Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
*; *
PNC TN942 85-02, 31 Pages, 1985/03
In the case of fast breeder reactors, the in-service inspection of the reactor vessel must be conducted under such severe conditions as relatively high temperature, high radiation dose, and narrow space. Therefore, the heat- and radiation- resistant sensors are required, which also should be compact and flexible for remote handling and installing. Authors reviewed the state of the fiber scopes for the visual in-service examination, and discussed some problems about applicability to FBR conditions. This report presents the technical information obtained from the survey conducted in 1983, and the brief draft of the development plan including some remained problems about application to FBR.
Kaneko, Yoshihisa*; Nishikimi, Masakazu*; Shirato, Seiichi*; *
PNC TN941 85-22, 142 Pages, 1985/02
Series of tests on water leak detection system for Monju steam generators have been excuted in the 50MW Steam Generator Test Facility (50MW SGTF). This paper describes the test results about the removal efficiency of hydrogen by the secondary cold trap, the hydrogen background concentration and hydrogen flux through heat transfer tubes to secondary sodium in steam generator (SG) in order to make clear the hydrogen behavior during ordinary plant operation from October in 1976 to July in 1983. Main results from these tests are: (1)The removal efficieney of hydrogen by the cold trap is 70 80 percents, but it shows tendency to decrease when difference between hydrogen concentration at cold trap and that in secondary main loop is small. (2)Hydrogen flux through tubes is smaller than the value which is reported in the first report of these series reports. (3)It is found that the hydrogen background concentration in the secondary main loop of 50MW SGTF is thoroughly low. (4)It is estimated that the hydrogen background concentration in the secondary main loop in Monju plant is lower than 169 ppb.
80 percents, but it shows tendency to decrease when difference between hydrogen concentration at cold trap and that in secondary main loop is small. (2)Hydrogen flux through tubes is smaller than the value which is reported in the first report of these series reports. (3)It is found that the hydrogen background concentration in the secondary main loop of 50MW SGTF is thoroughly low. (4)It is estimated that the hydrogen background concentration in the secondary main loop in Monju plant is lower than 169 ppb.
*; *; *; *; *; *; *
PNC TN941 84-169, 172 Pages, 1984/12
A design study was conducted in order to establish the concept of the FBR plant eliminating the secondary sodium loop. Conditions for realization and effectivenesses for cost reduction were also studied for this plant. The main topic for understanding this plant concept was recognized as to clearify "the influence of sodium-water reaction to the reactor core", broken out in the steam generator. Discussions were mainly focussed on the reactor core, the steam generator, the containment vessel, sodium-water reaction product relief system and so on, which were supposed to be especially important for this plant concept. Following items were recognized. (1) Total image and concept of the FBR plant eliminating the secondary sodium loop. (2) Influence of the sodium-water reaction product, especially hydrogen gas, to reactor core and limit of the water-leak rate for core damage. (3) Countermeasures for reduction and elimination of these influences. (4) Concepts of the safety map for sodium-water reaction of this plant and requirements for water leak detection systems. (5) Necessity of the duplex tube type steam generator from the view point of property protection. (6) Reduction effect for the amount of materials and construction cost by adopting this concept of plant. A overall process for design study was experienced throuqh the activities of this work.
Shirato, Seiichi*; Kaneko, Yoshihisa*; *; Nishikimi, Masakazu*; *; *; *
PNC TN941 84-136, 258 Pages, 1984/10
It is necessary to detect the water leak (sodium-water reaction) as fast as possible in a steam generator for liquid metal fast breeder reactor, and hydrogen meter has been developed for detection of water leak. In-sodium hydrogen meter and in-cover gas hydrogen meter have been developed in 50 MW steam generator test facility for the purpose of leak detection system of LMFBR "Monju" plant. This paper reports the development of each hydrogen meter, operational experience and evaluation of performance. Some proposals for design, manufacture, operation and maintenance of "Monju" plant 1eak detection system are also described.
Kaneko, Yoshihisa*; *; Nishikimi, Masakazu*; *; *
PNC TN941 84-93, 139 Pages, 1984/06
Rupture disks were tested for a purpose of examination of burst characteristic, corrosion, change of metal formation and mechanical characteristic. Those rupture disks were installed at evaporator (reverse buckling type), superheater (reverse buckling type) and reaction product vessel (tension loaded type) and were used from September, 1975 to January, 1983 at 50 MW steam generator test facility (50 MW SGTF). Main results are the following; (1)Burst pressure of used and unused rupture disks of steam generator and reaction product vessel was lower than the value measured at producted time. But it satisfied specification in purchase. (2)Burst characteristic of rupture disk for steam generator did not Change even after they were used for 10138 12387 hours through at the condition of 200
12387 hours through at the condition of 200 430
430 C and 0.7
C and 0.7  1.4kg/cm
1.4kg/cm g. (3)Rupture disks of steam generator and reaction product vessel opened perfectly at burst test. (4)Corrosion was scarcely found. (5)Metal formation and mechanical and physical characteristics of material (Inconel X-750) of rupture disk has changed (age hardnening) through environment effect. (6)If we use Inconel X-750 as rupture disk material for steam generator, we must put in operation after ageing treatment. Otherwise it is desirable to use Inconel 600 or 625 which is not effected by age hardnening and has heatproof and corrosion-resistance characteristics.
g. (3)Rupture disks of steam generator and reaction product vessel opened perfectly at burst test. (4)Corrosion was scarcely found. (5)Metal formation and mechanical and physical characteristics of material (Inconel X-750) of rupture disk has changed (age hardnening) through environment effect. (6)If we use Inconel X-750 as rupture disk material for steam generator, we must put in operation after ageing treatment. Otherwise it is desirable to use Inconel 600 or 625 which is not effected by age hardnening and has heatproof and corrosion-resistance characteristics.
