焼岳中尾テフラ; 北アルプス南部における完新世後期の年代指標としての有用性の検討
Yakedake Nakao tephra; An Attempt to use the local tephra as a Late Holocene age marker for the southern part of the Northern Japan Alps
西尾 学*; 鏡味 沙耶 

 ; 横山 立憲
; 横山 立憲 

 ; 苅谷 愛彦*; 小嶋 智*
; 苅谷 愛彦*; 小嶋 智*
Nishio, Gaku*; Kagami, Saya; Yokoyama, Tatsunori; Kariya, Yoshihiko*; Kojima, Satoru*
東アジアにおける第四紀の広域火山灰を用いた年代測定法はほぼ確立しているが、日本のように火山の多い地域では、近傍の火山の噴出物の影響が強く、広域火山灰の産出ピークを検出できない場合が多い。そこで、近傍の火山による特徴的な地域性火山灰を年代指標とする方法を開発することを本研究の目的とした。研究対象地域は、焼岳火山の影響を強く受ける北アルプス南部の上高地周辺地域である。(1)焼岳の北東約4.7kmに位置する「きぬがさの池」湖畔で掘削されたハンドオーガーボーリングコアに含まれるガラス質火山灰(苅谷・高岡, 2019)1試料と、(2)焼岳の北北西約1.5kmの地点に分布する約2,300年前の中尾火砕流堆積物に挟まれるガラス質火山灰2試料である。これらの火山灰の粒子組成、火山ガラスの化学組成・屈折率を測定し、その特徴を明らかにした。各試料につき200個以上の粒子を偏光顕微鏡を用いて同定した結果、これらの火山灰の構成粒子の約70%は火山ガラスから成り、その大半がvesicularとblockyであることが明らかとなった。火山ガラスの化学組成は、日本原子力研究開発機構東濃地科学センターの電子プローブマイクロアナライザ(EPMA)を用いて測定した。その結果、3試料中の火山ガラスの化学組成は、SiO , K
, K O, Na
O, Na Oが多く、Al
Oが多く、Al O
O , FeOが少ないという特徴を持ち、東アジアにおける第四紀広域火山灰中の火山ガラスの化学組成とは明瞭に区別できる。3試料それぞれ30個の火山ガラスを対象に、中央大学の温度変化型屈折率測定器(RIMS)を用いて屈折率を測定した。その結果、火山ガラスの屈折率は1.4958-1.5011の範囲の値を示し、1.497-1.499の範囲にピークを持つことが明らかとなった。以上のように、「きぬがさの池」で見出された火山灰は、中尾火砕流堆積物に挟まれる火山灰と、粒子組成,火山ガラスの屈折率・化学組成の点で一致し、約2,300年前の焼岳の噴火活動による火山灰であることがわかった。したがって、上記の特徴を持った火山灰は、北アルプス南部における約2,300年前の有用な年代指標とすることができると考えられる。
, FeOが少ないという特徴を持ち、東アジアにおける第四紀広域火山灰中の火山ガラスの化学組成とは明瞭に区別できる。3試料それぞれ30個の火山ガラスを対象に、中央大学の温度変化型屈折率測定器(RIMS)を用いて屈折率を測定した。その結果、火山ガラスの屈折率は1.4958-1.5011の範囲の値を示し、1.497-1.499の範囲にピークを持つことが明らかとなった。以上のように、「きぬがさの池」で見出された火山灰は、中尾火砕流堆積物に挟まれる火山灰と、粒子組成,火山ガラスの屈折率・化学組成の点で一致し、約2,300年前の焼岳の噴火活動による火山灰であることがわかった。したがって、上記の特徴を持った火山灰は、北アルプス南部における約2,300年前の有用な年代指標とすることができると考えられる。
We attempt to use local tephra derived from nearby volcanoes as an age marker. The Kamikochi area in the southern part of the Northern Alps is strongly affected by the Yakedake volcano. We prepared distinctive tephras, (1) one sample of glassy volcanic ash in hand auger boring cores drilled at the near-shore Kinugasanoike Pond, about 4.7 km northeast of Mt. Yakedake and (2) two samples of glassy volcanic ash in the Nakao pyroclastic flow deposites, which is considered to be a product of the last magmatic eruption about 2,300 years ago, distributed about 1.5 km north-northwest of Mt. Yakedake. We investigated the clast composition of these tephras and the chemical composition and refractive index of volcanic glass. Approximately 70% of the clasts were volcanic glasses, and most of them were vesicular and blocky types. These glasses were characterized by high SiO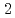 , K
, K O, Na
O, Na O and low Al
O and low Al O
O , FeO, which were clearly distinguishable from the volcanic glasses in Quaternary widespread tephras. The refractive indices of 30 volcanic glasses for each tephra were 1.4958-1.5011 with a peak in the range of 1.497 to 1.499. The results of this study indicate the tephra from Kinugasanoike Pond were erupted from Mt. Yakedake about 2,300 years ago. Therefore, the tephra with the above characteristics can be used as a useful age marker for the southern part of the Northern Alps about 2,300 years ago.
, FeO, which were clearly distinguishable from the volcanic glasses in Quaternary widespread tephras. The refractive indices of 30 volcanic glasses for each tephra were 1.4958-1.5011 with a peak in the range of 1.497 to 1.499. The results of this study indicate the tephra from Kinugasanoike Pond were erupted from Mt. Yakedake about 2,300 years ago. Therefore, the tephra with the above characteristics can be used as a useful age marker for the southern part of the Northern Alps about 2,300 years ago.