Oxygen potentials of Am and Np-bearing MOX
Hirooka, Shun  ; Matsumoto, Taku; Kato, Masato
; Matsumoto, Taku; Kato, Masato 

 ; Sunaoshi, Takeo*
; Sunaoshi, Takeo*
Oxygen potentials of (U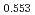 Pu
Pu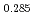 Am
Am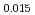 Np
Np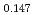 )O
)O pellet sintered in the atmosphere of Ar/H
pellet sintered in the atmosphere of Ar/H /H
/H O mixture gas were measured at 1600
O mixture gas were measured at 1600 C and 1650
C and 1650 C by the gas equilibrium method. The oxygen partial pressure of the atmosphere was accurately adjusted by changing H
C by the gas equilibrium method. The oxygen partial pressure of the atmosphere was accurately adjusted by changing H O content in the gas and monitored with oxygen sensors. Simultaneously, weight change originated by oxidation or reduction was measured by thermo-gravimetry method and O/M was calculated by the weight change. The measured data showed that the substitution of minor actinide with U increased the oxygen potential, indicating that O/M could be lowered by adding minor actinide if temperature and oxygen partial pressure of the surrounding gas was preserved. The present data was analyzed together with the previous Am-MOX data and led to the results that containing 1% of Am is equivalent to 4% of Pu on the effect of oxygen potential. Similarly, 1% of Np is equivalent to 0.2% of Pu. These effects were reflected to the defect formation energies and the relation among O/M, temperature, content ratio and oxygen partial pressure was derived. This relation can evaluate O/M of MA-MOX more accurately and, therefore, is the useful fuel technology for fuel design and evaluating irradiation behaviors.
O content in the gas and monitored with oxygen sensors. Simultaneously, weight change originated by oxidation or reduction was measured by thermo-gravimetry method and O/M was calculated by the weight change. The measured data showed that the substitution of minor actinide with U increased the oxygen potential, indicating that O/M could be lowered by adding minor actinide if temperature and oxygen partial pressure of the surrounding gas was preserved. The present data was analyzed together with the previous Am-MOX data and led to the results that containing 1% of Am is equivalent to 4% of Pu on the effect of oxygen potential. Similarly, 1% of Np is equivalent to 0.2% of Pu. These effects were reflected to the defect formation energies and the relation among O/M, temperature, content ratio and oxygen partial pressure was derived. This relation can evaluate O/M of MA-MOX more accurately and, therefore, is the useful fuel technology for fuel design and evaluating irradiation behaviors.