Quantitative study of the spin Hall magnetoresistance in ferromagnetic insulator/normal metal hybrids
Althammer, M.*; Meyer, S.*; Nakayama, Hiroyasu*; Schreier, M.*; Altmannshofer, S.*; Weiler, M.*; Huebl, H.*; Gepr gs, S.*; Opel, M.*; Gross, R.*; Meier, D.*; Klewe, C.*; Kuschel, T.*; Schmalhorst, J.-M.*; Reiss, G.*; Shen, L.*; Gupta, A.*; Chen, Y.-T.*; Bauer, G. E. W.*; Saito, Eiji; Goennenwein, S.*
gs, S.*; Opel, M.*; Gross, R.*; Meier, D.*; Klewe, C.*; Kuschel, T.*; Schmalhorst, J.-M.*; Reiss, G.*; Shen, L.*; Gupta, A.*; Chen, Y.-T.*; Bauer, G. E. W.*; Saito, Eiji; Goennenwein, S.*
We experimentally investigate and quantitatively analyze the spin Hall magnetoresistance (SMR) effect in ferromagnetic insulator (FI)/Pt and FI/nonmagnetic metal/Pt hybrid structures. For the FI, we use either YIG, nickel ferrite, or magnetite and for the nonmagnet, Cu or Au. The SMR is theoretically ascribed to the combined action of spin Hall and inverse spin Hall effect in the Pt top layer. It therefore should characteristically depend upon the orientation of the magnetization in the adjacent ferromagnet and prevail even if an additional, nonmagnetic metal layer is inserted between Pt and the ferromagnet. Our experimental data corroborate these theoretical conjectures. Using the SMR theory to analyze our data, we extract the spin Hall angle and the spin diffusion length in Pt. For a spin-mixing conductance of 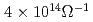 m
m , we obtain a spin Hall angle of 0.11
, we obtain a spin Hall angle of 0.11  0.08 and a spin diffusion length of (1.5
0.08 and a spin diffusion length of (1.5  0.5) nm for Pt in our samples.
0.5) nm for Pt in our samples.