Experimental determination of deposition velocity of CsOH aerosols on CaCO at temperature range 170 - 290
at temperature range 170 - 290 C
C
170-290 Cの温度範囲におけるCsOHエアロゾルのCaCO
Cの温度範囲におけるCsOHエアロゾルのCaCO 上への沈着速度測定
上への沈着速度測定
Luu, V. N.  ; 中島 邦久
; 中島 邦久 

Luu, V. N.; Nakajima, Kunihisa
A field assessment at the Fukushima-Daiichi Nuclear Power Station revealed high radioactivity on the concrete shield plugs, which is estimated above 20 PBq for Cs-137 at units 2 and 3. This leads to significant interest in the retention of Cs on concrete during severe accidents (SA). However, the interaction of CsOH, as one of the main Cs forms released in SA, with concrete surfaces at elevated temperatures remains poorly researched. In this study, we have experimentally investigated the deposition behavior of CsOH on CaCO , which is the primary phase existing on the surface of concrete, under humid atmosphere. As a result, the chemical reaction enhanced deposition rate (N), and increased linearly with CsOH concentration (C
, which is the primary phase existing on the surface of concrete, under humid atmosphere. As a result, the chemical reaction enhanced deposition rate (N), and increased linearly with CsOH concentration (C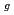 ), as following expression: N(
), as following expression: N( g/cm
g/cm
 s) = v
s) = v C
C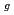 , where v
, where v is temperature-dependent deposition velocity as given by ln v
is temperature-dependent deposition velocity as given by ln v (cm/s) = -3785.8/T + 3.766, for T in the range of 170 and 290
(cm/s) = -3785.8/T + 3.766, for T in the range of 170 and 290  C. This empirical model can be integrated into severe accident codes to quantify the chemical trapping of cesium on concrete surfaces during ex-vessel release. Moreover, it can contribute to understanding the reasons behind the high dose rate on concrete shield plugs at the Fukushima Daiichi Nuclear power stations and aid in developing effective decommissioning practices for concrete structures.
C. This empirical model can be integrated into severe accident codes to quantify the chemical trapping of cesium on concrete surfaces during ex-vessel release. Moreover, it can contribute to understanding the reasons behind the high dose rate on concrete shield plugs at the Fukushima Daiichi Nuclear power stations and aid in developing effective decommissioning practices for concrete structures.