Tsuchiya, Tsuneo; ; ; ;
IAEA-IWGFR-53, p.2_62 - 2_72, 1984/06
no abstracts in English
*; *; Ohtaki, Akira; *; *
PNC TN941 83-96, 161 Pages, 1983/06
EXPRESS, 50 MW Steam Generator Test Facility Experimental Data Management and Retrieval System, was developed for the purpose of systematic utilization of experimental data acquired at the facility. This system consists of three kinds of functional subsystem as follows; (1)subsystem to accumulate experimental data into the data base. (2)subsystem to manage or retrieve the data base. (3)subsystem to figure some typical process values from a set of operating data in time series. These subsystems accumulate up-to-the-minute data, modify or refer corresponding records and grasp experimental conditions. It becomes possible to utilize many experimental data effectively and timely with the aid of EXPRESS. EXPRESS is executed in foreground or in background under the control of TSS on FACOM M-series computers system of O-arai Engineering Center, PNC, and is applicable to other systems.
Tsuchiya, Tsuneo
Nihon Genshiryoku Gakkai-Shi, 25(5), p.320 - 328, 1983/05
Times Cited Count:0 Percentile:0.02(Nuclear Science & Technology)None
*; *; *
PNC TN941 81-52, 296 Pages, 1981/02
Recently surveillance systems for nuclear power plants are increasingly required for the improvement of plant safety and availability. In order to establish the surveillance system of the prototype fast breeder reactor "MONJU", some techniques have been developed and applied to the 50MW Steam Generator Test Facility ty at OEC. As the first stage of the development, information display techniques for the plant operators and some anomalous state detection techniques are discussed in this paper. The operators can obtain such plant informations as digital and graphic outputs by cathode ray tubes (CRTs) and print out by a lineprinter and typewriters. Also the operators are informed of results of anomalous diagnosis by annunciator alarms moment by moment. Application tests of the anomalous state detection techniques have been carried out. These techniques include a cross check technique of multi-measuring system, a automatic detection system of a small scale sodium-water reaction, a differential alarm and prediction method of the time of anomalous occurrance and a display method of degree of superheat of evaporator (EV) outlet steam. It was concluded by our evaluation of the test results that those techniques are applicable to the "MONJU" design without major modification. We will develop new techniques and improve these systems to make them applicable to "MONJU", considering the "man-machine system", using this test facility.
*; *
PNC TN941 80-177, 170 Pages, 1980/10
In order to control evaporater outlet steam temperature of the sodium heated steam generator to a constant value, the direct digital control method applying the optimal control theory was designed and some tests were conducted at the 50MW Steam Generator Test Facility using PANAFACOM U-400 microcomputer system. The controllability by this method at 90% load level was resulted in being superior to that of analog PID control system which had been used previously. But to obtain good controllability for all over the load level, some items to be solved such as interporation and/or extraporation of feedback gain matrix were clarified.
*; *; *; *; *; *
PNC TN941 78-04, 41 Pages, 1978/01
In the sodium heated steam generator, the heat transfer coefficients are very high and thermal conduction through the tube walls contributes a large part (30 60%) of the total conduction between two fluids. Therefore, we must have available accurate value of thermal conductivity for analysis of all kinds of performance test results and design calculation and so on. We measured thermal diffusivity and thermal conductivity of 2.25Cr-1Mo steel by laser flash method. Test pieces are made from heat transfer tubes of Instability Test Rig (I.T.R.), 50MW Steam Generator (No.2 evaporator) and Ni-Nb stabilized steel. Results of measurement by laser flash method are agreed with the data of ORNL within 2
60%) of the total conduction between two fluids. Therefore, we must have available accurate value of thermal conductivity for analysis of all kinds of performance test results and design calculation and so on. We measured thermal diffusivity and thermal conductivity of 2.25Cr-1Mo steel by laser flash method. Test pieces are made from heat transfer tubes of Instability Test Rig (I.T.R.), 50MW Steam Generator (No.2 evaporator) and Ni-Nb stabilized steel. Results of measurement by laser flash method are agreed with the data of ORNL within 2 5%. Experimental equations of thermal conductivity by the least square method are as follows. 2.25Cr-1Mo steel (standard steel)
5%. Experimental equations of thermal conductivity by the least square method are as follows. 2.25Cr-1Mo steel (standard steel)  = -3.0199
= -3.0199  10
10 T
T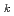
 + 2.9766
+ 2.9766  10
10 T
T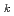 + 25.8071 Ni-Nb stabilized steel
+ 25.8071 Ni-Nb stabilized steel  = -2.7713
= -2.7713  10
10 T
T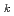
 + 2.7649
+ 2.7649  10
10 T
T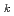 + 24.1383
+ 24.1383
; Kubota, Jun; Tsuchiya, Tsuneo
3rd Int.Conf.on Liquid Metal Engineering and Technology in Emergy Production, ,
None