Preparation of  -LiV
-LiV O
O from polyoxovanadate cluster Li
from polyoxovanadate cluster Li [V
[V O
O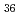 (CO
(CO )] as a high-performance cathode material and its reaction mechanism revealed by
)] as a high-performance cathode material and its reaction mechanism revealed by  XAFS
XAFS
バナジウム酸化物クラスターからの高性能正極電極作製および電極反応機構のオペランドXAFSによる解明
Wang, H.*; 磯部 仁*; 清水 剛志*; 松村 大樹 

 ; 伊奈 稔哲*; 吉川 浩史*
; 伊奈 稔哲*; 吉川 浩史*
Wang, H.*; Idobe, Jin*; Shimizu, Takeshi*; Matsumura, Daiju; Ina, Toshiaki*; Yoshikawa, Hirofumi*
 -phase LiV
-phase LiV O
O , which shows superior electrochemical performance as cathode material in Li-ion batteries, was prepared by annealing the polyoxovanadate cluster Li
, which shows superior electrochemical performance as cathode material in Li-ion batteries, was prepared by annealing the polyoxovanadate cluster Li [V
[V O
O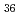 (CO
(CO )]. The reaction mechanism was studied using
)]. The reaction mechanism was studied using  X-ray absorption fine structure (XAFS), powder X-ray diffraction (PXRD), and X-ray photoelectron spectroscopy (XPS) analyses. The X-ray absorption near edge structure (XANES) and XPS results reveal that
X-ray absorption fine structure (XAFS), powder X-ray diffraction (PXRD), and X-ray photoelectron spectroscopy (XPS) analyses. The X-ray absorption near edge structure (XANES) and XPS results reveal that  -LiV
-LiV O
O undergoes two-electron redox reaction per V
undergoes two-electron redox reaction per V O
O pyramid unit, resulting in a large reversible capacity of 260 Ah/kg. The extended X-ray absorption fine structure (EXAFS) and PXRD analyses also suggest that the V-V distance slightly increases, due to the reduction of V
pyramid unit, resulting in a large reversible capacity of 260 Ah/kg. The extended X-ray absorption fine structure (EXAFS) and PXRD analyses also suggest that the V-V distance slightly increases, due to the reduction of V to V
to V during Li ion intercalation as the material structure is maintained. As a result,
during Li ion intercalation as the material structure is maintained. As a result,  -Li
-Li V
V O
O shows highly reversible electrochemical reaction with x = 0.1-1.9.
shows highly reversible electrochemical reaction with x = 0.1-1.9.