High-resolution crystal structure of copper amine oxidase from  ; Assignment of bound diatomic molecules as O
; Assignment of bound diatomic molecules as O
アルスロバクター-グロビフォルミス由来銅アミン酸化酵素の高分解能結晶構造; O 様結合二原子分子の同定
様結合二原子分子の同定
村川 武志*; 林 秀行*; 角南 智子; 栗原 和男; 玉田 太郎; 黒木 良太; 鈴木 守*; 谷澤 克行*; 岡島 俊英*
Murakawa, Takeshi*; Hayashi, Hideyuki*; Sunami, Tomoko; Kurihara, Kazuo; Tamada, Taro; Kuroki, Ryota; Suzuki, Mamoru*; Tanizawa, Katsuyuki*; Okajima, Toshihide*
アルスロバクター-グロビフォルミス由来銅アミン酸化酵素の結晶構造を抗凍結剤として低分子ポリエチレングリコール(LMW PEG; 平均分子量 200)を用いて1.08
200)を用いて1.08 分解能で決定した。最終的な結晶構造学的
分解能で決定した。最終的な結晶構造学的 因子と
因子と
 値は、それぞれ13.0%と15.0
値は、それぞれ13.0%と15.0 であった。LMW PEGの幾つかの分子は、活性部位を含むタンパク質内部の空洞を占めており、それが分子全体の温度因子の著しい低下をもたらし、結果として、単量体分子量が約70,000と比較的大きなタンパク質にも拘わらず原子分解能の構造に至ったことがわかった。推定される全水素原子の約40%は、
であった。LMW PEGの幾つかの分子は、活性部位を含むタンパク質内部の空洞を占めており、それが分子全体の温度因子の著しい低下をもたらし、結果として、単量体分子量が約70,000と比較的大きなタンパク質にも拘わらず原子分解能の構造に至ったことがわかった。推定される全水素原子の約40%は、
 -
-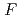
 差図中に明確な電子密度を持って観察され、複数のマイナーな配座異性体も多くの残基に対して同定された。また、翻訳後に誘導されたキノン補因子と銅原子を含む活性部位における異方的な変位の揺らぎを見積った。さらに、複数の二原子分子、恐らく分子性酸素がタンパク質と結合し、そのうちの一つは二量体界面の中央に位置する空洞から活性部位まで基質である二原子酸素のための進入経路として以前から提案されている領域に位置していた。
差図中に明確な電子密度を持って観察され、複数のマイナーな配座異性体も多くの残基に対して同定された。また、翻訳後に誘導されたキノン補因子と銅原子を含む活性部位における異方的な変位の揺らぎを見積った。さらに、複数の二原子分子、恐らく分子性酸素がタンパク質と結合し、そのうちの一つは二量体界面の中央に位置する空洞から活性部位まで基質である二原子酸素のための進入経路として以前から提案されている領域に位置していた。
The crystal structure of a Cu amine oxidase from 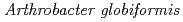 was determined at 1.08
was determined at 1.08  resolution with the use of low-molecular-weight polyethylene glycol (LMW PEG; average molecular weight
resolution with the use of low-molecular-weight polyethylene glycol (LMW PEG; average molecular weight  200) as a cryoprotectant. The final crystallographic
200) as a cryoprotectant. The final crystallographic  -factor and
-factor and 
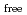 value are 13.0% and 15.0%, respectively. Several molecules of LMW PEG were found to occupy cavities in the protein interior including the active site, which resulted in the marked reduction of the overall
value are 13.0% and 15.0%, respectively. Several molecules of LMW PEG were found to occupy cavities in the protein interior including the active site, which resulted in the marked reduction of the overall 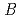 factor and consequently led to a sub-atomic resolution structure for a relatively large protein with a monomer molecular weight of
factor and consequently led to a sub-atomic resolution structure for a relatively large protein with a monomer molecular weight of  70,000. About 40% of all the presumed hydrogen atoms were observed as clear electron densities in the
70,000. About 40% of all the presumed hydrogen atoms were observed as clear electron densities in the 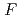
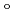 -
- 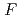
 difference map. Multiple minor conformers were also identified for many residues. Anisotropic displacement fluctuations were evaluated in the active site that contains a post-translationally derived quinone cofactor and a Cu atom. Furthermore, diatomic molecules, most likely molecular oxygen, are bound to the protein, one of which is located in the region that has been previously proposed as an entry route for the substrate dioxygen from the central cavity of the dimer interface to the active site.
difference map. Multiple minor conformers were also identified for many residues. Anisotropic displacement fluctuations were evaluated in the active site that contains a post-translationally derived quinone cofactor and a Cu atom. Furthermore, diatomic molecules, most likely molecular oxygen, are bound to the protein, one of which is located in the region that has been previously proposed as an entry route for the substrate dioxygen from the central cavity of the dimer interface to the active site.