Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
 ; Assignment of bound diatomic molecules as O
; Assignment of bound diatomic molecules as O
村川 武志*; 林 秀行*; 角南 智子; 栗原 和男; 玉田 太郎; 黒木 良太; 鈴木 守*; 谷澤 克行*; 岡島 俊英*
Acta Crystallographica Section D, 69(12), p.2483 - 2494, 2013/12
被引用回数:14 パーセンタイル:67.17(Biochemical Research Methods)アルスロバクター-グロビフォルミス由来銅アミン酸化酵素の結晶構造を抗凍結剤として低分子ポリエチレングリコール(LMW PEG; 平均分子量 200)を用いて1.08
200)を用いて1.08 分解能で決定した。最終的な結晶構造学的
分解能で決定した。最終的な結晶構造学的 因子と
因子と
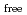 値は、それぞれ13.0%と15.0
値は、それぞれ13.0%と15.0 であった。LMW PEGの幾つかの分子は、活性部位を含むタンパク質内部の空洞を占めており、それが分子全体の温度因子の著しい低下をもたらし、結果として、単量体分子量が約70,000と比較的大きなタンパク質にも拘わらず原子分解能の構造に至ったことがわかった。推定される全水素原子の約40%は、
であった。LMW PEGの幾つかの分子は、活性部位を含むタンパク質内部の空洞を占めており、それが分子全体の温度因子の著しい低下をもたらし、結果として、単量体分子量が約70,000と比較的大きなタンパク質にも拘わらず原子分解能の構造に至ったことがわかった。推定される全水素原子の約40%は、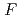
 -
-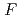
 差図中に明確な電子密度を持って観察され、複数のマイナーな配座異性体も多くの残基に対して同定された。また、翻訳後に誘導されたキノン補因子と銅原子を含む活性部位における異方的な変位の揺らぎを見積った。さらに、複数の二原子分子、恐らく分子性酸素がタンパク質と結合し、そのうちの一つは二量体界面の中央に位置する空洞から活性部位まで基質である二原子酸素のための進入経路として以前から提案されている領域に位置していた。
差図中に明確な電子密度を持って観察され、複数のマイナーな配座異性体も多くの残基に対して同定された。また、翻訳後に誘導されたキノン補因子と銅原子を含む活性部位における異方的な変位の揺らぎを見積った。さらに、複数の二原子分子、恐らく分子性酸素がタンパク質と結合し、そのうちの一つは二量体界面の中央に位置する空洞から活性部位まで基質である二原子酸素のための進入経路として以前から提案されている領域に位置していた。
 and CaCl
and CaCl
茶竹 俊行*; 角南 智子
Journal of Inorganic Biochemistry, 124, p.15 - 25, 2013/07
被引用回数:16 パーセンタイル:57.94(Biochemistry & Molecular Biology)In this study, crystals of Z-DNA hexamer d(CGCGCG) complexed with MgCl and CaCl
and CaCl were obtained in the presence of high concentrations of alkaline earth salts (500 mM) using a temperature control technique, and their crystal structures were determined at 1.3
were obtained in the presence of high concentrations of alkaline earth salts (500 mM) using a temperature control technique, and their crystal structures were determined at 1.3 resolution. Mg
resolution. Mg and Ca
and Ca cations in these structures tend to interact directly with phosphate groups of Z-DNA duplexes; however, they tend to form water-mediated interactions with Z-DNA in the presence of lower concentrations of alkaline earth salts. In these crystals, a DNA duplex was laid along its c-axis and interacted with its 6 neighboring DNA duplexes through coordination bonds of P-O...(Mg
cations in these structures tend to interact directly with phosphate groups of Z-DNA duplexes; however, they tend to form water-mediated interactions with Z-DNA in the presence of lower concentrations of alkaline earth salts. In these crystals, a DNA duplex was laid along its c-axis and interacted with its 6 neighboring DNA duplexes through coordination bonds of P-O...(Mg or Ca
or Ca )...O-P. A symmetrical hexagonal Z-DNA duplex assembly model may explain DNA condensation caused by alkaline earth salts. These structures offer insights into the functions of alkaline earth cations essential to the structures and assembly of Z-DNA duplexes.
)...O-P. A symmetrical hexagonal Z-DNA duplex assembly model may explain DNA condensation caused by alkaline earth salts. These structures offer insights into the functions of alkaline earth cations essential to the structures and assembly of Z-DNA duplexes.
