Hybridization of Bogoliubov quasiparticles between adjacent CuO layers in the triple-layer cuprate Bi
layers in the triple-layer cuprate Bi Sr
Sr Ca
Ca Cu
Cu O
O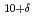 studied by angle-resolved photoemission spectroscopy
studied by angle-resolved photoemission spectroscopy
角度分解光電子分光を用いた三層系銅酸化物におけるボゴリウボフ準粒子の混成
出田 真一郎*; Johnston, S.*; 吉田 鉄平*; 田中 清尚*; 森 道康 
 ; 安齋 太陽*; 井野 明洋*; 有田 将司*; 生天目 博文*; 谷口 雅樹*; 石田 茂之*; 高島 憲一*; 小嶋 健児*; Devereaux, T. P.*; 内田 慎一*; 藤森 淳*
; 安齋 太陽*; 井野 明洋*; 有田 将司*; 生天目 博文*; 谷口 雅樹*; 石田 茂之*; 高島 憲一*; 小嶋 健児*; Devereaux, T. P.*; 内田 慎一*; 藤森 淳*
Ideta, Shinichiro*; Johnston, S.*; Yoshida, Teppei*; Tanaka, Kiyohisa*; Mori, Michiyasu; Anzai, Hiroaki*; Ino, Akihiro*; Arita, Masashi*; Namatame, Hirofumi*; Taniguchi, Masaki*; Ishida, Shigeyuki*; Takakura, Kenichi*; Kojima, Kenji M*; Devereaux, T. P.*; Uchida, Shinichi*; Fujimori, Atsushi*
Hybridization of Bogoliubov quasiparticles (BQPs) between the CuO layers in the triple-layer cuprate high-temperature superconductor Bi
layers in the triple-layer cuprate high-temperature superconductor Bi Sr
Sr Ca
Ca Cu
Cu O
O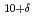 is studied by angle-resolved photoemission spectroscopy (ARPES). In the superconducting state, an anti-crossing gap opens between the outer- and inner-BQP bands, which we attribute primarily to interlayer single-particle hopping with possible contributions from interlayer Cooper pairing. We find that the
is studied by angle-resolved photoemission spectroscopy (ARPES). In the superconducting state, an anti-crossing gap opens between the outer- and inner-BQP bands, which we attribute primarily to interlayer single-particle hopping with possible contributions from interlayer Cooper pairing. We find that the  -wave superconducting gap of both BQP bands smoothly develops with momentum without abrupt jump in contrast to a previous ARPES study. Hybridization between the BQPs also gradually increases in going from the off-nodal to the anti-nodal region, which is explained by the momentum-dependence of the interlayer single-particle hopping. As possible mechanisms for the enhancement of the superconducting transition temperature, the hybridization between the BQPs, as well as the combination of phonon modes of the triple CuO
-wave superconducting gap of both BQP bands smoothly develops with momentum without abrupt jump in contrast to a previous ARPES study. Hybridization between the BQPs also gradually increases in going from the off-nodal to the anti-nodal region, which is explained by the momentum-dependence of the interlayer single-particle hopping. As possible mechanisms for the enhancement of the superconducting transition temperature, the hybridization between the BQPs, as well as the combination of phonon modes of the triple CuO layers and spin fluctuations are discussed.
layers and spin fluctuations are discussed.