高温水クレビス模擬環境におけるFe-Cr-Ni合金の粒界腐食挙動に及ぼすCr濃度の影響
Effects of Cr on intergranular corrosion behavior of Fe-Cr-Ni alloys in simulated crevice environments in high temperature water
相馬 康孝 

 ; 五十嵐 誉廣
; 五十嵐 誉廣 

Soma, Yasutaka; Igarashi, Takahiro
高温水中におけるステンレス鋼の応力腐食割れ(SCC)内部では酸性の腐食環境(クレビス環境)が形成すると考えられることから、SCC挙動を解明するためにはクレビス環境においての腐食挙動解明が重要である。過去にわれわれはクレビス内部の導電率を測定し、すき間腐食が発生する場合としない場合でそれぞれ380 S/cm、1600
S/cm、1600 S/cmの数値を得たことから、本研究ではこれらの数値に対応する環境をそれぞれクレビス環境I(pH
S/cmの数値を得たことから、本研究ではこれらの数値に対応する環境をそれぞれクレビス環境I(pH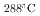 =4.41)、及びII(pH
=4.41)、及びII(pH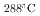 =3.13)とし、それぞれの環境中におけるFe-xCr-20Ni(x=16.9, 19.8, 22.9, 24.3, 25.9)の腐食挙動を調べた。この結果、クレビス模擬環境Iではすべての合金組成で不働態化が見られた一方、クレビス模擬環境IIではx=16.9、及び19.8で粒界の割れを伴う激しい腐食が見られ、厚い酸化皮膜が形成した。一方、x=22.9以上では酸化皮膜成長は抑制され、明確な分極曲線上に明確な不働態域が形成された。
=3.13)とし、それぞれの環境中におけるFe-xCr-20Ni(x=16.9, 19.8, 22.9, 24.3, 25.9)の腐食挙動を調べた。この結果、クレビス模擬環境Iではすべての合金組成で不働態化が見られた一方、クレビス模擬環境IIではx=16.9、及び19.8で粒界の割れを伴う激しい腐食が見られ、厚い酸化皮膜が形成した。一方、x=22.9以上では酸化皮膜成長は抑制され、明確な分極曲線上に明確な不働態域が形成された。
Since an acidic corrosive environment (crevice environment) is formed inside the stress corrosion cracking (SCC) of stainless steel in high temperature water, it is important to understand the corrosion behavior in the crevice environment for the better understanding of crack growth behavior. In the previous study, the authors measured the electrical conductivity inside the crevice and obtained values of 380  S/cm and 1600
S/cm and 1600  S/cm for the crevice with and without intergranular corrosion, respectively. In this study, we defined the crevice environment I (pH
S/cm for the crevice with and without intergranular corrosion, respectively. In this study, we defined the crevice environment I (pH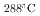 =4.41) and II (pH
=4.41) and II (pH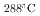 =3.13) corresponding the above conductivity values, and the corrosion behavior of Fe-xCr-20Ni (x=16.9, 19.8, 22.9, 24.3, 25.9) in each crevice environment was investigated. In the simulated crevice environment-I, the all alloys showed passive behavior, while in the environment-II, severe corrosion with intergranular cracking was observed for x = 16.9 and 19.8, and a thick oxide film was formed. On the other hand, above x=22.9, oxide film growth was suppressed and a clear passive region appeared on the polarization curve.
=3.13) corresponding the above conductivity values, and the corrosion behavior of Fe-xCr-20Ni (x=16.9, 19.8, 22.9, 24.3, 25.9) in each crevice environment was investigated. In the simulated crevice environment-I, the all alloys showed passive behavior, while in the environment-II, severe corrosion with intergranular cracking was observed for x = 16.9 and 19.8, and a thick oxide film was formed. On the other hand, above x=22.9, oxide film growth was suppressed and a clear passive region appeared on the polarization curve.