Nonperturbative transverse-momentum-dependent effects in dihadron and direct photon-hadron angular correlations in  collisions at
collisions at 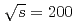 GeV
GeV
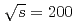 GeVでの陽子-陽子衝突におけるハドロン対および直接光子-ハドロン角度相関測定による非摂動的横運動量効果
GeVでの陽子-陽子衝突におけるハドロン対および直接光子-ハドロン角度相関測定による非摂動的横運動量効果
Aidala, C.*; 長谷川 勝一 

 ; 今井 憲一; 佐甲 博之
; 今井 憲一; 佐甲 博之 

 ; 佐藤 進
; 佐藤 進 
 ; 谷田 聖
; 谷田 聖 

 ; PHENIX Collaboration*; 他287名*
; PHENIX Collaboration*; 他287名*
Aidala, C.*; Hasegawa, Shoichi; Imai, Kenichi; Sako, Hiroyuki; Sato, Susumu; Tanida, Kiyoshi; PHENIX Collaboration*; 287 of others*
Dihadron and isolated direct photon-hadron angular correlations are measured in 

 collisions at
collisions at 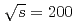 GeV. The correlations are sensitive to nonperturbative initial-state and final-state transverse momentum
GeV. The correlations are sensitive to nonperturbative initial-state and final-state transverse momentum 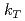 and
and 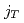 in the azimuthal nearly back-to-back region
in the azimuthal nearly back-to-back region 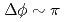 . In this region, transverse-momentum-dependent evolution can be studied when several different hard scales are measured. To have sensitivity to small transverse momentum scales, nonperturbative momentum widths of
. In this region, transverse-momentum-dependent evolution can be studied when several different hard scales are measured. To have sensitivity to small transverse momentum scales, nonperturbative momentum widths of 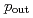 , the out-of-plane transverse momentum component perpendicular to the trigger particle, are measured. These widths are used to investigate possible effects from transverse-momentum-dependent factorization breaking. When accounting for the longitudinal momentum fraction of the away-side hadron with respect to the near-side trigger particle, the widths are found to increase with the hard scale; this is qualitatively similar to the observed behavior in Drell-Yan and semi-inclusive deep-inelastic scattering interactions. The momentum widths are also studied as a function of center-of-mass energy by comparing to previous measurements at
, the out-of-plane transverse momentum component perpendicular to the trigger particle, are measured. These widths are used to investigate possible effects from transverse-momentum-dependent factorization breaking. When accounting for the longitudinal momentum fraction of the away-side hadron with respect to the near-side trigger particle, the widths are found to increase with the hard scale; this is qualitatively similar to the observed behavior in Drell-Yan and semi-inclusive deep-inelastic scattering interactions. The momentum widths are also studied as a function of center-of-mass energy by comparing to previous measurements at 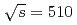 GeV. The nonperturbative jet widths also appear to increase with
GeV. The nonperturbative jet widths also appear to increase with  at a similar
at a similar  , which is qualitatively consistent to similar measurements in Drell-Yan interactions.
, which is qualitatively consistent to similar measurements in Drell-Yan interactions.