角南 智子; 河野 秀俊
PLOS ONE (Internet), 8(2), p.e56080_1 - e56080_12, 2013/02
被引用回数:13 パーセンタイル:28.58(Multidisciplinary Sciences)When a protein binds to DNA, a conformational change is often induced so that the protein will fit into the DNA structure. Therefore, quantitative analyses were conducted to understand the conformational changes in proteins. The results showed that conformational changes in DNA interfaces are more frequent than in non-interfaces, and DNA interfaces have more conformational variations in the DNA-free form. As expected, the former indicates that interaction with DNA has some influence on protein structure. The latter suggests that the intrinsic conformational flexibility of DNA interfaces is important for adjusting their conformation for DNA. The amino acid propensities of the conformationally changed regions in DNA interfaces indicate that hydrophilic residues are preferred over the amino acids that appear in the conformationally unchanged regions. This trend is true for disordered regions, suggesting again that intrinsic flexibility is of importance not only for DNA binding but also for interactions with other molecules. These results demonstrate that fragments destined to be DNA interfaces have an intrinsic flexibility and are composed of amino acids with the capability of binding to DNA. This information suggests that the prediction of DNA binding sites may be improved by the integration of amino acid preference for DNA and one for disordered regions.
安達 基泰; 角南 智子; 黒木 良太
酵素利用技術大系, p.34 - 37, 2010/04
酵素は、病気の解明,医薬品の創製,医薬品の生産過程,臨床検査などに関係し、医療と密接なつながりを持っている。例えばガンでは、ガン化した細胞の増殖や浸潤にプロテインキナーゼをはじめとした多くの酵素がかかわっており、エイズでは、HIV(Human Immunodeficiency Virus)プロテアーゼがウイルスの増殖に必須の役割を果たしている。多くの病気の進行において、酵素が中心的な役割を果たしていることから、酵素を阻害することが治療における有効な手段の一つとなっている。現代では、疾患とその原因酵素との複雑な関係に対する理解がますます深まりつつあり、病気を治療するために、どのような酵素をどのように阻害すればよいのかについても、精力的な研究が続けられている。本稿では、医療関連酵素のX線解析手法と、創薬をめざして数多くの研究がなされているプロテアーゼとプロテインキナーゼとチトクロームP450という3つの酵素群と、世界的な流行(パンデミック)が懸念されている新型インフルエンザウイルスの創薬標的分子(ノイラミニダーゼ)の立体構造解析について概説する。
角南 智子; 河野 秀俊
no journal, ,
To better understand the conformational changes of proteins upon DNA binding, we carried out quantitative analyses. We first described the proteins using a structural alphabet library of backbone geometries created by Kolodony et al. and then detected the conformational changes as changes in alphabets between DNA-free and bound forms. We first divided protein surface into two regions, DNA interface and protein surface which exclude the DNA interface and carried out the analyses. The results show that (1) the conformational changes at DNA interfaces are more frequent than those at the other surfaces; (2) DNA interfaces have more conformational variation even in the DNA-free form. The latter suggests that intrinsic, conformational flexibility of DNA interface seems to be important to adjust their conformations to DNA. In amino acid propensities, the conformationally changed regions in DNA interfaces as well as those in the other protein surfaces show that hydrophilic and glycine residues are more preferred compared with the conformation-unchanged regions. This trend is also found in the propensity for disordered regions, suggesting that the intrinsic flexibility be of importance not only for DNA binding but also for interacting with other molecules. Comparison of distributions of the structural alphabets between DNA interfaces and the other surfaces shows that some specific alphabets appear more often in DNA interfaces.
