The Influence of porosity on thermal conductivity of low-density uranium oxide
低密度ウラン酸化物の熱伝導率における気孔率の影響
森本 恭一  ; 小笠原 誠洋*
; 小笠原 誠洋*
Morimoto, Kyoichi; Ogasawara, Masahiro*
燃料製造では経済性向上の観点から密度仕様の緩和が検討されている。燃料密度は燃料設計上重要な仕様であり、これは原料粉末の特性によって変動する。密度仕様緩和の検討において、燃料設計で使用する熱伝導率の気孔率補正式については低密度領域での適用性を確認する必要がある。ここで、気孔率(p), 密度(d), 理論密度(d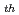 )には次の関係がある; p=1-(d/d
)には次の関係がある; p=1-(d/d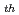 )。本研究では熱伝導率測定中のO/Mの安定性に優れているUO
)。本研究では熱伝導率測定中のO/Mの安定性に優れているUO ペレットを試験用試料とし、密度を広い範囲で調整した。これらの試料について熱伝導率測定を実施し、気孔率補正式の適用性を評価した。
ペレットを試験用試料とし、密度を広い範囲で調整した。これらの試料について熱伝導率測定を実施し、気孔率補正式の適用性を評価した。
In MOX fuel fabrication, the mitigation of specifications on fuel design is considered from a viewpoint of improvement of economic efficiency. As the one of the mitigations of specifications, the tolerance expansion of the density specification is considered. In this consideration, it is necessary to confirm the applicability of the porosity correction equation to the thermal conductivity in a low density region. In this study, UO pellet was adopted as test specimen for the following reasons. The stability of O/M ratio of UO
pellet was adopted as test specimen for the following reasons. The stability of O/M ratio of UO pellets in the thermal conductivity measurement is superior to that of MOX pellets. The densities of the specimens were adjusted in the wide range by using crystalline cellulose. The thermal conductivities of these specimens were measured and the applicability of the porosity correction equation to the thermal conductivity in a low density region was evaluated.
pellets in the thermal conductivity measurement is superior to that of MOX pellets. The densities of the specimens were adjusted in the wide range by using crystalline cellulose. The thermal conductivities of these specimens were measured and the applicability of the porosity correction equation to the thermal conductivity in a low density region was evaluated.