Structural basis for acceptor-substrate recognition of UDP-glucose: anthocyanidin 3- -glucosyltransferase from
-glucosyltransferase from 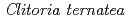
Hiromoto, Takeshi; Honjo, Eijiro*; Tamada, Taro; Kuroki, Ryota; Noda, Hisanobu*; Kazuma, Kohei*; Suzuki, Masahiko*
UDP-glucose: anthocyanidin 3- -glucosyltransferase from
-glucosyltransferase from 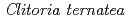 (
( 3GT-A) catalyzes the transfer of glucose from UDP-glucose to anthocyanidins such as delphinidin. The glucosylation of delphinidin at the 3-hydroxyl group has been proposed as an initial glucosylation step toward the biosynthesis of ternatins, which are blue anthocyanins found in the petals of
3GT-A) catalyzes the transfer of glucose from UDP-glucose to anthocyanidins such as delphinidin. The glucosylation of delphinidin at the 3-hydroxyl group has been proposed as an initial glucosylation step toward the biosynthesis of ternatins, which are blue anthocyanins found in the petals of  . Although the crystal structures of several flavonoid glycosyltransferases (UGTs) were determined, the acceptor-substrate complexes were limited to the flavonol-bound forms. Here, in order to understand the acceptor-recognition scheme of
. Although the crystal structures of several flavonoid glycosyltransferases (UGTs) were determined, the acceptor-substrate complexes were limited to the flavonol-bound forms. Here, in order to understand the acceptor-recognition scheme of  3GT-A, the crystal structures in complex with anthocyanidin delphinidin and petunidin, and flavonol kaempferol were determined to resolutions of 2.6
3GT-A, the crystal structures in complex with anthocyanidin delphinidin and petunidin, and flavonol kaempferol were determined to resolutions of 2.6  , 2.7
, 2.7  , and 1.8
, and 1.8  respectively. The enzyme recognition of unstable anthocyanidins was firstly observed in this structural determination; nevertheless, the molecular orientations of these three acceptors in the binding site are different from those of the known flavonoid UGTs,
respectively. The enzyme recognition of unstable anthocyanidins was firstly observed in this structural determination; nevertheless, the molecular orientations of these three acceptors in the binding site are different from those of the known flavonoid UGTs, 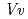 GT1 and UGT78G1. The crystal structures of
GT1 and UGT78G1. The crystal structures of  3GT-A provide insight not only into anthocyanidin configurations in enzyme, but also into a different binding scheme for acceptor-substrate recognition compared with the known UGTs.
3GT-A provide insight not only into anthocyanidin configurations in enzyme, but also into a different binding scheme for acceptor-substrate recognition compared with the known UGTs.