角南 智子; 河野 秀俊
no journal, ,
転写因子がゲノム中のある特定の塩基配列を正確に認識することは、遺伝子の発現制御のために重要な役割を果たしている。任意のDNA配列を特異的に認識する蛋白質を人工的に作製することができれば、遺伝情報の発現制御や修復など様々な分野への応用が考えられる。近年、遺伝情報を書き換えるための人工転写因子として、TALNやCRISPRといった蛋白質が広く使われ始めている。しかし、特に、CRISPRの場合に顕著であるが、既存の人工転写因子は依然として、配列特異性が不十分であるために、目的とする配列以外のDNA配列が切断されてしまうという問題点がある。我々は、より特異性が高い蛋白質を設計するために、エングレイルドホメオドメイン蛋白質(EN)に注目し、新たな配列特異性を持つ転写因子の開発を目指して研究を進めている。ENは6塩基長の塩基配列を特異的に認識する小型の球状蛋白質である。原核生物でも真核生物でもよく発現し、変異体の調製が容易である利点がある。我々は、より長い領域結合するように、2つのENをGlyリンカーを介してタンデムにつないだ蛋白質を作成した。そして、ゲルシフトアッセイ法を用いて、この蛋白質が高い結合活性と高い配列特異性を有していることを明らかにした。我々は、更に、結合活性及び配列特異性を最適化するため、現在、この2つのドメイン間をつなぐリンカー領域に注目して、B1H法(Meng et al., 2006)などを利用してスクリーニングを行っている。本発表では、その結果を報告する。
角南 智子; 河野 秀俊
no journal, ,
DNA-protein interaction plays a key role in many cellular functions such as transcription, replication, recombination and DNA packaging. Understanding the mechanisms by which the protein recognizes DNA is one of the main topics in biology. With increased amount of crystal structures, conformational changes of proteins in DNA interfaces are suggested to be one of important factors in DNA recognition. To better understand a role of the flexibility of proteins in DNA recognition, quantitative analyses of local conformational changes in DNA interfaces of proteins are required. In order to analyze such conformational changes in DNA interfaces, we extracted crystal structures of DNA-unbound and DNA-bound states from PDB. The backbone structures were described by 7 letters that were pre-defined according to conformations of consecutive overlapping fragments of 4-residues. Using the letter codes, any conformational change from DNA-unbound state to DNA-bound state was described as one of 49 patterns of changes. We statistically analyzed the frequency of these conformational changes in DNA interfaces and protein surfaces. As a result, we found 4 structural changes preferred in DNA interfaces compared with that of protein interfaces.
角南 智子; 河野 秀俊
no journal, ,
DNAとタンパク質の相互作用は翻訳や複製など生物機能において重要な役割を果たしている。そのため、DNAとタンパク質の相互作用機構を解明することは、生物学上の重要なテーマの一つである。近年、結晶構造解析を用いて、多くのDNA結合タンパク質の原子構造が明らかとなりつつある。これらから、タンパク質がDNAと結合した際に、しばしばDNA界面で構造変化を生じることが明らかとされつつある。われわれの研究の目的は、DNAと結合した際にタンパク質がどのような構造変化を生じるのかを明らかとすることである。われわれは、PDBより抽出したDNA結合タンパク質の構造を4残基長のフラグメントに分割し、これらのフラグメントを既知のライブラリを用いて7つのコードに分類することによって、DNA結合前後のタンパク質の局所構造の変化を解析した。その結果、(1)高い確率でDNA結合前後でDNA界面の構造変化が観察されること、(2)DNA非結合状態では構造の多様性が高いが、DNAに結合することで多様性が下がること、(3)DNA界面で変化する領域のアミノ酸組成は、それ以外の領域で変化する領域のアミノ酸組成とは異なるが、両者の局所構造の特徴は似通っていること、がわかった。
 -Lactamase TOHO-1 determined by combined high-resolution neutron and X-ray crystallography
-Lactamase TOHO-1 determined by combined high-resolution neutron and X-ray crystallography栗原 和男; 角南 智子; 山田 貢; 似内 靖*; 岡崎 伸生; 安達 基泰; 玉田 太郎; 島村 達郎*; 宮野 雅司*; 石井 良和*; et al.
