High-resolution crystal structure of copper amine oxidase from  ; Assignment of bound diatomic molecules as O
; Assignment of bound diatomic molecules as O
Murakawa, Takeshi*; Hayashi, Hideyuki*; Sunami, Tomoko; Kurihara, Kazuo; Tamada, Taro; Kuroki, Ryota; Suzuki, Mamoru*; Tanizawa, Katsuyuki*; Okajima, Toshihide*
The crystal structure of a Cu amine oxidase from  was determined at 1.08
was determined at 1.08  resolution with the use of low-molecular-weight polyethylene glycol (LMW PEG; average molecular weight
resolution with the use of low-molecular-weight polyethylene glycol (LMW PEG; average molecular weight  200) as a cryoprotectant. The final crystallographic
200) as a cryoprotectant. The final crystallographic  -factor and
-factor and 
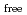 value are 13.0% and 15.0%, respectively. Several molecules of LMW PEG were found to occupy cavities in the protein interior including the active site, which resulted in the marked reduction of the overall
value are 13.0% and 15.0%, respectively. Several molecules of LMW PEG were found to occupy cavities in the protein interior including the active site, which resulted in the marked reduction of the overall 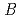 factor and consequently led to a sub-atomic resolution structure for a relatively large protein with a monomer molecular weight of
factor and consequently led to a sub-atomic resolution structure for a relatively large protein with a monomer molecular weight of  70,000. About 40% of all the presumed hydrogen atoms were observed as clear electron densities in the
70,000. About 40% of all the presumed hydrogen atoms were observed as clear electron densities in the 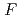
 -
- 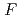
 difference map. Multiple minor conformers were also identified for many residues. Anisotropic displacement fluctuations were evaluated in the active site that contains a post-translationally derived quinone cofactor and a Cu atom. Furthermore, diatomic molecules, most likely molecular oxygen, are bound to the protein, one of which is located in the region that has been previously proposed as an entry route for the substrate dioxygen from the central cavity of the dimer interface to the active site.
difference map. Multiple minor conformers were also identified for many residues. Anisotropic displacement fluctuations were evaluated in the active site that contains a post-translationally derived quinone cofactor and a Cu atom. Furthermore, diatomic molecules, most likely molecular oxygen, are bound to the protein, one of which is located in the region that has been previously proposed as an entry route for the substrate dioxygen from the central cavity of the dimer interface to the active site.