Measurement of spent nuclear fuel burn-up using a new H method
method
新しいH 法を用いた使用済燃料燃焼度の測定
法を用いた使用済燃料燃焼度の測定
名内 泰志*; 佐藤 駿介*; 早川 岳人*; 木村 康彦; 須山 賢也; 鹿島 陽夫*; 二上 和広*
Nauchi, Yasushi*; Sato, Shunsuke*; Hayakawa, Takehito*; Kimura, Yasuhiko; Suyama, Kenya; Kashima, Takao*; Futakami, Kazuhiro*
水素の中性子捕獲反応による2.223MeVの 線を高純度ゲルマニウム(HPGe)検出器を用いて検出するH
線を高純度ゲルマニウム(HPGe)検出器を用いて検出するH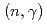 法によって使用済核燃料からの中性子測定を行った。この2.223MeVの
法によって使用済核燃料からの中性子測定を行った。この2.223MeVの 線の検出は、7桁も高い核分裂生成物(FP)からの
線の検出は、7桁も高い核分裂生成物(FP)からの 線に強い影響を受ける。FPからの強い
線に強い影響を受ける。FPからの強い を遮蔽するために、ポリエチレンブロックをコリメータの軸上に置くとともに、HPGe検出器をコリメーターの軸から外して設置した。この体系によって検出器はFPからの強い
を遮蔽するために、ポリエチレンブロックをコリメータの軸上に置くとともに、HPGe検出器をコリメーターの軸から外して設置した。この体系によって検出器はFPからの強い 線から遮蔽され、ポリエチレンブロック中のH
線から遮蔽され、ポリエチレンブロック中のH 反応によって2.223MeVの
反応によって2.223MeVの 線が測定できる。測定された2.223MeVの
線が測定できる。測定された2.223MeVの 線の計数率は、燃焼崩壊計算により見積もられた核種組成、主には
線の計数率は、燃焼崩壊計算により見積もられた核種組成、主には Cmによるものと、統計誤差の範囲内で想定される値と一貫性のある値となる。このことから、H
Cmによるものと、統計誤差の範囲内で想定される値と一貫性のある値となる。このことから、H 法は、使用済核燃料集合体からの中性子漏洩数の定量化に適用可能であり、集合体の燃焼度の確認に適用可能であると考えられる。
法は、使用済核燃料集合体からの中性子漏洩数の定量化に適用可能であり、集合体の燃焼度の確認に適用可能であると考えられる。
Measurement of neutrons from spent nuclear fuel is performed in this study using the H method, which detects 2.223 MeV
method, which detects 2.223 MeV  rays from neutron capture reaction of hydrogen using a highly pure germanium (HPGe) detector. The detection of the 2.223 MeV
rays from neutron capture reaction of hydrogen using a highly pure germanium (HPGe) detector. The detection of the 2.223 MeV  ray is affected by intense
ray is affected by intense  ray emission from fission products (FPs) because the emission rate of
ray emission from fission products (FPs) because the emission rate of  rays from the FP is seven orders of magnitude higher than the emission rate of neutrons. To shield the intense
rays from the FP is seven orders of magnitude higher than the emission rate of neutrons. To shield the intense  ray from the FP, the HPGe detector is placed off the axis of a collimator, whereas a polyethylene block is placed on the axis. In this geometry, the detector is shielded from the intense
ray from the FP, the HPGe detector is placed off the axis of a collimator, whereas a polyethylene block is placed on the axis. In this geometry, the detector is shielded from the intense  rays from the FP, but the detector can measure 2.223 MeV
rays from the FP, but the detector can measure 2.223 MeV  rays from the H
rays from the H reactions in the polyethylene block. The measured count rate of the 2.223 MeV
reactions in the polyethylene block. The measured count rate of the 2.223 MeV  rays is consistent with the expected rate within the statistical error, which is calculated based on the nuclide composition, which is primary
rays is consistent with the expected rate within the statistical error, which is calculated based on the nuclide composition, which is primary  Cm, estimated via depletion and decay calculations. Accordingly, the H
Cm, estimated via depletion and decay calculations. Accordingly, the H method is considered feasible to quantify the number of neutron leakage from spent nuclear fuel assembly, which is applicable to certify burn up of the assembly.
method is considered feasible to quantify the number of neutron leakage from spent nuclear fuel assembly, which is applicable to certify burn up of the assembly.