no journal, ,
 -ラクタマーゼの活性を議論するため、
-ラクタマーゼの活性を議論するため、 -ラクタマーゼToho-1・R274N/R276N変異体(Toho-1/NN)結晶(サイズ: 2.6
-ラクタマーゼToho-1・R274N/R276N変異体(Toho-1/NN)結晶(サイズ: 2.6 2.5
2.5 1.3mm
1.3mm )に対してリガンドが結合していない状態の中性子/X線結晶構造解析を高分解能(中性子: 1.5
)に対してリガンドが結合していない状態の中性子/X線結晶構造解析を高分解能(中性子: 1.5 , X線: 1.4
, X線: 1.4 )で行うことに成功した。プログラムPHENIXを用い構造精密化を行った結果(R-factor: 19.7%)、Glu166はLys73のアミノ基(-NH3
)で行うことに成功した。プログラムPHENIXを用い構造精密化を行った結果(R-factor: 19.7%)、Glu166はLys73のアミノ基(-NH3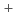 )の正電荷に隣接した位置にもかかわらずpH7においてもプロトン化していることが示された。また、プロトン化したGlu166とSer70・Ser237の主鎖の窒素原子によって形成されるオキシアニオンホールとの間を繋ぐ水和水ネットワークの存在を見いだした。さらに、Glu166とSer70間を繋ぐ触媒水と推定されている水分子の詳細な配置が明らかになった。これらの観察結果は、
)の正電荷に隣接した位置にもかかわらずpH7においてもプロトン化していることが示された。また、プロトン化したGlu166とSer70・Ser237の主鎖の窒素原子によって形成されるオキシアニオンホールとの間を繋ぐ水和水ネットワークの存在を見いだした。さらに、Glu166とSer70間を繋ぐ触媒水と推定されている水分子の詳細な配置が明らかになった。これらの観察結果は、 -ラクタマーゼToho-1の触媒反応機構の理解のために重要である。
-ラクタマーゼToho-1の触媒反応機構の理解のために重要である。
角南 智子; 河野 秀俊
no journal, ,
転写因子がゲノム中のある特定の塩基配列を正確に認識することは、遺伝子の発現制御のために重要な役割を果たしている。任意のDNA配列を特異的に認識する蛋白質を人工的に作製することができれば、遺伝情報の発現制御や修復など様々な分野への応用が考えられる。近年、このような人工転写因子として、TALEや亜鉛フィンガー蛋白質をベースとして、いくつかの開発例が報告されている。しかし、現存の人工転写因子は依然として、低配列特異性による毒性などの問題があり、特異性を上げることが望まれている。そのためには、DNAと転写因子の相互作用を解析し、特異性を出している仕組みを理解する必要がある。我々は、この目的のために、エングレイルドホメオドメイン蛋白質(EN)に注目し、新たな配列特異性を持つ転写因子の開発を目指して研究を進めている。ENは6塩基長の塩基配列を特異的に認識する小型の球状蛋白質である。原核生物でも真核生物でもよく発現し、変異体の調製が容易である利点がある。我々は、配列特性を上げるためにより長い領域結合するように、2つのENをタンデムにつないだ蛋白質を作成した。そして、この蛋白質は高い結合活性と高い配列特異性を有していることを明らかにした。我々は、結合活性及び配列特異性を最適化するため、現在、この2つのドメイン間をつなぐリンカーの長さに注目して、B1H法(Meng et al., 2006)などを利用してスクリーニングを行っているので、進捗を報告する。
角南 智子; 河野 秀俊
no journal, ,
Using structural alphabets, we performed quantitative analyses of conformational changes of DNA binding proteins using the sets of proteins in DNA-free and DNA-bound forms. The results show that (1) the conformational changes in the DNA interfaces are more frequent than those in the non-interface; (2) DNA interfaces have more conformational variations even in the DNA-free forms. The latter suggests that the intrinsic, conformational flexibility of DNA interfaces seems to be important to adjust their conformations to DNA. In amino acid propensities, the conformation-changed regions in the DNA interfaces as well as those in the non-interface show that hydrophilic residues in addition to proline and glycine are more preferred compared with the conformation-unchanged regions. This trend is also found in the amino acid propensity for disordered regions, suggesting that the intrinsic flexibility be of importance not only for DNA binding but also for interactions with other molecules. Comparison of the distributions of the structural alphabets between the DNA interfaces and the non-interfaces shows that three specific alphabets appear more often in the DNA interfaces of DNA-bound forms. One of them is a helix-like structure. This is likely to consecutively show up to extend the helix that exists in the free form, which, as a result, will enhance the dipole moment of the helix. This may be why the alphabet is favored in the DNA interface.
角南 智子; 河野 秀俊
no journal, ,
Conformational flexibility of DNA plays important roles on biological processes such as transcriptional regulations. Therefore, it is important to analyze when and how DNA shows conformational variations. Electron density maps in crystallographic analyses contain information of conformational variations. But such information is typically discarded in the refinement process. To extract the information about conformational variations, we have performed comprehensive analysis of the electron density maps of DNA crystals. We found that positive FoFc densities are observed more frequently around phosphates than around bases, indicating high flexibility of DNA phosphates. In the presentation, we will discuss more details.
角南 智子; 河野 秀俊
no journal, ,
Recently, zinc finger nucleases which are artificially fused a zincfinger transcription factor and a nuclease have been widely used for genome editing. However, the applications are limited because they only recognize GC-rich sequences. To make such artificial proteins recognize broader sequences other than GC-rich ones, we are rationally designing novel proteins based on an engrailed homeodomain. Engrailed homeodomain proteins recognize six bases. To recognize longer DNA sequences, we connected two homeodomains with a short linker. We will report that the designed molecule show a strong affinity and high specificity for the target sequence. We will also report a DNA sequence profile of the protein obtained by B1H assay.