Measurements of thermal conductivity for near stoichiometric (U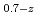 Pu
Pu Am
Am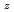 )O
)O (z = 0.05, 0.10, and 0.15)
(z = 0.05, 0.10, and 0.15)
化学量論組成近傍における(U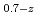 Pu
Pu Am
Am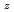 )O
)O (z = 0.05, 0.10, and 0.15)の熱伝導率測定
(z = 0.05, 0.10, and 0.15)の熱伝導率測定
横山 佳祐  ; 渡部 雅
; 渡部 雅 
 ; 所 大志郎*; 杉本 理峻*; 森本 恭一
; 所 大志郎*; 杉本 理峻*; 森本 恭一  ; 加藤 正人
; 加藤 正人 

 ; 日野 哲士*
; 日野 哲士*
Yokoyama, Keisuke; Watanabe, Masashi; Tokoro, Daishiro*; Sugimoto, Masatoshi*; Morimoto, Kyoichi; Kato, Masato; Hino, Tetsushi*
高レベル放射性廃棄物の減容化の一環として、マイナーアクチニドを含んだ酸化物燃料が高速炉における選択の一つである。しかし、高Am含有MOX燃料の熱伝導率に関する実験データがないために、燃料中のAm含有量が熱伝導率に及ぼす影響は明らかとなっていない。本研究では化学量論組成近傍における(U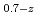 Pu
Pu Am
Am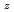 )O
)O (z = 0.05, 0.10, and 0.15)の熱伝導率をレーザーフラッシュ法を用いて室温から1473Kまでの範囲で測定した。結果として、熱伝導率はAm含有量が増加するに従い低下する傾向を示し、1473Kまでは古典的フォノン輸送モデル((A+BT)
(z = 0.05, 0.10, and 0.15)の熱伝導率をレーザーフラッシュ法を用いて室温から1473Kまでの範囲で測定した。結果として、熱伝導率はAm含有量が増加するに従い低下する傾向を示し、1473Kまでは古典的フォノン輸送モデル((A+BT) )に従うことが明らかとなった。係数AはAm含有量に比例して増加する傾向を示し、U
)に従うことが明らかとなった。係数AはAm含有量に比例して増加する傾向を示し、U 及びAm
及びAm が固溶することによるイオン半径の変化がフォノン伝導に影響したためであると考えられる。係数BはAm含有量に依存しない傾向を示した。
が固溶することによるイオン半径の変化がフォノン伝導に影響したためであると考えられる。係数BはAm含有量に依存しない傾向を示した。
In current nuclear fuel cycle systems, to reduce the amount of high-level radioactive waste, minor actinides (MAs) bearing MOX fuel is one option for burning MAs using fast reactor. However, the effects of Am content in fuel on thermal conductivity are unclear because there are no experimental data on thermal conductivity of high Am bearing MOX fuel. In this study, The thermal conductivities of near stoichiometric (U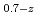 Pu
Pu Am
Am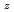 )O
)O solid solutions(z = 0.05, 0.10, and 0.15) have been measured between room temperature (RT) and 1473 K. The thermal conductivities decreased with increasing Am content and satisfied the classical phonon transport model ((A+BT)
solid solutions(z = 0.05, 0.10, and 0.15) have been measured between room temperature (RT) and 1473 K. The thermal conductivities decreased with increasing Am content and satisfied the classical phonon transport model ((A+BT) ) up to about 1473 K. A values increased linearly with increasing Am content because the change in ionic radius affects the conduction of the phonon due to the solid solution in U
) up to about 1473 K. A values increased linearly with increasing Am content because the change in ionic radius affects the conduction of the phonon due to the solid solution in U and Am
and Am . B values were independent of Am content.
. B values were independent of Am content.