Screening of novel anthocyanin mutants by re-irradiation of ion beams in  mutant
mutant
イオンビーム再照射によるシロイヌナズナの新規フラボノイド変異体の作出
北村 智; 大野 豊; 鳴海 一成*
Kitamura, Satoshi; Ono, Yutaka; Narumi, Issey*
イオンビームは新しい変異体を誘発するのに効果的である。既存のイオンビーム変異体に対するイオンビーム再照射は、イオンビームがゲノムの一部のみを改変する特徴を活かした変異誘発法で、植物の形質を一歩ずつ改変していくのに有効である。今回、シロイヌナズナにおいてイオンビーム照射法を適用し、従来法では得られないような色素蓄積変異体の選抜を行った。
Forward genetics approaches have helped elucidate the anthocyanin biosynthetic pathway in plants. We used the 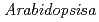 banyuls (ban) mutant, which accumulates anthocyanins, instead of colorless proanthocyanidin precursors, in immature seeds. In contrast to standard screens for mutants lacking anthocyanins in leaves/stems, we mutagenized ban plants and screened for mutants showing differences in pigmentation of immature seeds. The pale banyuls1 (pab1) mutation was found to show reduced levels of anthocyanins in immature seed coat. Here we characterize this mutant at the molecular level.
banyuls (ban) mutant, which accumulates anthocyanins, instead of colorless proanthocyanidin precursors, in immature seeds. In contrast to standard screens for mutants lacking anthocyanins in leaves/stems, we mutagenized ban plants and screened for mutants showing differences in pigmentation of immature seeds. The pale banyuls1 (pab1) mutation was found to show reduced levels of anthocyanins in immature seed coat. Here we characterize this mutant at the molecular level.