)上への4-シアノ-4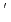 -ヨードビフェニル分子結晶成長中のN-I分子間相互作用の観察
-ヨードビフェニル分子結晶成長中のN-I分子間相互作用の観察
隅井 良平*; 酒巻 真粧子*; 松本 吉弘; 雨宮 健太*; 金井 要*; 関 一彦*
Sumii, Ryohei*; Sakamaki, Masako*; Matsumoto, Yoshihiro; Amemiya, Kenta*; Kanai, Kaname*; Seki, Kazuhiko*
The electronic and atomic structures of 4-cyano-4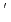 -iodobiphenyl (CIB) during the growth of a molecular crystal on a GeS(001) substrate were studied by ultraviolet photoemission spectroscopy (UPS), atomic force microscopy (AFM), and extended X-ray absorption fine structure (EXAFS) spectroscopy. AFM images suggest that the CIB molecule grows as a microcrystal at a nominal thickness of 80
-iodobiphenyl (CIB) during the growth of a molecular crystal on a GeS(001) substrate were studied by ultraviolet photoemission spectroscopy (UPS), atomic force microscopy (AFM), and extended X-ray absorption fine structure (EXAFS) spectroscopy. AFM images suggest that the CIB molecule grows as a microcrystal at a nominal thickness of 80 . The microcrystal grows with the crystal plane parallel to the surface and isotropic crystal axis orientation. EXAFS analysis suggests that a CIB crystal forms by strong N-I interaction, called halogen bonding. The formation of the intermolecular N-I bond was demonstrated by EXAFS analyses in which the N-I distance was determined to be 3.29
. The microcrystal grows with the crystal plane parallel to the surface and isotropic crystal axis orientation. EXAFS analysis suggests that a CIB crystal forms by strong N-I interaction, called halogen bonding. The formation of the intermolecular N-I bond was demonstrated by EXAFS analyses in which the N-I distance was determined to be 3.29 . An upward shift of the highest occupied molecular orbital level was observed by UPS and can be attributed to the aggregation of CIB molecules caused by halogen bonding.
. An upward shift of the highest occupied molecular orbital level was observed by UPS and can be attributed to the aggregation of CIB molecules caused by halogen bonding.