Oxidation behavior of high-burnup advanced fuel cladding tubes in high-temperature steam
高燃焼度改良型燃料被覆管の高温水蒸気中酸化挙動
成川 隆文  ; 天谷 政樹
; 天谷 政樹 

Narukawa, Takafumi; Amaya, Masaki
To evaluate the oxidation behavior of high-burnup advanced fuel cladding tubes in high-temperature steam, laboratory-scale isothermal oxidation tests were conducted using the following advanced fuel cladding tubes with burnups of up to 85 GWd/t: M-MDA , low-tin ZIRLO
, low-tin ZIRLO , M5
, M5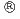 , and Zircaloy-2 (LK3). These oxidation tests were performed in steam-flowing conditions at temperatures ranging from 1173 to 1473 K for durations between 120 and 4000 s, and the oxidation kinetics was evaluated. The oxidation kinetics of the high-burnup advanced fuel cladding tube specimens estimated by assuming the parabolic rate law was comparable to or slower than that of the unirradiated Zircaloy-4 cladding tube specimens reported in a previous study. It is considered that the protective effect of the corrosion layer hindered oxidation. Furthermore, no increase in the oxidation kinetics because of the pre-hydriding was observed. The onset times of the breakaway oxidations of these cladding tube specimens were comparable to those of the unirradiated Zircaloy-4 cladding tubes reported in previous studies. Therefore, it is considered that the burnup extension up to 85 GWd/t and the use of the advanced fuel cladding tubes do not significantly increase the oxidation kinetics and do not significantly reduce the onset time of the breakaway oxidation.
, and Zircaloy-2 (LK3). These oxidation tests were performed in steam-flowing conditions at temperatures ranging from 1173 to 1473 K for durations between 120 and 4000 s, and the oxidation kinetics was evaluated. The oxidation kinetics of the high-burnup advanced fuel cladding tube specimens estimated by assuming the parabolic rate law was comparable to or slower than that of the unirradiated Zircaloy-4 cladding tube specimens reported in a previous study. It is considered that the protective effect of the corrosion layer hindered oxidation. Furthermore, no increase in the oxidation kinetics because of the pre-hydriding was observed. The onset times of the breakaway oxidations of these cladding tube specimens were comparable to those of the unirradiated Zircaloy-4 cladding tubes reported in previous studies. Therefore, it is considered that the burnup extension up to 85 GWd/t and the use of the advanced fuel cladding tubes do not significantly increase the oxidation kinetics and do not significantly reduce the onset time of the breakaway oxidation.